As enterprises increasingly move to the cloud, many organizations still require on-premises infrastructure for compliance, performance, or legacy system support. AWS Storage Gateway provides a hybrid cloud storage solution that enables seamless integration between on-premises data centres and AWS cloud storage services like Amazon S3, Amazon EBS, and Amazon FSx.
This article explores AWS Storage Gateway, its types, use cases, and how it enables hybrid cloud storage architectures.
Understanding Hybrid Cloud Storage
Hybrid cloud storage combines on-premises and cloud storage to balance performance, scalability, and cost efficiency. It enables organizations to:
- Extend on-premises storage to the cloud without disrupting applications.
- Use cloud storage for backup and disaster recovery while keeping frequently accessed data locally.
- Meet compliance and latency requirements by storing sensitive data on-premises while leveraging the cloud for processing and analytics.
What is AWS Storage Gateway?
AWS Storage Gateway is a hybrid cloud storage service that provides on-premises applications low-latency access to AWS storage while enabling seamless integration with AWS cloud services.
Key Benefits
- Seamless cloud integration – Extends on-premises workloads to AWS.
- Efficient data transfer – Uses compression and caching to optimize performance.
- Cost-effective – Reduces on-premises storage costs by leveraging AWS S3 and Glacier.
- Secure and scalable – Supports encryption, access controls, and automatic scaling.
Types of AWS Storage Gateway
AWS offers three types of Storage Gateway, each designed for specific use cases:
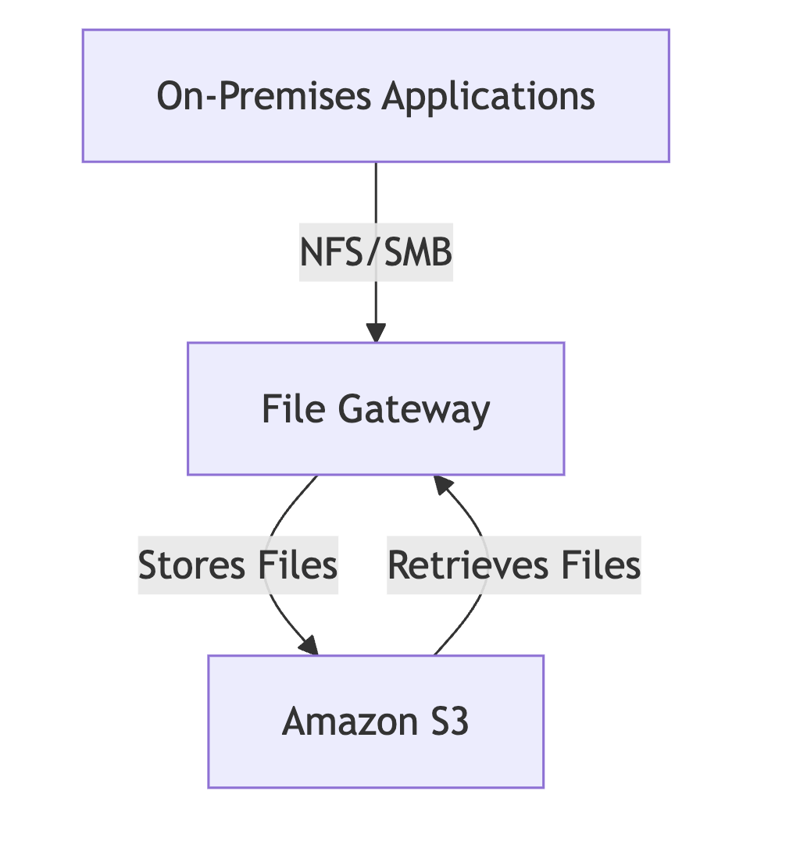
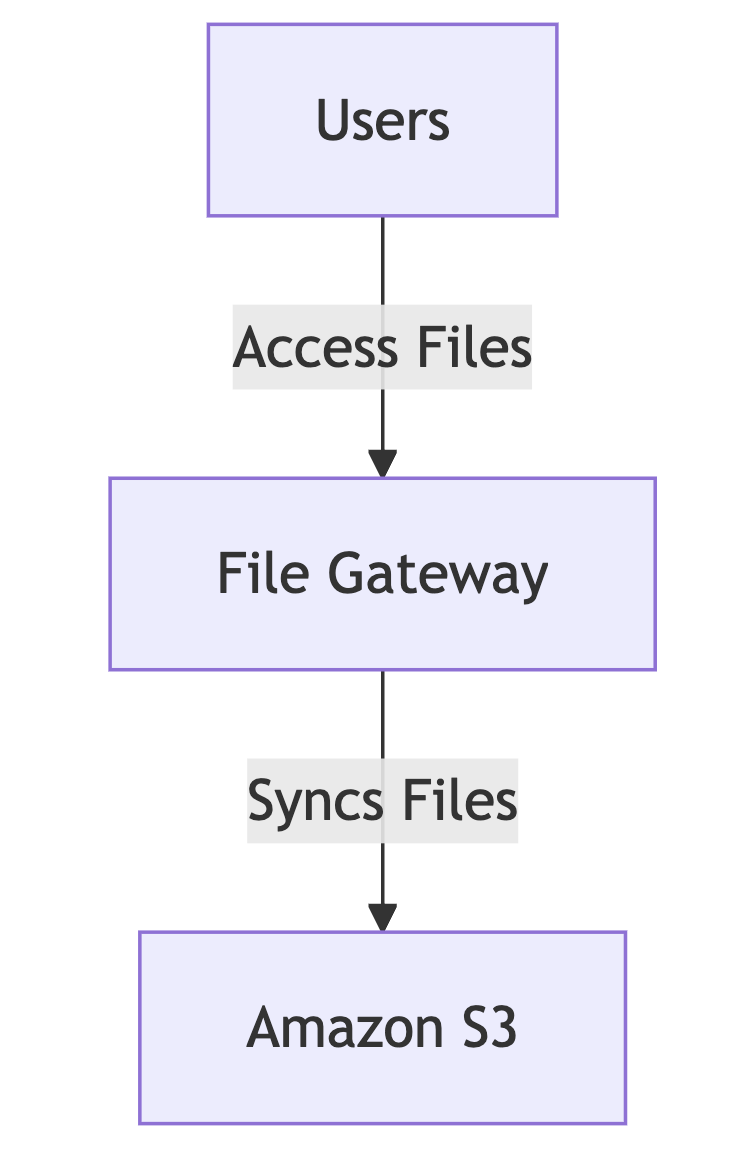
A. File Gateway (NFS & SMB)
- Provides a network file system interface (NFS or SMB).
- Stores files in Amazon S3, while keeping local copies in cache for fast access.
- Ideal for file sharing, backup, and data archival.
Example Use Case: A media company needs scalable storage for videos and images. File Gateway allows them to store files in Amazon S3 while providing local access for editing.
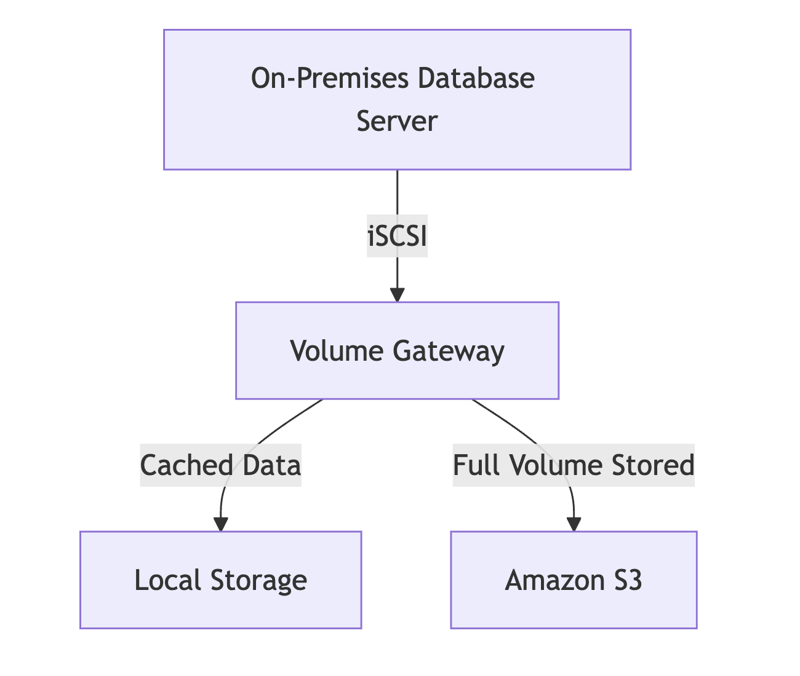
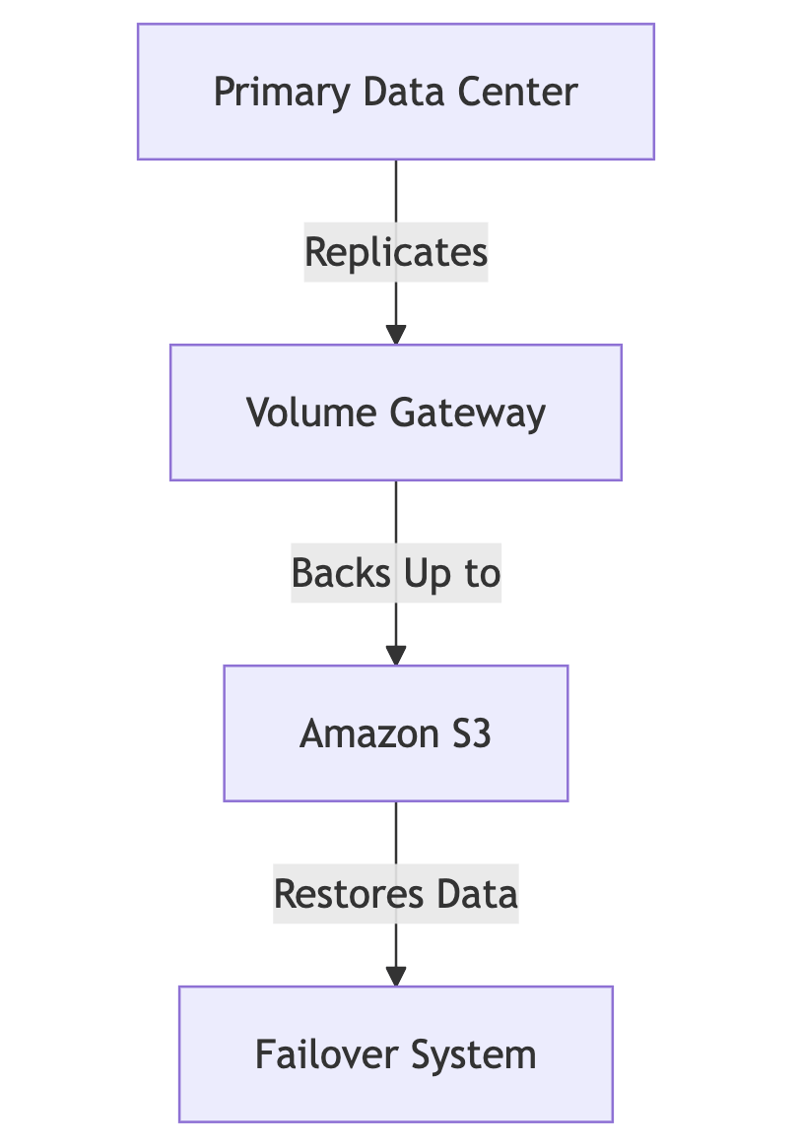
B. Volume Gateway (iSCSI)
- Provides block storage via the iSCSI protocol.
- Supports two modes:
- Cached Mode – Stores frequently accessed data locally while keeping full volumes in Amazon S3.
- Stored Mode – Keeps full copies on-premises and replicates to AWS for backup.
- Ideal for database storage and disaster recovery.
Example Use Case: A financial firm runs a database application on-premises but needs cloud backups. Volume Gateway allows them to store primary data locally while backing up volumes to AWS.
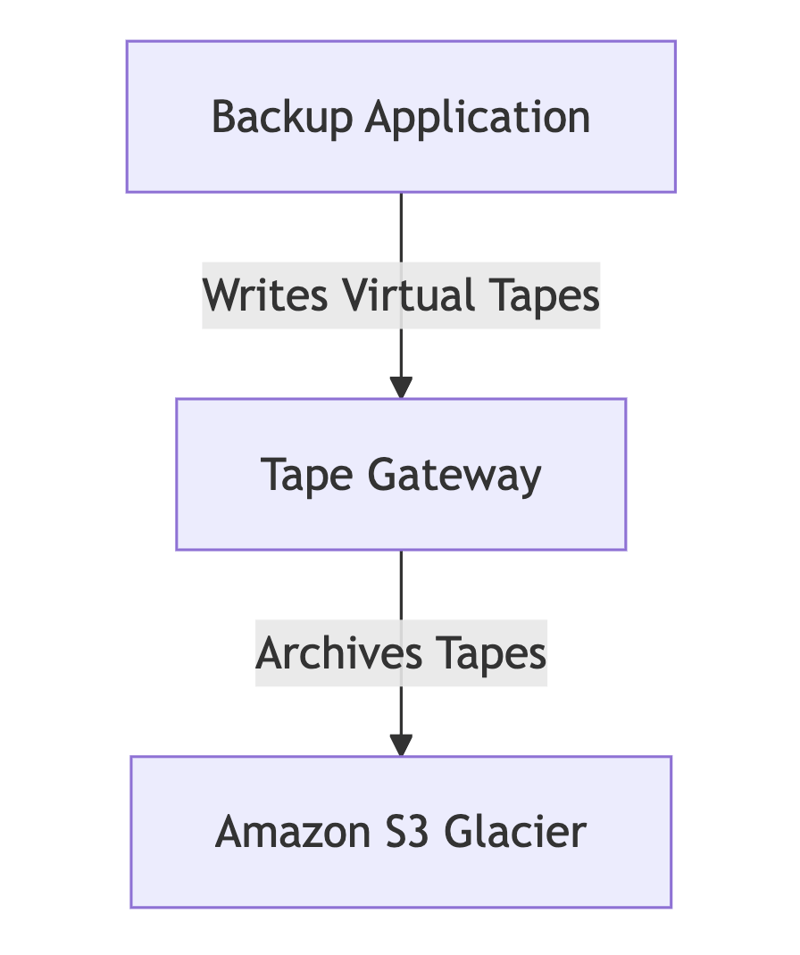
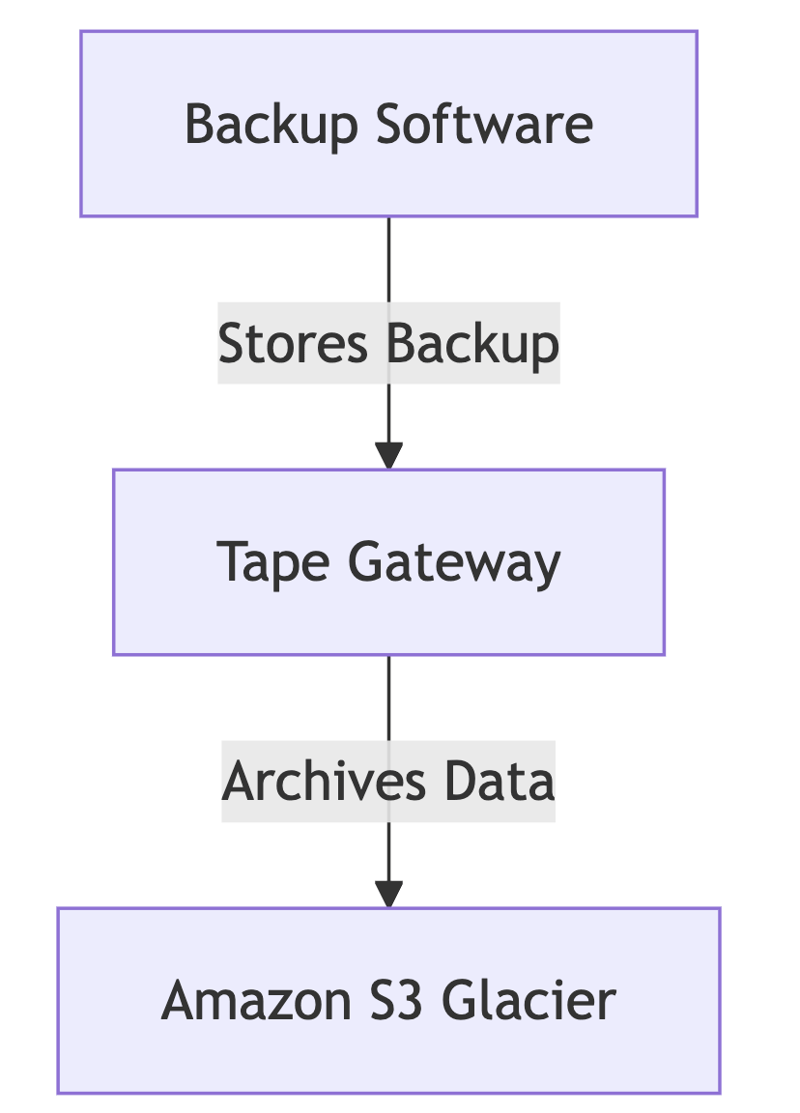
C. Tape Gateway (VTL for Backup & Archival)
- Replaces physical tape libraries with virtual tapes stored in Amazon S3 Glacier.
- Supports industry-standard backup applications (e.g., Veeam, NetBackup).
- Ideal for long-term archival, compliance, and regulatory requirements.
Example Use Case: A healthcare provider must retain medical records for decades. Tape Gateway allows them to archive data in Amazon S3 Glacier while reducing on-premises storage costs.
Hybrid Cloud Storage Architectures
A. Active Data with S3 File Gateway
Used for applications needing high-speed local access to active datasets while leveraging Amazon S3 for durability.
B. Disaster Recovery with Volume Gateway
Used for business continuity by replicating local volumes to AWS.
C. Archival Storage with Tape Gateway
Used for long-term data retention and compliance.
Integrating AWS Storage Gateway with Other AWS Services
AWS Storage Gateway integrates with several AWS services to enable a full-fledged hybrid cloud storage strategy:
| AWS Service | Integration Benefit |
|---|---|
| Amazon S3 | Stores primary and backup data from File/Volume Gateway. |
| Amazon EBS | Supports iSCSI-based storage for databases via Volume Gateway. |
| AWS Backup | Automates backup scheduling for hybrid storage solutions. |
| AWS S3 Glacier | Archives long-term data via Tape Gateway. |
| Amazon FSx | Provides Windows File Server integration for File Gateway. |
Best Practices for Hybrid Cloud Storage
- Enable data caching – Reduce latency by storing frequently accessed data locally.
- Use lifecycle policies – Move infrequently used data to S3 Glacier for cost savings.
- Encrypt data – Use AWS Key Management Service (KMS) to protect sensitive information.
- Monitor storage performance – Leverage Amazon CloudWatch for insights.
- Optimize data transfer – Use AWS Direct Connect or AWS Snowball for large-scale migrations.
Conclusion
AWS Storage Gateway enables businesses to seamlessly extend on-premises storage to the cloud, providing scalability, cost savings, and disaster recovery capabilities. By leveraging File, Volume, and Tape Gateway, organizations can efficiently store, back up, and archive data while maintaining low-latency access.
In our next article, we will explore AWS Data Analytics services, including AWS Glue for ETL, Amazon Athena for serverless querying, and Amazon Redshift for data warehousing.



Top comments (0)