As a student who recently started learning Data Engineering, one of the first tools we were introduced to was Git and GitHub it is one of the most important tools for anyone working with code and data and planning to collaborate with my fellow students at LuxDevHQ
This article explains in a simple way:
- What Git and GitHub are
- How to set up Git Bash
- How to connect Git to GitHub
- How to push and pull code
- How version control works
What is Git?
Git is a version control system.
It helps you keep track of every change you make to your files and keep track of each version of your code.
This is very important in Data Engineering because we:
- Experiment with data
- Change code often
- Work on long projects
Git makes sure nothing gets lost.
What is GitHub?
GitHub is a website where Git projects are stored online.
It allows you to:
- Back up your work
- Share your projects
- Work with other people
- Show your work to employers
Git works on your computer.
GitHub stores your Git projects on the internet.
Installing Git Bash
For my case, i use a macbook so i dont install Git Bash natively so i install git via the terminal.
On macOS
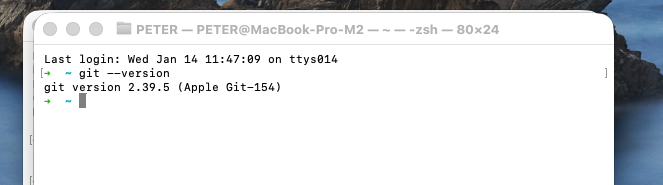
Open Terminal and type
git --version
# Connecting to a GitHub Account
## Step 1: Login or Create a GitHub account., since i have an account i just login
## Step 2: Configure Git with your details
Run the following commands:
bash
git config --global user.name "Your Name"
git config --global user.email "youremail@example.com"
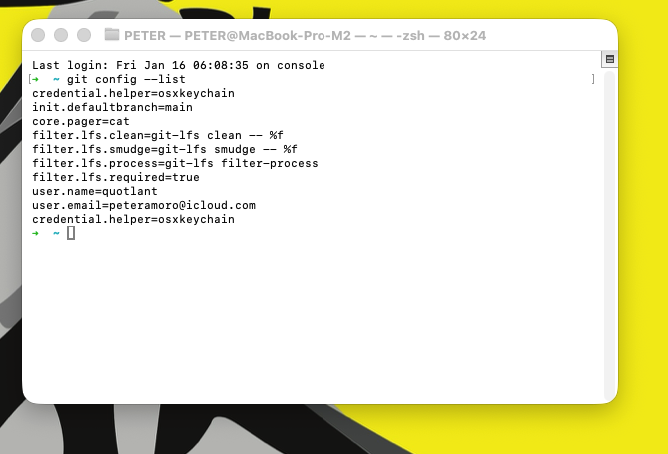
Confirm the setup:
bash
git config --list
# Connecting Git to GitHub Using SSH
Using **SSH** allows you to push and pull code **without entering your password every time**.
## Generate an SSH key
bash
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C "youremail@example.com"
Press **Enter** for all prompts.
## Start the SSH agent and add the key
bash
eval "$(ssh-agent -s)"
ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_ed25519
## Copy the SSH key
bash
pbcopy < ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub
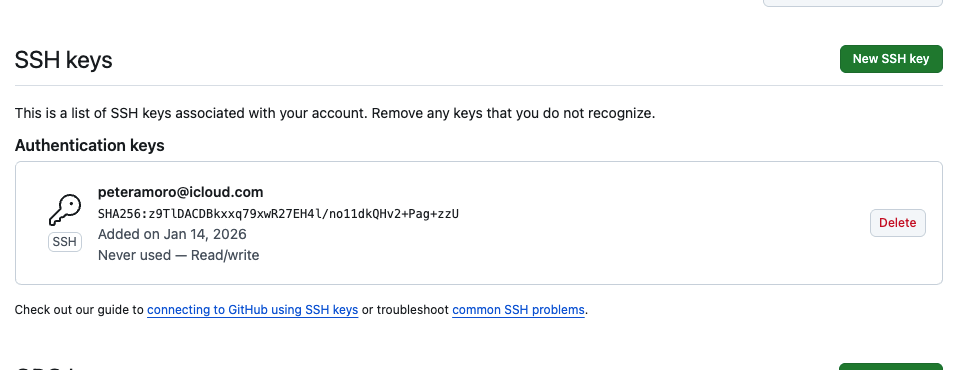
## Add the SSH key to GitHub
1. Go to **GitHub Settings**
2. Select **SSH and GPG keys**
3. Click **New SSH key**
4. Paste the key and save
Test the connection:
bash
ssh -T git@github.com
A success message confirms the connection.
# Understanding Version Control
**Version control** is a system that:
* Tracks **file changes**
* Saves a **history of your project**
* Allows you to **restore previous versions**
* Enables **safe collaboration**
Git works like a **timeline**, recording every meaningful change.
# Creating a Local Git Repository
## Create a project folder
bash
mkdir luxDev
cd luxdev
## Initialize Git
bash
git init
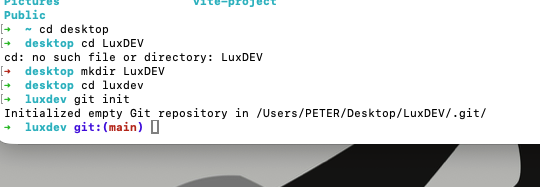
Git now tracks this folder.
# Tracking Changes with Git
## Check file status
bash
git status
## Add files to the staging area
bash
git add .
## Commit changes
bash
git commit -m "Initial commit"
A **commit** is a saved snapshot of your project.
# Pushing Code to GitHub
## Create a repository on GitHub
* Click **New Repository**
* Do **not** add a README file
* Copy the **SSH repository link**
## Connect the local project to GitHub
bash
git remote add origin git@github.com:username/repository-name.git
## Push code to GitHub
bash
git branch -M main
git push -u origin main
Your code is now available on **GitHub**.
# Pulling Code from GitHub
To download updates from GitHub:
bash
git pull origin main
This is useful when:
* Working on **multiple devices**
* Collaborating with **other developers**
* Updating **shared projects**
# Viewing Project History
bash
git log
This command shows **previous commits**, authors, and dates.


Top comments (0)