In the world of web application security, CRLF (Carriage Return Line Feed) Injection is a lesser-known but critical vulnerability. While developers focus on SQLi, XSS, and CSRF, CRLF can sneak through and open the door to HTTP response splitting, log poisoning, and more.
In this post, we’ll walk through:
- What CRLF Injection is
- How it works in Laravel applications
- Real coding examples
- How to prevent it
- How to scan your site using our website vulnerability scanner
- Internal link to our blog at Pentest Testing Corp.
Let’s dive in 👇
🚨 What is CRLF Injection?
CRLF stands for Carriage Return (CR, \r) and Line Feed (LF, \n). These are special characters used to terminate lines in HTTP headers. When an attacker can inject CRLF characters into server responses, it can lead to:
- HTTP response splitting
- Web cache poisoning
- XSS attacks
- Log injection
This becomes dangerous when user input isn't properly sanitized before being sent to the response header.
🧠 How Laravel Can Be Vulnerable
Laravel’s response system makes it relatively easy to manipulate headers. For example, consider this snippet:
return redirect('/download?file=' . $filename);
If $filename is not validated, an attacker could inject CRLF like this:
/download?file=test.txt%0D%0AContent-Length:%200%0D%0A
This could result in the HTTP response being split, with custom headers or even fake content being injected.
🔥 Real CRLF Injection Example in Laravel
Let’s take a look at a vulnerable route:
Route::get('/redirect', function (Request $request) {
$url = $request->input('url');
return redirect($url);
});
If an attacker sends a request to:
/redirect?url=https://example.com%0D%0ASet-Cookie:%20malicious=1
The resulting response may look like:
HTTP/1.1 302 Found
Location: https://example.com
Set-Cookie: malicious=1
🎯 Impact: The user’s browser receives a fake cookie—potentially exposing the site to session hijacking.
🧪 Screenshot: Scanning with Our Free Tool
📸 _Below is a screenshot of our free online tool to check Website vulnerability that detects CRLF injection and other vulnerabilities.
 Screenshot of the free tools webpage where you can access security assessment tools.
Screenshot of the free tools webpage where you can access security assessment tools.
🧪 Screenshot: Vulnerability Report
📸 And here’s a sample vulnerability report generated by our free Website Security Scanner tool after scanning a Laravel app vulnerable to CRLF Injection.
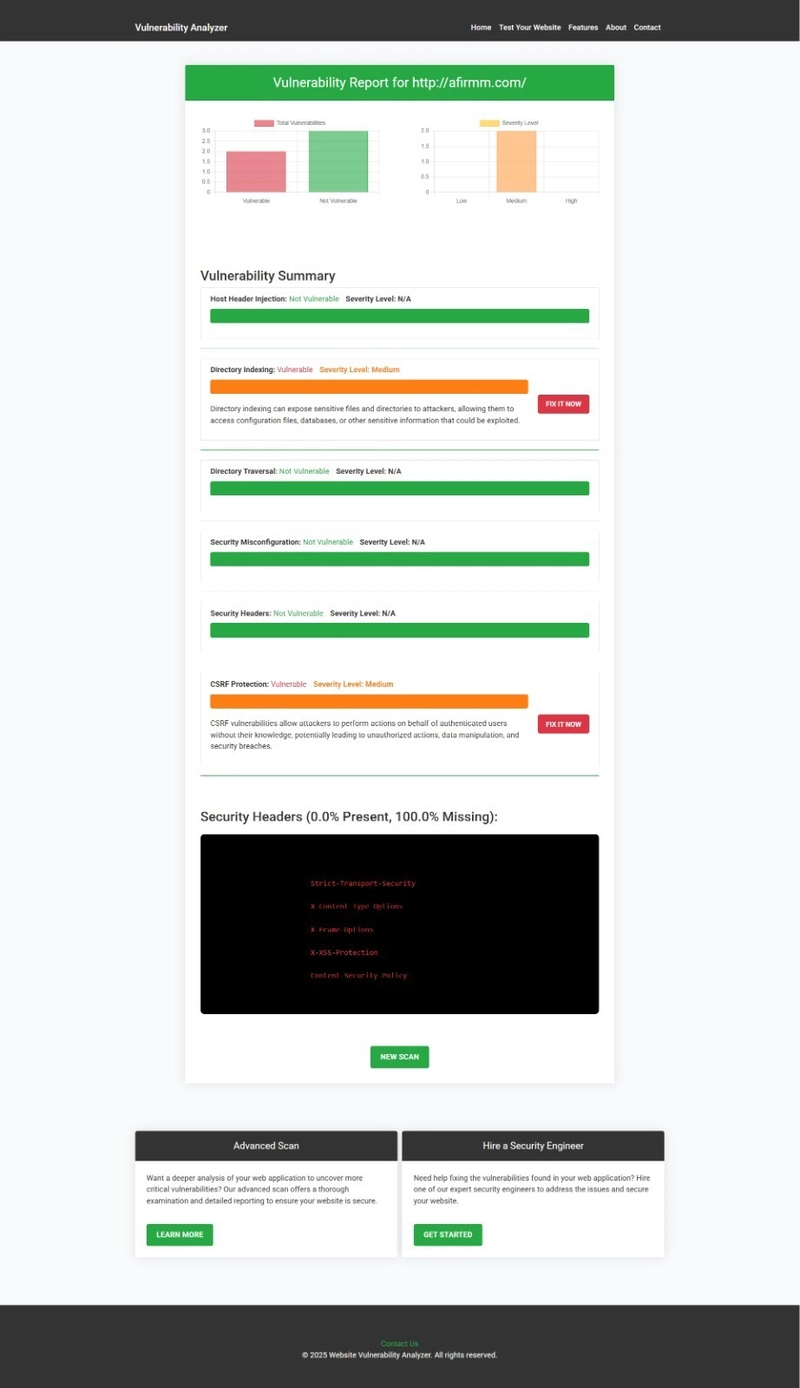 An Example of a vulnerability assessment report generated with our free tool, providing insights into possible vulnerabilities.
An Example of a vulnerability assessment report generated with our free tool, providing insights into possible vulnerabilities.
🔐 How to Prevent CRLF Injection in Laravel
Here are some security best practices to avoid CRLF in Laravel:
✅ Always sanitize user input
Avoid directly placing user input into headers. Use Laravel’s built-in validate() or filter_var() for sanitization.
$url = $request->validate([
'url' => 'required|url',
]);
✅ Use redirect()->away() cautiously
If you're using redirect()->away($url), ensure that $url is validated as a safe domain:
$allowedDomains = ['example.com', 'trusted.com'];
$host = parse_url($url, PHP_URL_HOST);
if (in_array($host, $allowedDomains)) {
return redirect()->away($url);
}
✅ URL-encode user input
$url = urlencode($request->input('url'));
return redirect('/download?file=' . $url);
🧰 Bonus: Laravel Middleware for CRLF Protection
You can create a custom middleware to check for CRLF in headers.
public function handle($request, Closure $next)
{
foreach ($request->all() as $key => $value) {
if (preg_match("/(\r|\n)/", $value)) {
abort(400, 'Invalid input detected');
}
}
return $next($request);
}
Register this middleware to automatically sanitize input in your routes.
🛡️ Scan Your Website for Free
Want to check if your Laravel site is vulnerable to CRLF Injection and other threats?
👉 Use our free Website Security Checker at
🔗 https://free.pentesttesting.com
The scan is fast, easy, and gives you a full vulnerability assessment report.
📚 Explore More Web Security Topics
Visit our blog at Pentest Testing Corp. for more articles on:
- SQL Injection in Laravel
- XML Injection in OpenCart
- Web Cache Deception in ERP systems
- And much more...
🧵 Final Thoughts
CRLF Injection might not get as much attention as other vulnerabilities, but it can cause serious issues if exploited. Laravel developers must stay alert and follow secure coding practices, especially when handling redirects or custom headers.
🔒 Secure your app.
🛠️ Test it with our free tool.
📢 Share this post to spread awareness.




Top comments (0)