Red Hat Linux powers countless websites, but how do popular web technologies work on it—conceptually and on the server? Here’s a concise step-by-step guide.
1. The Conceptual Flow
Web technologies (e.g., Apache, Nginx, Node.js) serve websites by handling HTTP requests. A client (browser) sends a request to a Red Hat Linux server, which processes it via:
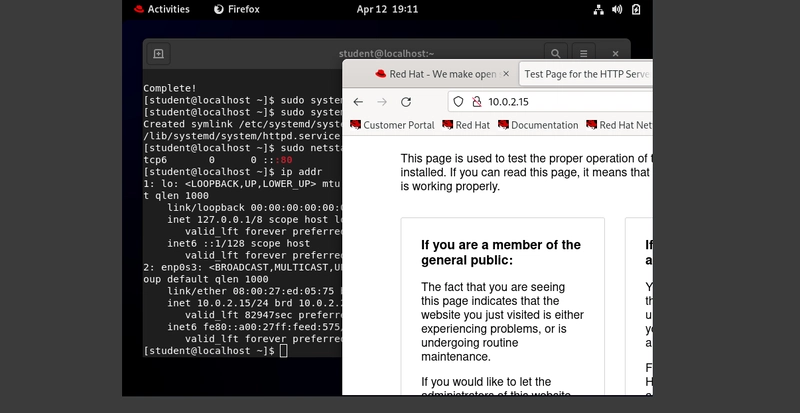
- Web Server: Listens for requests (ports 80/443).
- Application Logic: Executes code (e.g., PHP, Python).
- Data Storage: Fetches data (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL). The server then sends the response (HTML, JSON) back to the client.
2. On the Server: Key Technologies
Here’s how popular tools operate on Red Hat Linux:
-
Apache HTTP Server:
- Role: Serves static/dynamic content.
- Setup: Install via
sudo dnf install httpd, configure in/etc/httpd/. - Official Source: apache.org
-
Nginx:
- Role: Lightweight, high-performance web server/reverse proxy.
- Setup: Install with
sudo dnf install nginx, tweak/etc/nginx/. - Official Source: nginx.org
-
Node.js:
- Role: Runs JavaScript server-side for dynamic apps.
- Setup: Install via
sudo dnf module install nodejs, deploy apps in/var/www/. - Official Source: nodejs.org
-
PHP:
- Role: Processes dynamic content (e.g., WordPress).
- Setup: Install with
sudo dnf install php, integrate with Apache/Nginx. - Official Source: php.net
3. Why Red Hat Linux?
Red Hat’s stability, security (SELinux), and dnf package manager make it ideal for hosting. It supports containerization (Podman) for scalable deployments.
ස්ත්රී: Want More?
For deeper dives:
- Red Hat Documentation: redhat.com
- Try Red Hat Enterprise Linux: developers.redhat.com
Start experimenting on a Red Hat VM and share your findings below!



Top comments (0)