1.Entity:
package com.example.demo.entity;
import jakarta.persistence.Entity;
import jakarta.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import jakarta.persistence.GenerationType;
import jakarta.persistence.Id;
import jakarta.persistence.Table;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Entity
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Getter
@Table(name="product")
public class Product {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public String getImg() {
return img;
}
public void setImg(String img) {
this.img = img;
}
public Integer getRating() {
return rating;
}
public void setRating(Integer rating) {
this.rating = rating;
}
public Integer getStock() {
return stock;
}
public void setStock(Integer stock) {
this.stock = stock;
}
public Long getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(Long price) {
this.price = price;
}
private String name, description, img;
private Integer rating, stock;
private Long price;
}
2.repository:
package com.example.demo.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.example.demo.entity.Product;
@Repository
public interface ProductRepository extends
JpaRepository<Product, Long>{
}
3.Service:
package com.example.demo.service;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.example.demo.entity.Product;
import com.example.demo.repository.ProductRepository;
@Service
public class ProductService {
private final ProductRepository repository;
public ProductService(ProductRepository repository)
{
this.repository = repository;
}
public List<Product> getAllProducts()
{
return repository.findAll();
}
public Product addProduct(Product product)
{
return repository.save(product);
}
}
4.Controller:
package com.example.demo.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.example.demo.entity.Product;
import com.example.demo.service.ProductService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/products")
public class ProductController {
private final ProductService service;
public ProductController(ProductService service)
{
this.service = service;
}
@GetMapping
public List<Product> showAllProducts()
{
return service.getAllProducts();
}
@PostMapping
public Product addProduct(@RequestBody Product product)
{
return service.addProduct(product);
}
}
neelakandan@neelakandan-HP-Laptop-15s-eq2xxx:~$ sudo -i -u postgres
[sudo] password for neelakandan:
postgres@neelakandan-HP-Laptop-15s-eq2xxx:~$ psql
psql (16.8 (Ubuntu 16.8-0ubuntu0.24.04.1))
Type "help" for help.
postgres=# \c ecommerce
You are now connected to database "ecommerce" as user "postgres".
ecommerce=# \d
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+----------------+----------+-------
public | cart | table | ecom3
public | cart_id_seq | sequence | ecom3
public | payment | table | ecom3
public | payment_id_seq | sequence | ecom3
public | product | table | ecom3
public | product_id_seq | sequence | ecom3
(6 rows)
ecommerce=# \d product
ecommerce=# SELECT * FROM product
ecommerce-# SELECT * FROM product
ecommerce-# \l
ecommerce-# ^C
ecommerce=# SELECT * FROM product;
id | description | img | name | price | rating | stock
----+-------------+--------+--------+-------+--------+-------
1 | Good prod | link-1 | prod-1 | 10000 | 4 | 10
(1 row)
ecommerce=#
ERROR: database "ecommerce" is being accessed by other users
DETAIL: There are 10 other sessions using the database.
**
*Create file called APP.js and base below code *
import logo from './logo.svg';
import './App.css';
import ProductCard from './components/ProductCard';
import { getProducts } from './api';
import { useEffect, useState } from 'react';
function App() {
const [productList,setProductList] = useState([]);
useEffect(()=>{
getProducts()
.then((res)=>setProductList(res.data))
.catch((err)=>console.log(err));
},[])
return (
<div className="App">
<header className="App-header">
{
productList.map((prod)=><ProductCard items={prod}/>)
// <ProductCard items = {productList[3]}/>
}
</header>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
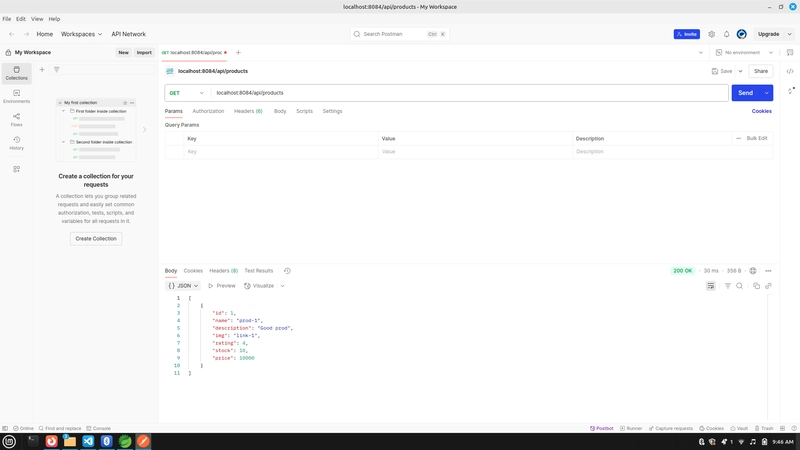
API Endpoint URL** :localhost:8084/api/products
In a React application, you can send data to a backend server (like a Spring Boot API) using a POST request. To do this, we use the fetch() method or a library like axios. In the example above, we created a simple form that accepts a product's name and price. When the form is submitted, the handleSubmit function is called. Inside handleSubmit, we send a POST request to http://localhost:8084/api/products, with the form data converted into JSON format. The server is expected to accept this data, save it (e.g., into a database), and return a response. To allow this, the Spring Boot backend must have a controller method with @PostMapping("/api/products") and accept the incoming JSON using @RequestBody. This setup allows the React frontend and Spring Boot backend to communicate, making it possible to add new products dynamically from the user interface.
*Create file called API.js and base below code *
import axios from "axios";
export const getProducts = ()=> axios.get("http://localhost:8084/api/products");
Create file component file and create file called name.jsx
function ProductCard({items})
{
return(
<div>
<img src={items.img} alt="" />
name : {items.name}
price : {items.price}
</div>
)
}
export default ProductCard;



Top comments (3)
pretty solid walkthrough ngl- i always mess up somewhere connecting backend and frontend, so this helps. you think making everything from scratch is worth the hassle or nah?
Great job! Thanks for sharing!
Hi! I recently built an e-commerce project using Spring Boot 3 and would love your feedback or suggestions on how I can expand and improve it.
🔗ecommerce-render-2.onrender.com