Hello everyone! Today, I will guide you through the priority levels of configuration files in a Java Spring Boot project and the differences between .yaml and .properties files. Let’s dive in!
1. Priority Levels of Configuration Files
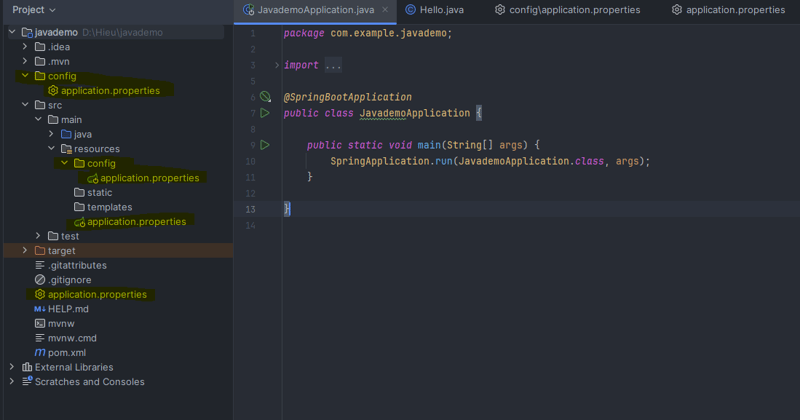
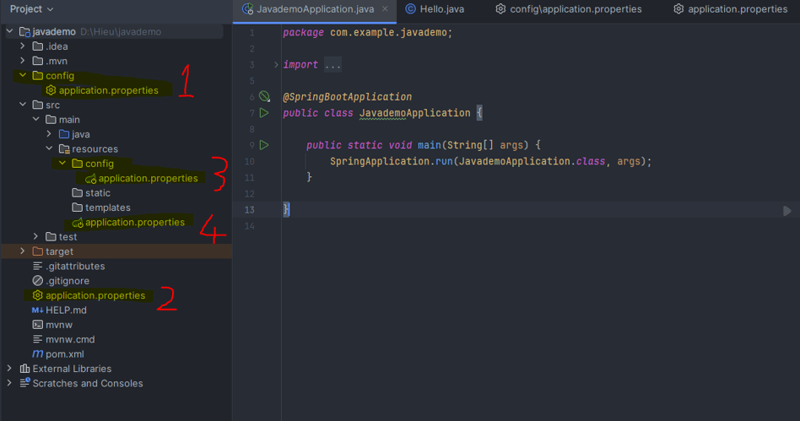
In Spring Boot, configuration files can be placed in various locations, each with its own priority level. The common structure of configuration files in a project is as follows:
The structure of configuration files in the project will be arranged in the following order of priority:
2. Checking the Priority Levels
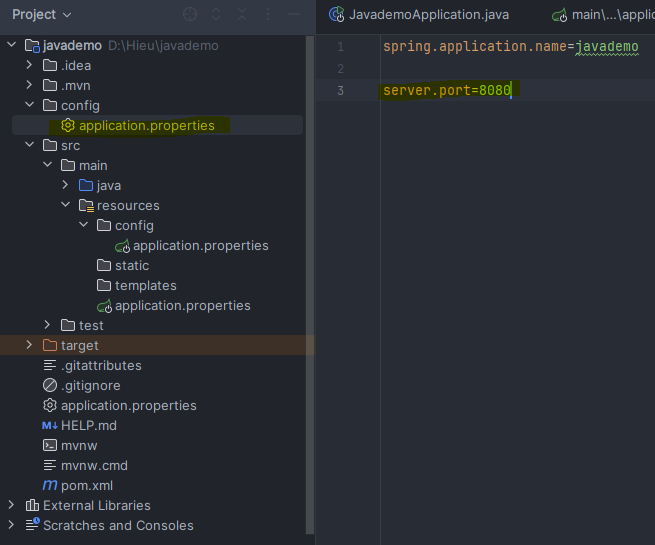
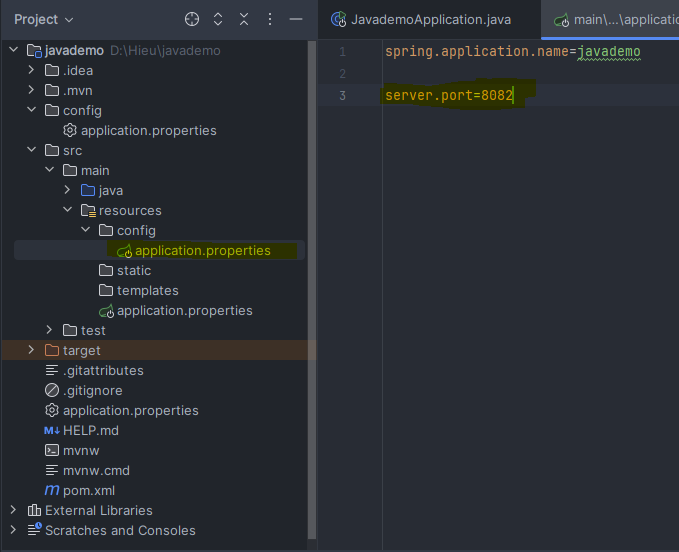
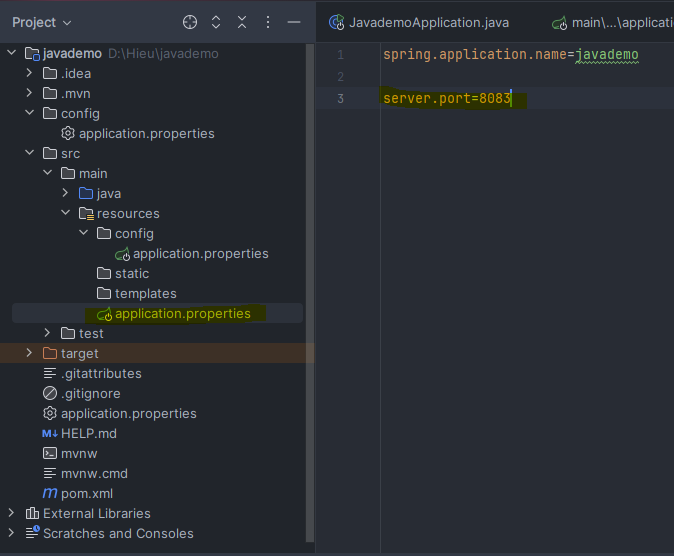
To test if the priority levels work as described, I changed the port in several configuration files:
- File 1: port 8080
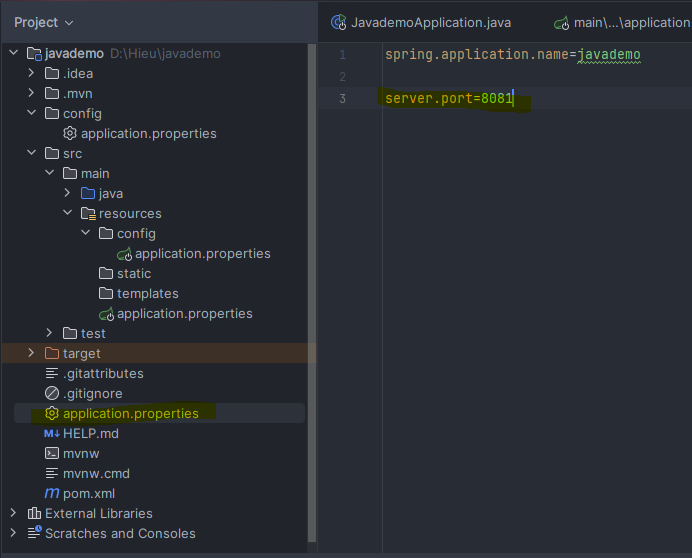
- File 2: port 8081
- File 3: port 8082
- File 4: port 8083
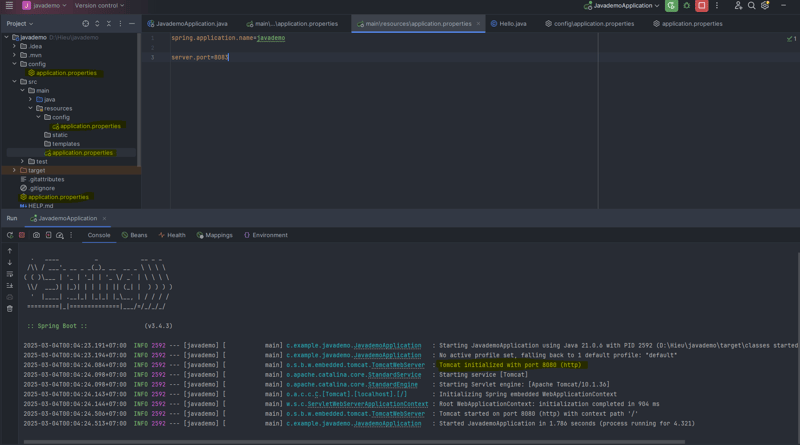
After running the application, the port that was set is 8080.
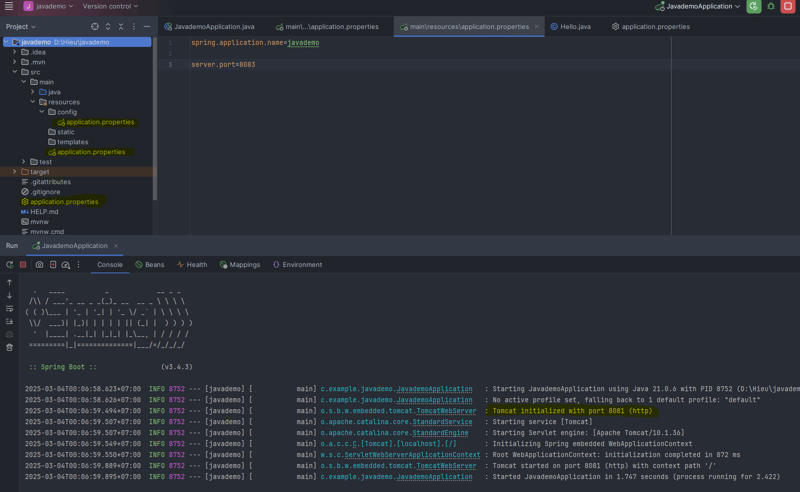
Then, I deleted the outermost configuration file and ran the application again. The result showed the port as 8081.
Similarly, you can test with the remaining configuration files.
Isn’t it amazing? From these examples, we can clearly distinguish the priority of configuration files in a project.
3. Differentiating .properties and .yaml Files
In Java Spring Boot, both .properties and .yaml files are used to configure the application. However, they have some differences:
-
.properties
- Simple "key-value" structure.
- Stores data as strings. For complex data types, additional processing is required.
- Example:
server.port=8080
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb
-
.yaml:
- Hierarchical structure, making it easy to read and organize complex information.
- Supports multiple data types (strings, numbers, arrays, objects, booleans), making the configuration more flexible.
- Example
server:
port: 8080
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb
4. Priority Levels When Both .properties and .yaml Files Exist
Let’s say we have both .properties and .yaml files in the project. Let’s check the priority level:
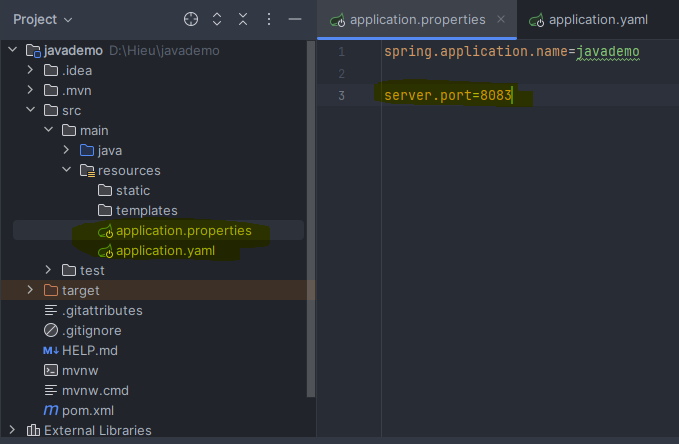
File .properties: port 8083
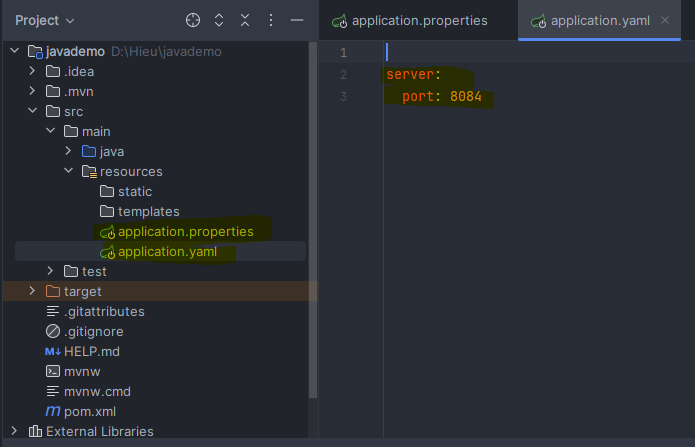
File .yaml: port 8084
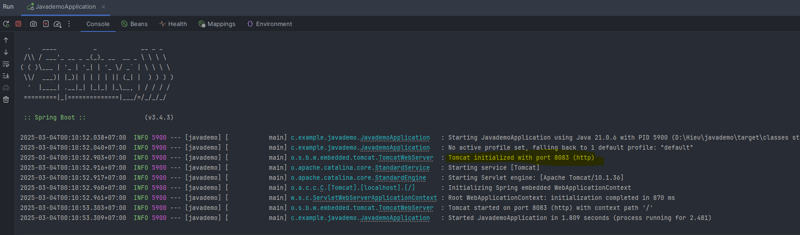
After running the application, the port that was set is 8083.
Conclusion
From the examples above, you should now have a clearer understanding of the priority levels of configuration files in Spring Boot and the differences between .properties and .yaml. I hope this article helps you gain more useful knowledge. If you found it helpful, don’t forget to leave me a reaction!
If you found this article useful and interesting, please share it with your friends and family. I hope you found it helpful. Thanks for reading 🙏
Let's get connected! You can find me on:
- Medium: Quang Hieu (Bee) -- Medium
- Dev: Quang Hieu (Bee) -- Dev
- Linkedin: Quang Hieu (Bee) -- Linkedin
- Buy Me a Coffee: Quang Hieu (Bee) -- buymeacoffee



Top comments (0)