Wazuh, as a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tool, is a critical component in securing Kubernetes clusters. It excels in real-time log data analysis, providing early threat detection and facilitating swift incident response. Wazuh’s ability to gather and interpret data from the Kubernetes environment allows security teams to identify and respond to threats promptly, minimizing potential damage.
In addition to threat management, Wazuh aids in demonstrating compliance with industry-specific security standards by generating detailed reports on security events and measures. Post-incident, it offers valuable data for forensic analysis, enabling teams to understand the incident’s cause and prevent future occurrences.
In this blog post we will go through the basic process of creating Alert for Kubernetes Events with Wazuh, especially for RKE2 cluster.
Steps:
- Create a webhook listener on the Wazuh server to receive logs from the Kubernetes cluster.(This process is same for all despite any kind of deployment tool for managing kubernetes cluster)
- Enable auditing on the Kubernetes cluster and configure it to forward audit logs to the Wazuh webhook listener. (Differs in RKE2 from kubeadm and minikube)
- Create rules on the Wazuh server to alert about audit events received from Kubernetes.
Requirements:
- A Wazuh server
- A self managed kubernetes cluster
Configure the Wazuh Server:
We create a webhook listener on the Wazuh server to receive the Kubernetes audit logs. Here we create certificates for communication between the Wazuh server and Kubernetes.
- Login to your Wazuh server:
ssh user@wazuhServer
- Create a directory for the webhook endpoint:
mkdir -p /var/ossec/integrations/kubernetes-webhook/
- Create a certificate configuration file
/var/ossec/integrations/kubernetes-webhook/csr.conf: Replace<wazuh_server_ip>and<wazuh_server_ip>with your server’s IP address.
[ req ]
prompt = no
default_bits = 2048
default_md = sha256
distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name
x509_extensions = v3_req
[req_distinguished_name]
C = US
ST = California
L = San Jose
O = Wazuh
OU = Research and development
emailAddress = info@wazuh.com
CN = <wazuh_server_ip>
[ v3_req ]
authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid,issuer
basicConstraints = CA:FALSE
keyUsage = digitalSignature, nonRepudiation, keyEncipherment, dataEncipherment
subjectAltName = @alt_names
[alt_names]
IP.1 = <wazuh_server_ip>
- Create the root CA public and private keys:
openssl req -x509 -new -nodes -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /var/ossec/integrations/kubernetes-webhook/rootCA.key -out /var/ossec/integrations/kubernetes-webhook/rootCA.pem -batch -subj "/C=US/ST=California/L=San Jose/O=Wazuh"
- Create the certificate signing request (csr) and the server private key
openssl req -new -nodes -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /var/ossec/integrations/kubernetes-webhook/server.key -out /var/ossec/integrations/kubernetes-webhook/server.csr -config /var/ossec/integrations/kubernetes-webhook/csr.conf
- Generate the server certificate:
openssl x509 -req -in /var/ossec/integrations/kubernetes-webhook/server.csr -CA /var/ossec/integrations/kubernetes-webhook/rootCA.pem -CAkey /var/ossec/integrations/kubernetes-webhook/rootCA.key -CAcreateserial -out /var/ossec/integrations/kubernetes-webhook/server.crt -extfile /var/ossec/integrations/kubernetes-webhook/csr.conf -extensions v3_req
Create the webhook listener:
- Install Flask using pip:
/var/ossec/framework/python/bin/pip3 install flask
- Create the Python webhook listener
/var/ossec/integrations/custom-webhook.py. Replace<wazuh_server_ip>with your Wazuh server IP address:
#!/var/ossec/framework/python/bin/python3
import json
from socket import socket, AF_UNIX, SOCK_DGRAM
from flask import Flask, request
PORT = 8080
CERT = '/var/ossec/integrations/kubernetes-webhook/server.crt'
CERT_KEY = '/var/ossec/integrations/kubernetes-webhook/server.key'
socket_addr = '/var/ossec/queue/sockets/queue'
def send_event(msg):
string = '1:k8s:{0}'.format(json.dumps(msg))
sock = socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_DGRAM)
sock.connect(socket_addr)
sock.send(string.encode())
sock.close()
return True
app = Flask(__name__)
context = (CERT, CERT_KEY)
@app.route('/', methods=['POST'])
def webhook():
if request.method == 'POST':
if send_event(request.json):
print("Request sent to Wazuh")
else:
print("Failed to send request to Wazuh")
return "Webhook received!"
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='<wazuh_server_ip>', port=PORT, ssl_context=context)
- Create a systemd service at
/lib/systemd/system/wazuh-webhook.service:
[Unit]
Description=Wazuh webhook
Wants=network-online.target
After=network.target network-online.target
[Service]
ExecStart=/var/ossec/framework/python/bin/python3 /var/ossec/integrations/custom-webhook.py
Restart=on-failure
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
- Start service:
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable wazuh-webhook.service
systemctl start wazuh-webhook.service
Note:
- Enable access to port 8080 if a firewall is running on the Wazuh server.
Configure the Kubernetes Cluster:
Create log directory:
mkdir -p -m 700 /var/lib/rancher/rke2/server/logs
- Create an audit policy at
/var/lib/rancher/rke2/server/audit.yaml:
apiVersion: [audit.k8s.io/v1](http://audit.k8s.io/v1)
kind: Policy
rules:
# Don’t log requests to the following API endpoints
- level: None
nonResourceURLs:
- '/healthz*'
- '/logs'
- '/metrics'
- '/swagger*'
- '/version'
# Limit requests containing tokens to Metadata level so the token is not included in the log
- level: Metadata
omitStages:
- RequestReceived
resources:
- group: authentication.k8s.io
resources:
- tokenreviews
# Extended audit of auth delegation
- level: RequestResponse
omitStages:
- RequestReceived
resources:
- group: authorization.k8s.io
resources:
- subjectaccessreviews
# Log changes to pods at RequestResponse level
- level: RequestResponse
omitStages:
- RequestReceived
resources:
# core API group; add third-party API services and your API services if needed
- group: ''
resources: ['pods']
verbs: ['create', 'patch', 'update', 'delete']
# Log everything else at Metadata level
- level: Metadata
omitStages:
- RequestReceived
- Replace
<wazuh_server_ip>and create the webhook configuration file/var/lib/rancher/rke2/server/audit-webhook.yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Config
preferences: {}
clusters:
- name: wazuh-webhook
cluster:
insecure-skip-tls-verify: true
server: https://<wazuh_server_ip>:8080
# kubeconfig files require a context. Provide one for the API server.
current-context: webhook
contexts:
- context:
cluster: wazuh-webhook
user: kube-apiserver # Replace with name of API server if it’s different
name: webhook
- Add the Kubeapi parameters to load the auditing and webhook configurations:
Path for systemd service file for rke2-server.service:
/usr/lib/systemd/system/rke2-server.service:
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/rke2 \
server \
'--kube-apiserver-arg=audit-log-path=/var/lib/rancher/rke2/server/logs/audit.log' \
'--kube-apiserver-arg=audit-policy-file=/var/lib/rancher/rke2/server/audit.yaml' \
'--kube-apiserver-arg=audit-webhook-config-file=/var/lib/rancher/rke2/server/audit-webhook.yaml' \
'--kube-apiserver-arg=audit-webhook-batch-max-size=1' \
Create detection rule on Wazuh Server:
- Add the following rules to the Wazuh server at
/var/ossec/etc/rules/local_rules.xml:
<group name="k8s_audit,">
<rule id="110002" level="0">
<location>k8s</location>
<field name="apiVersion">audit</field>
<description>Kubernetes audit log.</description>
</rule>
<rule id="110003" level="5">
<if_sid>110002</if_sid>
<regex type="pcre2">requestURI\":.+", \"verb\": \"create</regex>
<description>Kubernetes request to create resource</description>
</rule>
<rule id="110004" level="5">
<if_sid>110002</if_sid>
<regex type="pcre2">requestURI\":.+", \"verb\": \"delete</regex>
<description>Kubernetes request to delete resource</description>
</rule>
</group>
- Restart wazuh-manager service:
systemctl restart wazuh-manager
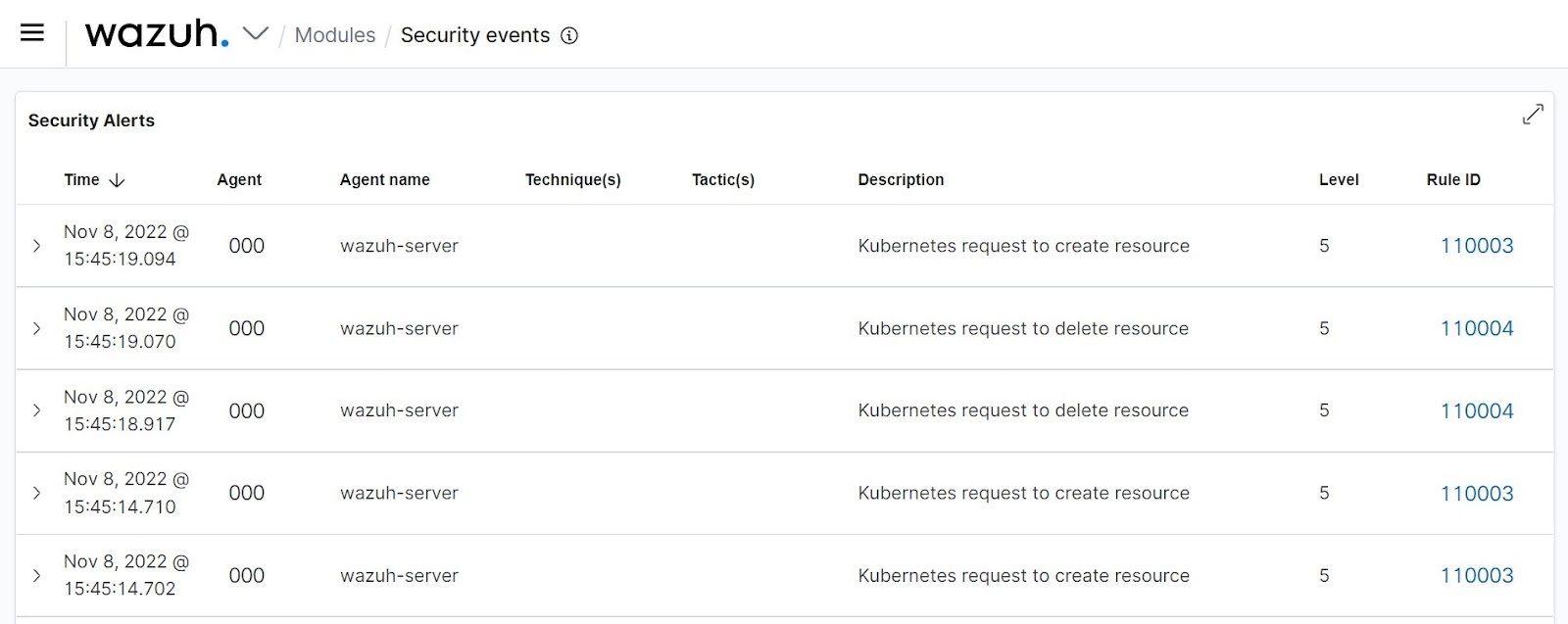
- Test the configuration Test the rules by creating and deleting a deployment on the Kubernetes cluster.
- Run the following command on the Kubernetes master node to create a new deployment:
kubectl create deployment hello-minikube --image=[k8s.gcr.io/echoserver:1.4](http://k8s.gcr.io/echoserver:1.4)
- Run the following command to delete the deployment: ```bash
kubectl delete deployment hello-minikube
## Slack Alerting:
The integrations are configured on the Wazuh manager `ossec.conf` file. You can find this file in the Wazuh installation folder `/var/ossec/etc/`. To configure an integration, add the following configuration within the `<ossec_config>` section:
```xml
<integration>
<name>slack</name>
<hook_url>SLACK_WEBHOOK_URL</hook_url>
<level>10</level>
<rule_id>110003</rule_id>
<rule_id>110004</rule_id>
<alert_format>json</alert_format>
</integration>
- Restart the Wazuh manager to apply the changes:
systemctl restart wazuh-manager
- Once the configuration is complete, alerts start showing in the selected channel:
Special thanks to the awesome documentation from the Wazuh team. Where I got the first part of this blog post from.



Top comments (0)