Man-In-The Middle:
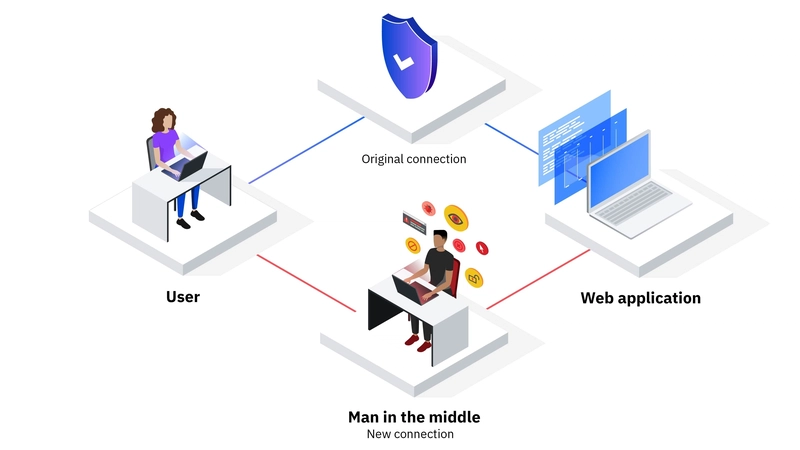
A Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attack is a cyberattack where a hacker secretly intercepts communication between two parties, such as a user and a website, without their knowledge. The attacker can eavesdrop, steal sensitive information, or even manipulate the data being exchanged. This type of attack is especially dangerous when dealing with financial transactions, login credentials, and personal data.
Here's How It Work:
1. Interception:
The attacker places themselves between the two communicating parties, often by exploiting weak or unsecured networks. This can be done through techniques like rogue Wi-Fi hotspots or DNS spoofing.
2. Eavesdropping:
Once in position, the attacker can silently monitor and record the communication. This allows them to capture sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, credit card details, and private messages.
3. Manipulation:
In some cases, the hacker doesn’t just listen—they modify the data being sent. This could involve redirecting the victim to a fake website, injecting malicious code, or altering financial transactions.
Here's The Framework That For Understanding Quickly!
Some Common Type Of MITM:
1. Fake Wi-Fi Hotspots:
Hackers set up robust public Wi-Fi networks that appear legitimate (e.g., “Free Airport Wi-Fi”). When users connect, the attacker can monitor all unencrypted traffic and steal sensitive data.
2. DNS Spoofing:
In this method, the attacker tricks your device into visiting a fake website instead of the real one. For example, you think you're logging into "yourbank.com," but you're actually on a fraudulent site that looks identical, designed to steal your credentials.
3. HTTPS Downgrade (SSL Stripping):
Some attackers force your connection to switch from secure HTTPS to insecure HTTP, making it easier for them to intercept and read your data. Always check for the lock icon in the browser’s address bar.
4. Session Hijacking (Cookies):
Here, the hacker steals session cookies (small pieces of data that keep you logged into websites). With these cookies, they can impersonate you and gain access to your accounts without needing your password.
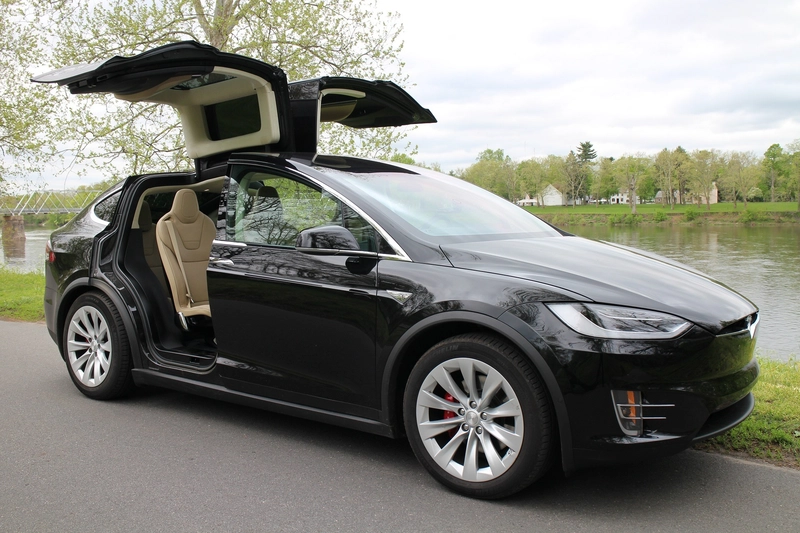
(MITM) Real-World Attack:
In 2024, security researchers reported that a vulnerability enables hackers to launch an MITM attack to unlock and steal Tesla vehicles.1
Using a spoofed wifi hotspot at a Tesla charging station, an attacker could harvest the account credentials of a Tesla owner. The attacker could then add a new “phone key” that unlocks and starts the vehicle without the knowledge of the vehicle owner, according to the researchers.
Robust Security Preventions:
1. Use HTTPS websites: Users should only visit websites with a secure connection, indicated by “HTTPS” and a padlock icon in the browser’s address bar. Websites that only offer unsecured HTTP connections should be avoided, especially when entering sensitive information.
2. Avoid public Wi-Fi: Hackers often exploit unsecured networks. If you must use public Wi-Fi, always connect through a VPN (Virtual Private Network) to encrypt your data. Users should avoid public Wi-Fi networks when performing transactions involving sensitive data, such as making purchases or logging into financial accounts.
3. Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN): A VPN provides strong protection against MITM attacks by encrypting all network traffic. Even if a breach occurs, hackers won’t be able to read sensitive data like login credentials, credit card numbers, or personal account details.
4. Keep your software updated: Security patches help fix vulnerabilities that hackers exploit in MITM attacks. Always update your operating system, browser, and applications to stay protected. If possible, upgrade to Windows 10 or 11 for enhanced security features and better privacy protection.
5. Use strong, unique passwords: A password manager can help generate and store secure passwords for each site. Passwords should be at least 10 to 15 characters long, including a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special symbols for maximum security.
6. Be cautious of suspicious links and emails: Phishing emails often contain fake login pages designed to steal your credentials. Always verify links before clicking and never enter sensitive information on unknown websites. Educate others about the latest security threats and vulnerabilities to help them stay protected as well.
Final Thoughts:
Man-in-the-Middle attacks are like digital pickpocketing—they’re sneaky, dangerous, and hard to notice. But by staying cautious and following these security steps, you can make yourself a much harder target.
Your data is valuable treat it like your wallet. If you wouldn’t hand your wallet to a stranger, don’t hand your information to an unsecured connection!




Top comments (0)