Table of Contents
Overview
Managing files and folders well is key to any IT setup. Whether you're in the cloud, on on-prem servers, or using DevOps, knowing Linux commands helps keep things running smoothly, organized, and automated.
This guide explains essential Linux file management commands including:
| Command | Function |
|---|---|
mkdir |
Creates new directories. Use -p to create parent directories as needed. |
touch |
Creates empty files or updates the last modified timestamp of existing files. |
cat |
Displays, creates, or appends content to files. |
cp |
Copies files and directories. Use -r for directories, -v for verbose output, and -f to force overwrite. |
rm |
Removes files or directories. Use -r for recursive and -f to force deletion. |
mv |
Moves or renames files and directories. |
Business Use Case
Scenario: Automating File and Directory Management for a SaaS Company
- Create daily log folders using
mkdir -p - Generate log files using
touch - Append real-time logs with
cat >> - Move daily logs to archive folders with
mv - Delete logs older than 30 days with
rm
This improves audit readiness, saves disk space, and supports compliance.
Benefits
i.Efficiency and Automation
Quickly create multiple files or folders using braces and ranges:
ii. Organization and Clarity
Maintain a clean, easy-to-navigate directory structure for logs, configs, backups, and deployments.
Performance and Storage Management
Clean up unused files:
rm -rvf *.tmp
Prevents unnecessary disk usage.
Security & Hygiene
Deleting old or sensitive data helps reduce risks and data exposure.
DevOps & CI/CD Integration
Copying or moving files in scripts enables build automation, artifact handling, and environment promotion.
Practical Examples
Each command below includes its function for better understanding.
1. Create single directory
mkdir – Make Directory
This command creates a single directory.

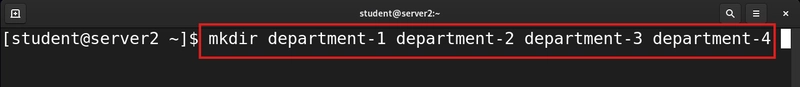
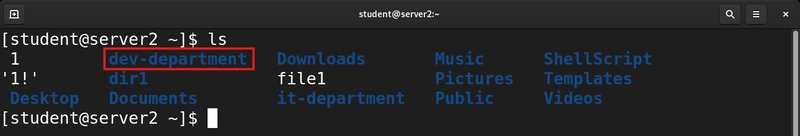
2. Create multiple directories
mkdir department-1 department-2 department-3 department-4
The above command creates multiple directory
3. Create multiple directories in sequence
mkdir faculty{1..5}

4.Create a directory path (directory inside another directory)
mkdir -p /data/projects/backend/logs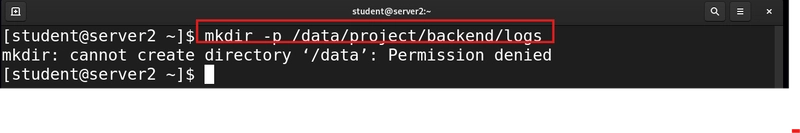
![]()

Creating Empty files
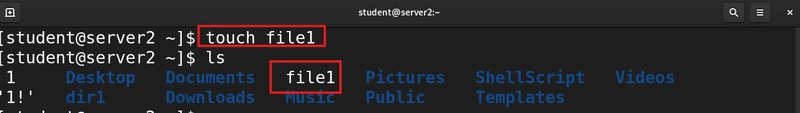
5. Create File
To create a file we use the touch command. This command creates and empty file without any content.
touch file1
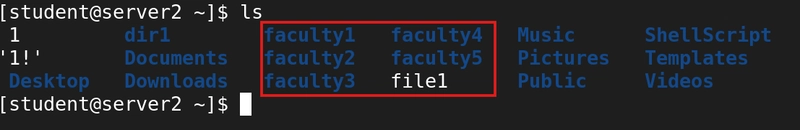
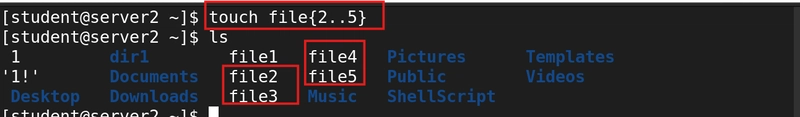
6. Create several files in sequence
touch file{2..5}
This command creates file2-file5 at the same time.
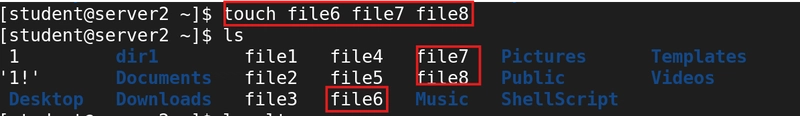
7. Create multiple files
touch file6 file7 file8
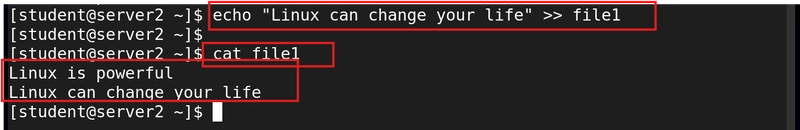
8. Create content into a file
The echo command helps us to save content to an empty file or append content to an exiting file using the redirect > or append >> symbols.
echo "Linux is powerful" > file1
echo "Linux can change your life" >> file1
The cat command helps us to view the content of a file.
cat file1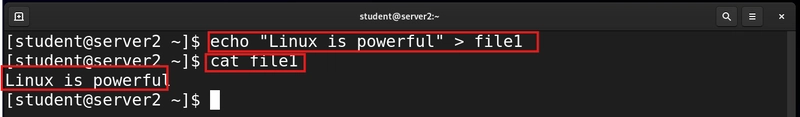
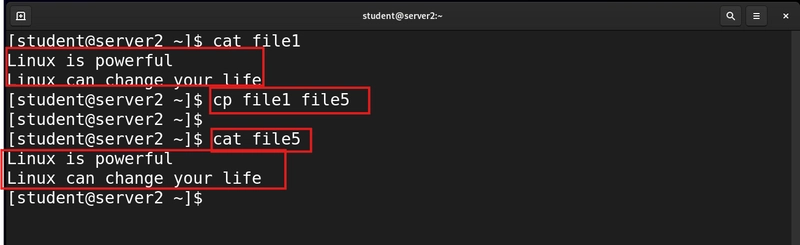
9. Copy files and directories
To copy a file or directory we use the cp command'
cp file1 file5
This command will copy the content of file1 into file5.
cat file5
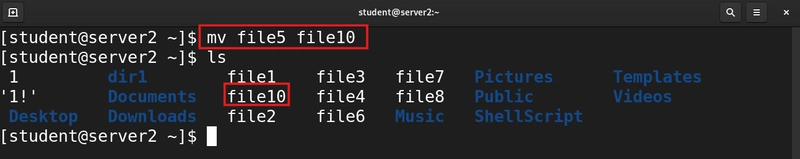
10. To move file or rename file
We use the mv command to move files or directories
mv file5 file10
file5 will be renamed as file10
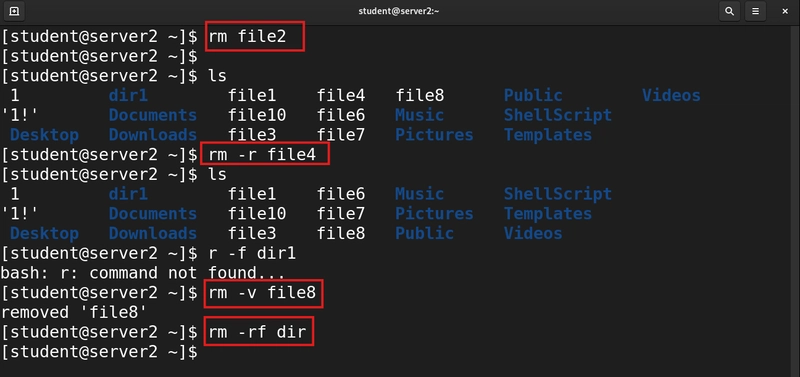
11. Remove Files or Directories
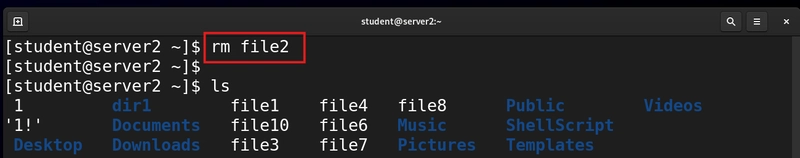
We use the rm command to accomplish that task. The rm command in Linux is used to delete files and directories permanently.
rm file2
** Common Options**
-r (or --recursive): Remove a directory and its contents recursively
-f (or --force): Ignore nonexistent files and suppress prompts
-v Verbose mode — shows what’s being deleted
Conclusion
Managing files and directories is a powerful way to improve system efficiency, automate tasks, and keep environments clean and secure. With just a few commands, you can:
- Organize logs and config files
- Automate DevOps processes
- Save disk space and optimize performance
- Support compliance and audit readiness
Go back to - Overview



Top comments (0)