Text-Level Semantic Tags | Grouping and Media Semantic Tags | List Semantic Tags | Table Semantic Tags | Form Semantic Tags | Other Semantic Tags
img path | Marquee | entities | symbols | emojis
HTML Semantic Tags
Semantic tags give meaning to the content inside them. They help both search engines and developers understand the structure of a webpage.
1. Structural Semantic Tags
These tags define the layout of a webpage.
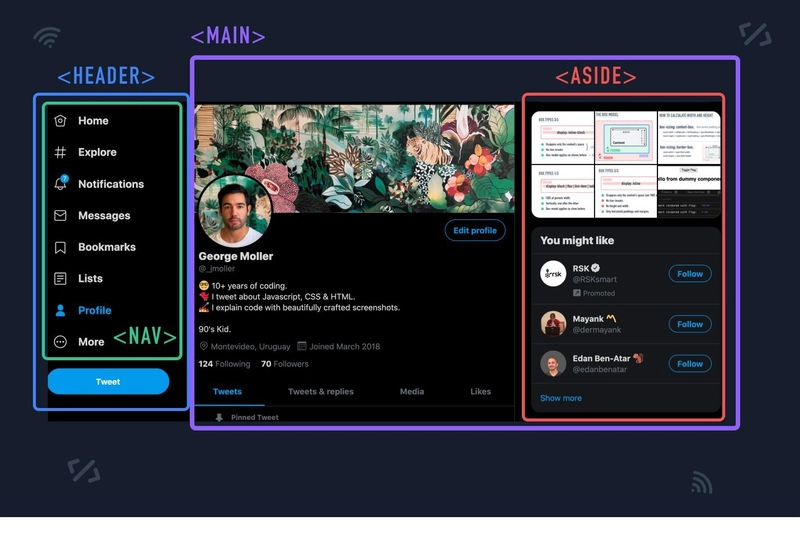
📍 <header> - Website Header
✅ Definition: Represents the top section of a page or a section.
✅ Usage: Usually contains logos, navigation menus, and headings.
🔹 Example:
<header>
<h1>My Website</h1>
<nav>
<ul>
<li><a href="#">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="#">About</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Contact</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
</header>
✅ Key Points:
- Can be used multiple times in a page (inside
<article>or<section>).
- Usually contains branding, logo, and navigation links.
📍 <nav> - Navigation Links
✅ Definition: Represents the navigation menu of a webpage.
✅ Usage: Used to group important links like Home, About, Contact.
🔹 Example:
<nav>
<ul>
<li><a href="#">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Services</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Blog</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Contact</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
✅ Key Points:
- Used for menus, sidebars, or footer links.
- Should only contain important navigation links.
📍 <main> - Main Content Area
✅ Definition: Represents the main content of the webpage.
✅ Usage: Contains the most important information (not repeated in other sections like header or footer).
🔹 Example:
<main>
<h2>Welcome to My Website</h2>
<p>This website shares useful programming tutorials.</p>
</main>
✅ Key Points:
-
Each webpage should have only one
<main>tag. - Should not contain
<header>,<footer>,<nav>.
📍 <article> - Independent Content
✅ Definition: Represents a self-contained, independent piece of content.
✅ Usage: Used for blog posts, news articles, or product descriptions.
🔹 Example:
html
CopyEdit
<article>
<h2>Learn HTML Semantic Tags</h2>
<p>HTML has semantic tags that give meaning to content...</p>
</article>
✅ Key Points:
- Can contain title, text, images, and links.
- Each
<article>should make sense even if taken out of the page.
📍 <section> - Thematic Section
✅ Definition: Represents a section inside a webpage that groups related content.
✅ Usage: Used for different sections like services, testimonials, or features.
🔹 Example:
<section>
<h2>Our Services</h2>
<p>We offer web development, design, and SEO services.</p>
</section>
✅ Key Points:
- Should always have a heading (
<h2>,<h3>). - Used for grouping related content.
📍 <aside> - Sidebar Content]
✅ Definition: Represents side content like ads, links, or related articles.
✅ Usage: Used for sidebars, advertisements, and related links.
🔹 Example:
<aside>
<h3>Related Articles</h3>
<ul>
<li><a href="#">HTML Basics</a></li>
<li><a href="#">CSS Flexbox</a></li>
<li><a href="#">JavaScript DOM</a></li>
</ul>
</aside>
✅ Key Points:
- Not part of the main content.
- Placed beside articles or main sections.
📍 <footer> - Bottom Section
✅ Definition: Represents the bottom section of a webpage.
✅ Usage: Used for copyright info, contact details, or social media links.
🔹 Example:
<footer>
<p>© 2025 My Website. All Rights Reserved.</p>
<nav>
<a href="#">Privacy Policy</a> | <a href="#">Terms of Use</a>
</nav>
</footer>
✅ Key Points:
- Used once per page (usually).
- Contains useful links, copyright, and credits.
📝 Summary of Structural Semantic Tags
| Tag | Meaning | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
<header> |
Top section of a page | Logo, navigation, welcome text |
<nav> |
Navigation links section | Menus, sidebar links |
<main> |
Main content of page | Articles, blog posts |
<article> |
Independent content block | Blog posts, news |
<section> |
Thematic section | Grouping related content |
<aside> |
Sidebar content | Ads, related links |
<footer> |
Bottom section | Copyright, contact info |
2. Text-Level Semantic Tags
These tags help format and structure text properly to give it meaning. They are useful for SEO, readability, and accessibility.
📍 <h1> to <h6> - Headings
✅ Definition: Used for headings in a document, where <h1> is the most important and <h6> is the least important.
✅ Usage: Used to structure the document into sections.
🔹 Example:
<h1>Main Heading</h1>
<h2>Subheading</h2>
<h3>Smaller Subheading</h3>
✅ Key Points:
- There should be only one
<h1>per page. - Helps with SEO (Search Engine Optimization).
- Do not use
<h1>just for big text; use CSS for styling.
📍 <p> - Paragraph
✅ Definition: Used to write a paragraph of text.
✅ Usage: Used for normal content inside a webpage.
🔹 Example:
<p>This is a paragraph. HTML makes it easy to structure content.</p>
✅ Key Points:
- Browsers automatically add space before and after
<p>. - Do not use multiple
<br>tags for spacing.
📍 <blockquote> - Quoting a Block of Text
✅ Definition: Used to quote long text from another source.
✅ Usage: Often used for citing references or articles.
🔹 Example:
<blockquote>
"The only limit to our realization of tomorrow is our doubts of today."
</blockquote>
✅ Key Points:
- Browsers indent
<blockquote>by default.
- Use <cite> inside it to give source information.
📍 <cite> - Citing a Source
✅ Definition: Used to cite the title of a book, article, or work.
✅ Usage: Helps indicate the author or reference.
🔹 Example:
<p><cite>The Great Gatsby</cite> is a novel by F. Scott Fitzgerald.</p>
✅ Key Points:
- It is usually displayed in italics.
📍 <q> - Short Inline Quote
✅ Definition: Used to add short inline quotes.
✅ Usage: Used for quoting words inside a sentence.
🔹 Example:
<p>As Albert Einstein said, <q>Imagination is more important than knowledge.</q></p>
✅ Key Points:
- Browsers automatically add quotation marks around
<q>.
📍 <time> - Representing Date and Time
✅ Definition: Defines a specific time, date, or duration.
✅ Usage: Useful for events, articles, or schedules.
🔹 Example:
<p>Our meeting is scheduled for <time datetime="2025-03-30T10:00">March 30 at 10 AM</time>.</p>
✅ Key Points:
- The
datetimeattribute makes it machine-readable.
📍 <address> - Contact Information
✅ Definition: Used to represent contact details like email or physical address.
✅ Usage: Often used inside <footer>.
🔹 Example:
<address>
Contact us at: <a href="mailto:info@example.com">info@example.com</a>
</address>
✅ Key Points:
- Usually contains emails, phone numbers, or physical addresses.
📍 <pre> - Preformatted Text
✅ Definition: Displays text exactly as written in the code, including spaces and line breaks.
✅ Usage: Used for code blocks, ASCII art, or poems.
🔹 Example:
<pre>
This text
is displayed
exactly as it is
</pre>
✅ Key Points:
- Maintains spaces and line breaks.
📍 <code> - Inline Code
✅ Definition: Used to display inline programming code.
✅ Usage: Helps show code snippets in a readable format.
🔹 Example:
<p>To print in Python, use <code>print("Hello, World!")</code>.</p>
✅ Key Points:
- Does not apply any syntax highlighting.
- Use
<pre><code>for longer code blocks.
📍 <kbd> - Keyboard Input
✅ Definition: Represents keyboard input (like key presses).
✅ Usage: Used for computer tutorials.
🔹 Example:
<p>Press <kbd>Ctrl</kbd> + <kbd>C</kbd> to copy text.</p>
✅ Key Points:
- Useful for shortcut key instructions.
📍 <samp> - Sample Output
✅ Definition: Represents output from a computer program.
✅ Usage: Used for displaying command-line results.
🔹 Example:
<p>The output is: <samp>Operation completed successfully</samp></p>
✅ Key Points:
- Often used with
<code>.
📍 <var> - Variable in Programming
✅ Definition: Used to define a variable in programming or math.
✅ Usage: Used in math equations or coding tutorials.
🔹 Example:
<p>The formula for area is <var>πr²</var></p>
✅ Key Points:
- Usually displayed in italics.
📍 <abbr> - Abbreviation
✅ Definition: Represents an abbreviation or acronym.
✅ Usage: Shows full meaning when hovered.
🔹 Example:
<p><abbr title="HyperText Markup Language">HTML</abbr> is a markup language.</p>
✅ Key Points:
- Helps with accessibility and SEO.
📍 <strong> - Important Text
✅ Definition: Represents strong importance (bold by default).
✅ Usage: Highlights critical words in a sentence.
🔹 Example:
<p><strong>Warning:</strong> Do not touch the wires.</p>
✅ Key Points:
- Use for important warnings or notices.
📍 <em> - Emphasized Text
✅ Definition: Used for emphasizing words (italic by default).
✅ Usage: Adds stress to words.
🔹 Example:
<p>This is <em>very important</em> information.</p>
✅ Key Points:
- Improves voice inflection for screen readers.
📍 <mark> - Highlighted Text
✅ Definition: Highlights important text (yellow by default).
✅ Usage: Used to grab attention.
🔹 Example:
<p>Please <mark>read this carefully</mark> before proceeding.</p>
✅ Key Points:
- Used for important highlights.
📍 <del> - Deleted Text
✅ Definition: Shows deleted text with a strike-through.
✅ Usage: Used for corrections or edits.
🔹 Example:
<p>This was <del>wrong</del> correct.</p>
✅ Key Points:
- Shows content that was removed.
📍 <ins> - Inserted Text
✅ Definition: Shows added text with an underline.
✅ Usage: Used to show updates or edits.
🔹 Example:
<p>This is <ins>newly added</ins> content.</p>
✅ Key Points:
- Helps track changes in content.
3. Grouping & Media Semantic Tags
These tags group related content and handle multimedia like images, videos, and audio. They improve SEO, readability, and accessibility.
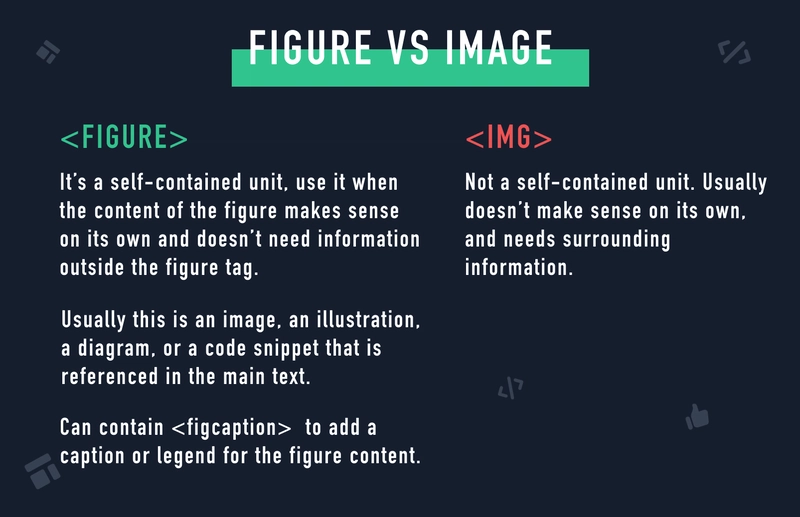
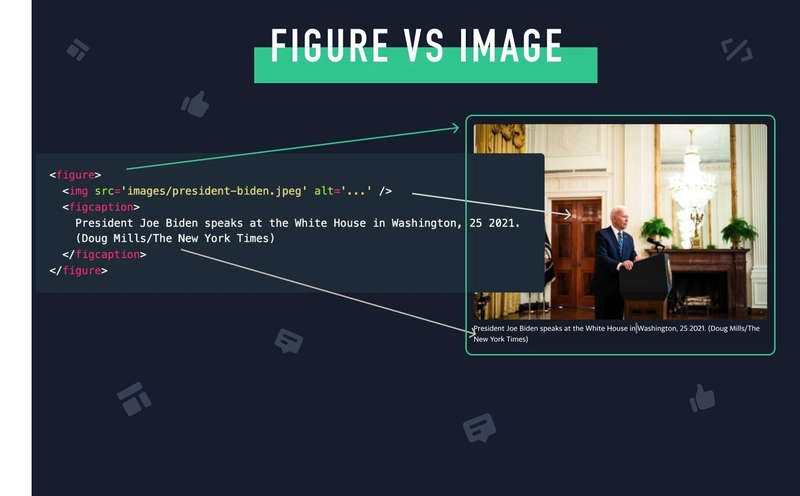
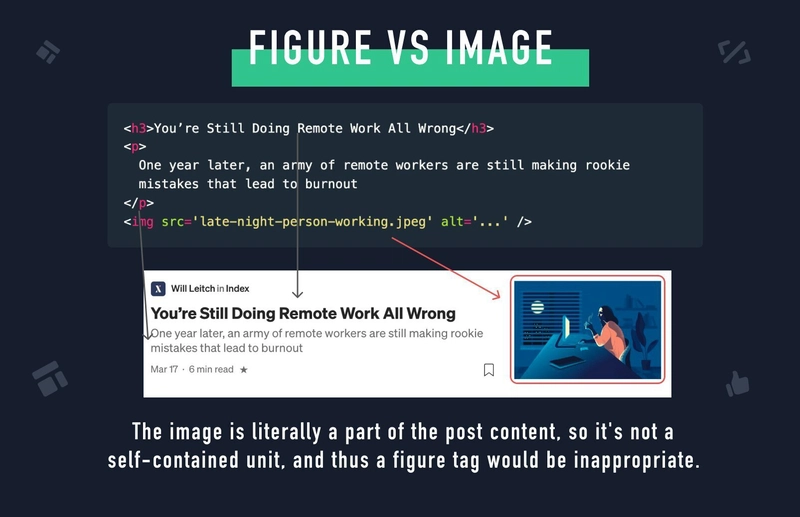
📍 <figure> - Self-contained Content (Image/Chart/Code Snippets)
✅ Definition: Groups images, charts, code snippets, or diagrams with a caption.
✅ Usage: Helps associate an image with its description.
🔹 Example:
<figure>
<img src="nature.jpg" alt="Beautiful Nature">
<figcaption>Nature is always beautiful.</figcaption>
</figure>
✅ Key Points:
-
<figcaption>is optional and provides a caption. - Improves SEO and screen reader accessibility.
📍 <figcaption> - Caption for <figure>
✅ Definition: Provides a description or title for content inside <figure>.
✅ Usage: Used inside <figure> to describe the content.
🔹 Example:
<figure>
<img src="car.jpg" alt="A red sports car">
<figcaption>A stylish red sports car.</figcaption>
</figure>
✅ Key Points:
- Always use it inside
<figure>.
📍 <picture> - Responsive Images
✅ Definition: Helps display different images for different screen sizes.
✅ Usage: Used for responsive design.
🔹 Example:
<picture>
<source srcset="small.jpg" media="(max-width: 600px)">
<source srcset="large.jpg" media="(min-width: 601px)">
<img src="default.jpg" alt="Default Image">
</picture>
✅ Key Points:
-
<source>chooses the best image based on screen size. - Always include a fallback
<img>.
📍 <audio> - Embedding Audio
✅ Definition: Embeds audio files in a webpage.
✅ Usage: Used for background music, podcasts, or sound effects.
🔹 Example:
<audio controls>
<source src="music.mp3" type="audio/mpeg">
<source src="music.ogg" type="audio/ogg">
Your browser does not support audio.
</audio>
✅ Key Points:
- Use
controlsto add play, pause, and volume buttons. - Always provide multiple formats (
.mp3,.ogg).
📍 <video> - Embedding Video
✅ Definition: Embeds video files in a webpage.
✅ Usage: Used for tutorials, clips, or background videos.
🔹 Example:
<video width="320" height="240" controls>
<source src="video.mp4" type="video/mp4">
<source src="video.ogg" type="video/ogg">
Your browser does not support video.
</video>
✅ Key Points:
- Use
controlsfor play/pause buttons. - Add multiple formats for better support.
📍 <source> - Alternative Media Sources
✅ Definition: Provides alternative media sources for <picture>, <audio>, and <video>.
✅ Usage: Used inside <picture>, <audio>, or <video> to support different file types.
🔹 Example:
<audio controls>
<source src="audio.mp3" type="audio/mpeg">
<source src="audio.ogg" type="audio/ogg">
</audio>
✅ Key Points:
- Helps provide backup formats for media.
📍 <track> - Subtitles and Captions for Video
✅ Definition: Adds subtitles, captions, or descriptions to <video>.
✅ Usage: Improves accessibility for deaf users.
🔹 Example:
<video controls>
<source src="movie.mp4" type="video/mp4">
<track src="subtitles.vtt" kind="subtitles" srclang="en" label="English">
</video>
✅ Key Points:
-
kind="subtitles"specifies that it's a subtitle file. -
Use
.vtt(WebVTT format) for subtitles.
4. List Semantic Tags
Lists are used to organize content in an ordered or unordered way. They help with readability, structure, and accessibility.
📍 <ul> - Unordered List
✅ Definition: Creates a bulleted list.
✅ Usage: Used when the order of items does not matter.
🔹 Example:
<ul>
<li>Apples</li>
<li>Bananas</li>
<li>Oranges</li>
</ul>
✅ Key Points:
- Each item in the list is inside
<li>(list item). - Browser automatically adds bullets.
📍 <ol> - Ordered List
✅ Definition: Creates a numbered list.
✅ Usage: Used when the order of items matters (like steps or rankings).
🔹 Example:
<ol>
<li>Wake up</li>
<li>Brush your teeth</li>
<li>Have breakfast</li>
</ol>
✅ Key Points:
- Items are numbered automatically (1, 2, 3…).
-
You can change the numbering style using the
typeattribute:
<ol type="A"> <li>Item 1</li> <li>Item 2</li> </ol>✅ Output: A. Item 1, B. Item 2…
📍 <li> - List Item
✅ Definition: Represents a single item in <ul> or <ol>.
✅ Usage: Used inside unordered (<ul>) or ordered (<ol>) lists.
🔹 Example:
<ul>
<li>HTML</li>
<li>CSS</li>
<li>JavaScript</li>
</ul>
✅ Key Points:
- Must always be inside
<ul>or<ol>.
📍 <dl> - Description List
✅ Definition: Creates a list of terms and descriptions.
✅ Usage: Used for glossaries, FAQs, or key-value pairs.
🔹 Example:
<dl>
<dt>HTML</dt>
<dd>HyperText Markup Language</dd>
<dt>CSS</dt>
<dd>Cascading Style Sheets</dd>
</dl>
✅ Key Points:
-
<dt>= Term (word or phrase) -
<dd>= Description (explanation of the term)
📍 <dt> - Definition Term
✅ Definition: Represents the term (title or keyword) in a description list.
✅ Usage: Used inside <dl> before <dd>.
🔹 Example:
<dt>Python</dt>
<dd>A popular programming language.</dd>
✅ Key Points:
- Must be inside
<dl>.
📍 <dd> - Definition Description
✅ Definition: Represents the description or explanation of a term.
✅ Usage: Used after <dt>.
🔹 Example:
<dl>
<dt>JavaScript</dt>
<dd>A language used for web development.</dd>
</dl>
✅ Key Points:
- Must be inside
<dl>after<dt>.
📌 Comparison of List Types
| Tag | Type of List | Uses |
|---|---|---|
<ul> |
Unordered (bullets) | Shopping lists, menus |
<ol> |
Ordered (numbers) | Steps, rankings, instructions |
<dl> |
Description list | Glossaries, FAQs |
5. Table Semantic Tags
Tables are used to organize data in rows and columns. They are useful for reports, pricing tables, and structured content.
📍 <table> - Table Container
✅ Definition: Defines a table in HTML.
✅ Usage: Used to display tabular data.
🔹 Example:
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Age</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>John</td>
<td>25</td>
</tr>
</table>
✅ Key Points:
-
<table>is the main container. - The
borderattribute adds a visible border (for learning). -
<tr>(table row),<th>(header cell), and<td>(data cell) are used inside.
📍 <thead> - Table Header Section
✅ Definition: Groups the header rows of a table.
✅ Usage: Used to separate headers from data.
🔹 Example:
<table border="1">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Age</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>Alice</td>
<td>22</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
✅ Key Points:
- Helps organize the table structure.
- Works with
<tbody>and<tfoot>.
📍 <tbody> - Table Body Section
✅ Definition: Groups the main data of the table.
✅ Usage: Used to separate table content from headers/footers.
🔹 Example:
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>Bob</td>
<td>30</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
✅ Key Points:
- Only contains table rows (
<tr>).
📍 <tfoot> - Table Footer Section
✅ Definition: Groups the footer content of a table.
✅ Usage: Used for totals, summaries, or extra information.
🔹 Example:
<tfoot>
<tr>
<td colspan="2">Total: 2 entries</td>
</tr>
</tfoot>
✅ Key Points:
- Used for summary rows.
-
colspan="2"makes one cell span two columns.
📍 <tr> - Table Row
✅ Definition: Represents a row in the table.
✅ Usage: Contains header (<th>) or data (<td>) cells.
🔹 Example:
<tr>
<td>Sam</td>
<td>28</td>
</tr>
✅ Key Points:
- A table must have at least one row.
📍 <td> - Table Data Cell
✅ Definition: Represents a single data cell.
✅ Usage: Used inside <tr> to hold table data.
🔹 Example:
<td>Emma</td>
✅ Key Points:
- Used to store regular data.
📍 <th> - Table Header Cell
✅ Definition: Defines a header cell.
✅ Usage: Used inside <tr> in <thead>.
🔹 Example:
<th>City</th>
✅ Key Points:
- Text is bold and centered by default.
📍 <caption> - Table Title
✅ Definition: Adds a title to the table.
✅ Usage: Describes the purpose of the table.
🔹 Example:
<table border="1">
<caption>Student Information</caption>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Age</th>
</tr>
</table>
✅ Key Points:
- Always placed inside
<table>, before<tr>.
📌 Full Table Example
<table border="1">
<caption>Employee Details</caption>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Position</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>John</td>
<td>Manager</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Lisa</td>
<td>Developer</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
<tfoot>
<tr>
<td colspan="2">Total Employees: 2</td>
</tr>
</tfoot>
</table>
✅ Key Points:
- Table is well-structured (Header, Body, Footer).
-
colspan="2"spans across 2 columns.
6. Form Semantic Tags
Forms are used to collect user input like login details, search queries, or contact information.
📍 <form> - Form Container
✅ Definition: The main container for user input fields.
✅ Usage: Used to group all form elements.
🔹 Example:
<form action="/submit" method="POST">
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<input type="text" id="name" name="name">
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
✅ Key Points:
-
action="/submit"→ Sends data to the server.
- method="POST" → Sends data securely.
📍 <label> - Input Label
✅ Definition: Adds a text label for an input field.
✅ Usage: Helps with accessibility and usability.
🔹 Example:
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email">
✅ Key Points:
-
for="email"should matchid="email".
📍 <input> - Input Field
✅ Definition: A single-line user input field.
✅ Usage: Used for text, numbers, passwords, etc.
🔹 Example:
<input type="text" name="username">
✅ Common type values:
| Type | Usage |
|---|---|
text |
Regular text input |
email |
Email validation |
password |
Hidden characters |
number |
Numeric input |
checkbox |
Multiple-choice selection |
radio |
Single-choice selection |
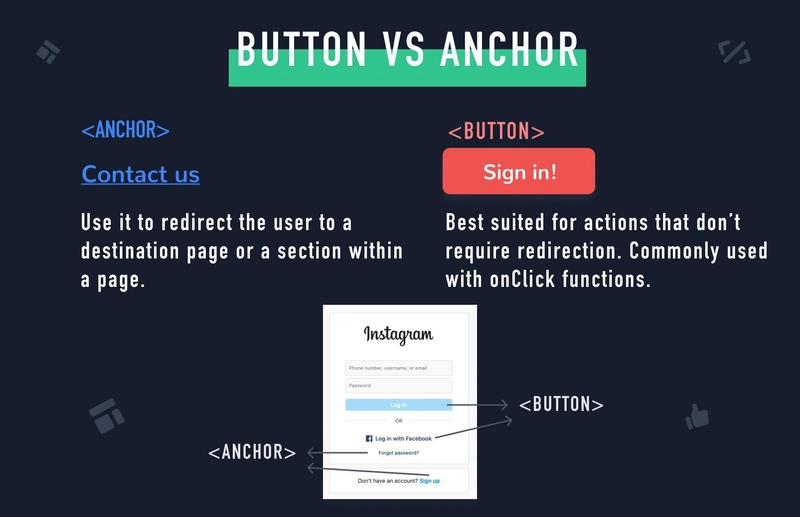
📍 <button> - Clickable Button
✅ Definition: A clickable button.
✅ Usage: Used to submit forms or trigger actions.
🔹 Example:
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
✅ Key Points:
-
type="submit"submits the form. -
type="button"does nothing by default.
📍 <select> - Dropdown List
✅ Definition: Creates a dropdown menu.
✅ Usage: Used when users select from options.
🔹 Example:
<label for="country">Choose a country:</label>
<select id="country" name="country">
<option value="us">USA</option>
<option value="uk">UK</option>
</select>
✅ Key Points:
-
<option>defines each choice. -
value="us"is sent to the server.
📍 <textarea> - Multi-line Textbox
✅ Definition: A large input box for long text.
✅ Usage: Used for comments or messages.
🔹 Example:
<textarea name="message" rows="4" cols="30">Type here...</textarea>
✅ Key Points:
-
rowsandcolscontrol the size.
📍 <fieldset> - Group Form Elements
✅ Definition: Groups related inputs.
✅ Usage: Used for better organization.
🔹 Example:
<fieldset>
<legend>Personal Info</legend>
<label>Name: <input type="text"></label>
</fieldset>
✅ Key Points:
- Improves form structure.
📍 <legend> - Fieldset Title
✅ Definition: Adds a title for <fieldset>.
✅ Usage: Helps describe the group of inputs.
🔹 Example:
<legend>Contact Details</legend>
✅ Key Points:
- Always placed inside
<fieldset>.
📍 <datalist> - Auto-Suggestions
✅ Definition: Provides predefined suggestions.
✅ Usage: Used for quick input selection.
🔹 Example:
<input list="colors">
<datalist id="colors">
<option value="Red">
<option value="Blue">
</datalist>
✅ Key Points:
- Users can type or select from options.
📍 <output> - Display Calculation Results
✅ Definition: Displays calculated values.
✅ Usage: Used for dynamic form outputs.
🔹 Example:
<output>50</output>
✅ Key Points:
- Often used with JavaScript.
📍 <progress> - Progress Bar
✅ Definition: Shows progress percentage.
✅ Usage: Used for loading indicators.
🔹 Example:
<progress value="50" max="100"></progress>
✅ Key Points:
-
value="50"shows progress out ofmax="100".
📍 <meter> - Measurement Bar
✅ Definition: Displays a value in a known range.
✅ Usage: Used for performance levels.
🔹 Example:
<meter value="7" min="0" max="10"></meter>
✅ Key Points:
- Good for battery life, scores, or ratings.
📌 Full Form Example
<form action="/submit" method="POST">
<fieldset>
<legend>Signup Form</legend>
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<input type="text" id="name" name="name">
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email">
<label for="age">Age:</label>
<input type="number" id="age" name="age">
<label for="country">Country:</label>
<select id="country" name="country">
<option value="us">USA</option>
<option value="uk">UK</option>
</select>
<label for="message">Message:</label>
<textarea id="message" name="message" rows="4"></textarea>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</fieldset>
</form>
✅ Key Points:
- Uses multiple input types.
- Well-structured with <fieldset> and <legend>.
🟢 7. Other Semantic Tags
These tags add meaning and functionality to content, making pages more interactive and accessible.
📍 <details> - Expandable Content
✅ Definition: Creates a collapsible section.
✅ Usage: Used for FAQs, extra info, or hidden content.
🔹 Example:
<details>
<summary>What is HTML?</summary>
<p>HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language.</p>
</details>
✅ Key Points:
-
Clicking
<summary>toggles visibility. - Can be used for FAQ sections.
📍 <summary> - Details Title
✅ Definition: Defines a clickable heading for <details>.
✅ Usage: Used to describe expandable content.
🔹 Example:
<summary>Click to reveal more</summary>
✅ Key Points:
- Always placed inside
<details>.
📍 <dialog> - Pop-up Box
✅ Definition: Creates a modal (popup) window.
✅ Usage: Used for alerts, confirmations, or messages.
🔹 Example:
<dialog id="myDialog">
<p>Welcome to my website!</p>
<button onclick="this.parentElement.close()">Close</button>
</dialog>
<button onclick="document.getElementById('myDialog').showModal()">Open Dialog</button>
✅ Key Points:
-
showModal()→ Opens the dialog as a popup.
- close() → Closes the popup.
📌 Full Example with All Tags
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Other Semantic Tags</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Expandable Content</h2>
<details>
<summary>What is JavaScript?</summary>
<p>JavaScript is a programming language for web development.</p>
</details>
<h2>Modal Dialog</h2>
<dialog id="infoDialog">
<p>This is a popup message.</p>
<button onclick="this.parentElement.close()">Close</button>
</dialog>
<button onclick="document.getElementById('infoDialog').showModal()">Open Popup</button>
</body>
</html>
✅ Key Points:
-
<details>and<summary>create an interactive expandable section. -
<dialog>is used for popup messages.
- Marquee in HTML
Definition:
The <marquee> tag is used to create scrolling text or images. However, it is deprecated in HTML5. Instead, CSS animations should be used.
Attributes:
-
direction: Specifies the scroll direction (left,right,up,down). -
behavior: Defines the scrolling type (scroll,slide,alternate). -
scrollamount: Controls the speed of the scrolling. -
loop: Specifies the number of times the marquee should loop.
Example (Deprecated Method):
<marquee bgcolor="green" direction="right">Welcome to HTML</marquee>
Example (Modern CSS Method):
<div style="background-color: green; overflow: hidden">
<div class="marquee">Welcome to HTML</div>
</div>
<style>
.marquee {
width: 150px;
padding: 10px;
white-space: nowrap;
animation: scroll 10s linear infinite;
}
@keyframes scroll {
0% { transform: translateX(100%); }
100% { transform: translateX(-100%); }
}
</style>
-
<details>and<summary>
Definition:
- The
<details>tag is used to create a collapsible content section. - The
<summary>tag provides a heading for the collapsible section.
Example:
<details>
<summary>What is HTML?</summary>
<p>HTML stands for Hypertext Markup Language.</p>
</details>
-
<dialog>Tag
Definition:
The <dialog> element is used to create modal dialogs in HTML.
Example:
<button onclick="document.getElementById('modal').show()">Show Dialog</button>
<dialog id="modal">
<h3>Sample Heading</h3>
<p>This is a sample dialog box.</p>
<button onclick="document.getElementById('modal').close()">Close</button>
</dialog>
- HTML Entities & Symbols
Definition:
HTML entities are special codes used to display reserved or special characters in HTML.
Common Entities:
| Entity Code | Symbol |
|---|---|
© |
© |
™ |
™ |
® |
® |
< |
< |
> |
> |
& |
& |
Example:
<p>© 2025 YourWebsite ™ ® </p>
Emojis:
| Emoji Code | Emoji |
|---|---|
😊 |
😊 |
👋 |
👋 |
😄 |
😄 |
<p>Hello! 👋 Welcome to my site! 😊</p>
- HTML File Paths
Definition:
File paths specify the location of files in a website.
Types of File Paths:
- Relative Path: References files within the same directory.
- Absolute Path: References files using a full URL.
-
Root-relative Path: Starts from the root directory (
/).
Examples:
Relative Path:
<img src="./photo.jpg" alt="Sample" width="300px" />
Absolute Path:
<img src="https://example.com/image.jpg" alt="Sample" width="300px" />
Root-relative Path:
<img src="/images/sample.jpg" alt="Sample" width="300px" />
- HTML Image Handling
Definition:
The <img> tag is used to display images in HTML.
Attributes:
-
src: Specifies the image source. -
alt: Provides alternative text if the image fails to load. -
width&height: Set the size of the image. -
loading: Specifies lazy loading for images (lazy,eager).
Example:
<img src="https://cdn.britannica.com/34/235834-050-C5843610/cat.jpg" alt="Cat" width="300px" loading="lazy" />
- Character Sets in HTML
Definition:
A character set in HTML defines how characters are encoded and displayed in web browsers.
Common Character Sets:
| Charset | Description |
|---|---|
| UTF-8 | Universal character set (supports most languages) |
| ISO-8859-1 | Western European languages |
| ASCII | Basic English characters |
Setting Character Encoding:
The <meta charset> tag specifies the character encoding of an HTML document.
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Character Encoding</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>© 2025 - Welcome to my website!</p>
</body>
</html>
Why Use UTF-8?
- It supports all languages and special characters.
- It prevents display issues with non-English characters.








Top comments (0)