The core architectural components of Azure are the fundamental building blocks used to design and deploy scalable, secure, and efficient cloud solutions. Here’s a concise breakdown:
1. Compute
Provides processing power for running applications and workloads.
Virtual Machines (VMs): Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) – full control over OS and compute resources.
App Services: Platform as a Service (PaaS) – host web apps and APIs.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS): Orchestrates containers.
Azure Functions: Serverless compute for lightweight event-driven code.
Container Instances: Easily run Docker containers without orchestration.
2. Networking
Enables connectivity, routing, and security.
Virtual Network (VNet): Secure network boundary within Azure.
- Subnets: Break VNets into smaller segments.
Load Balancer: Distributes traffic across multiple instances.
Application Gateway: Layer 7 load balancer with Web Application Firewall (WAF).
VPN Gateway / ExpressRoute: Hybrid connectivity to on-premises environments.
Azure DNS / Traffic Manager / Front Door: Manage global traffic and routing.
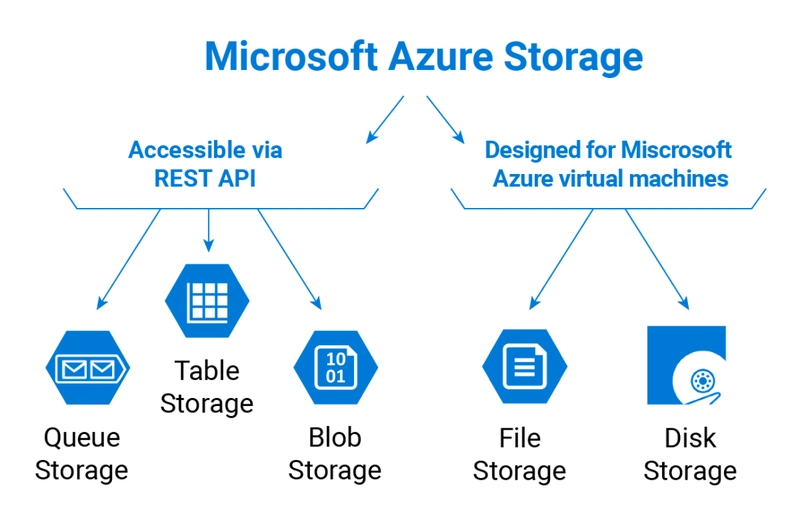
3. Azure Storage
Role: Durable, scalable cloud storage for unstructured and structured data.
Main Services:
Blob Storage: Object storage for massive unstructured data (images, videos, backups).
File Storage: Managed file shares for legacy apps using SMB protocol.
Queue Storage: Message queue system for decoupling applications.
Table Storage: NoSQL key-value store for semi-structured datasets.
Disk Storage: Persistent block storage for Azure VMs.
4. Azure Resource Manager (ARM)
The deployment and management service for Azure.
Enables infrastructure as code (IaC) via templates (ARM templates, Bicep).
Manages resource groups and role-based access control (RBAC).
5. Azure Regions and Availability Zones
Regions: Geographical areas where Azure data centers are located.
Availability Zones: Physically separate locations within a region, offering high availability and fault tolerance.
6. Monitoring and Management
Azure Monitor: Full observability into applications and infrastructure.
Log Analytics: Query logs from across Azure.
Azure Advisor: Personalized best practices recommendations.
Azure Automation: Automate frequent, time-consuming tasks.
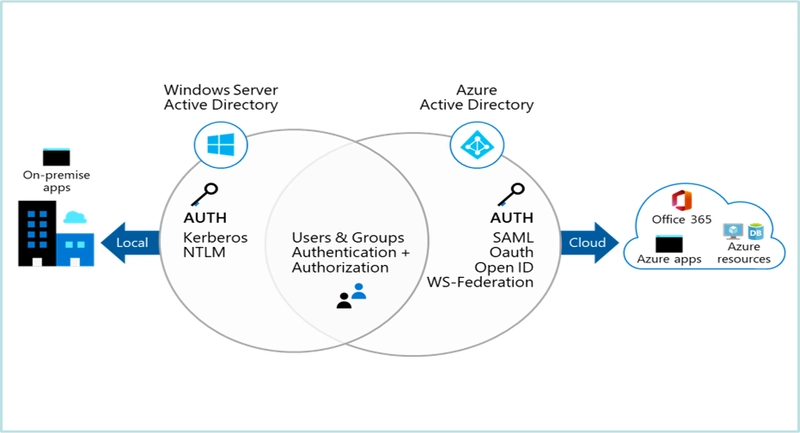
7. Identity and Access Management
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD): Identity management and authentication.
RBAC (Role-Based Access Control): Secure access to Azure resources.
Managed Identities: Provides Azure services with an automatically managed identity in Azure AD.
8. Security and Governance
Microsoft Defender for Cloud: Security management and threat protection.
Azure Policy: Enforce organizational standards and assess compliance.
Azure Key Vault: Secure storage for secrets, keys, and certificates.








Top comments (0)