Priority queues can be implemented using heaps. An ordinary queue is a first-in, first-out data structure. Elements are appended to the end of the queue and removed from the beginning. In a priority queue, elements are assigned with priorities. When accessing elements, the element with the highest priority is removed first. For example, the emergency room in a hospital assigns priority numbers to patients; the patient with the highest priority is treated first.
A priority queue can be implemented using a heap, in which the root is the object with the highest priority in the queue. Heaps were introduced in Heap Sort. The class diagram for the priority queue is shown in Figure below. Its implementation is given in the code below.
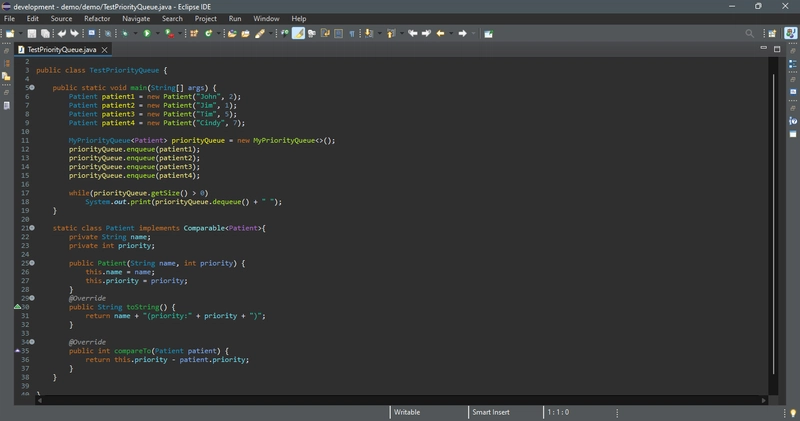
The code below gives an example of using a priority queue for patients. The Patient class is defined in lines 21–38. Four patients are created with associated priority values in lines 6–9. Line 8 creates a priority queue. The patients are enqueued in lines 12–15. Line 18 dequeues a patient from the queue.
Cindy(priority:7) Tim(priority:5) John(priority:2) Jim(priority:1)





Top comments (0)