Hello, I'm Maneshwar. I'm building git-lrc, an AI code reviewer that runs on every commit. It is free, unlimited, and source-available on Github. Star Us to help devs discover the project. Do give it a try and share your feedback for improving the product.
I'm working on FreeDevTools online currently building **one place for all dev tools, cheat codes, and TLDRs* — a free, open-source hub where developers can quickly find and use tools without any hassle of searching all over the internet.
Why Do You Need a Bundler?Modern web development often involves multiple JavaScript files, dependencies from npm, and the need for efficient performance.
A bundler helps by:
- Combining multiple JS files into one
- Reducing load times
- Allowing the use of modern JS features (import/export, ES6+)
- Simplifying dependency management
In this guide, we'll set up a basic, no-frame
work JavaScript bundler using Esbuild—one of the fast JS bundlers available.
No Webpack complexity, just pure bundling goodness! 😎
Step 1: Setup Your Project
First, create a new folder and initialize an npm project:
mkdir my-bundler-setup && cd my-bundler-setup
npm init -y
Now, install Esbuild as a development dependency:
npm install esbuild --save-dev
Step 2: Create JavaScript Files
We’ll create two JS files: file.js (main file) and file2.js (module file).
file2.js - A Simple Module
export function getMessage() {
return "Hello from bundled file2.js to dev.to!";
}
file.js - Main Script
import { getMessage } from "./file2.js";
function runDemo() {
console.log("Executing bundled script...");
document.getElementById("output").textContent = getMessage();
}
// Expose function to the browser
window.runDemo = runDemo;
Step 3: Create an HTML File
Create an index.html file to load our bundled script:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Esbuild Bundler Demo</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
text-align: center;
margin: 50px;
}
button {
padding: 10px 20px;
font-size: 16px;
cursor: pointer;
}
#output {
margin-top: 20px;
font-weight: bold;
color: #007bff;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Esbuild Bundler Demo</h1>
<p>Check the console for logs from the bundled script.</p>
<button onclick="runDemo()">Run Bundled Code</button>
<p id="output"></p>
<script src="http://localhost:3000/bundle.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Step 4: Bundle Everything with Esbuild
Now, let’s configure Esbuild to bundle our scripts into a single bundle.js file.
Add a Build Script to package.json
Modify your package.json to add a build script:
"scripts": {
"build": "esbuild file.js --bundle --outfile=bundle.js"
}
Now, run the build command:
npm run build
Expected output:
Awesome! 🚀 We now have a bundled JavaScript file (bundle.js) that combines both file.js and file2.js.
🌍 Step 5: Serve the Project Locally
To serve the project locally, install serve, a lightweight static server:
npm install -g serve
Run the server:
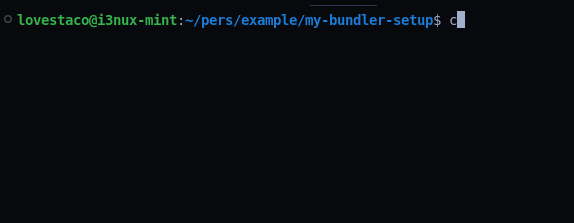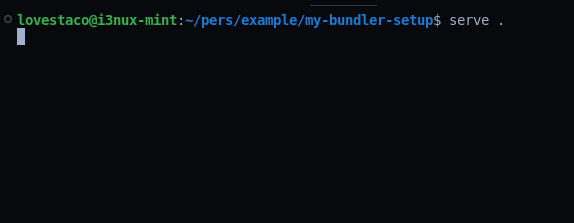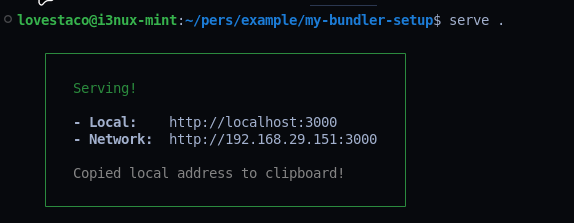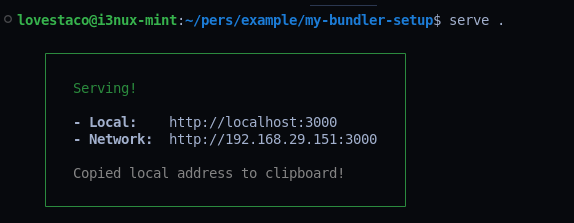
serve .
You should see an output like this:
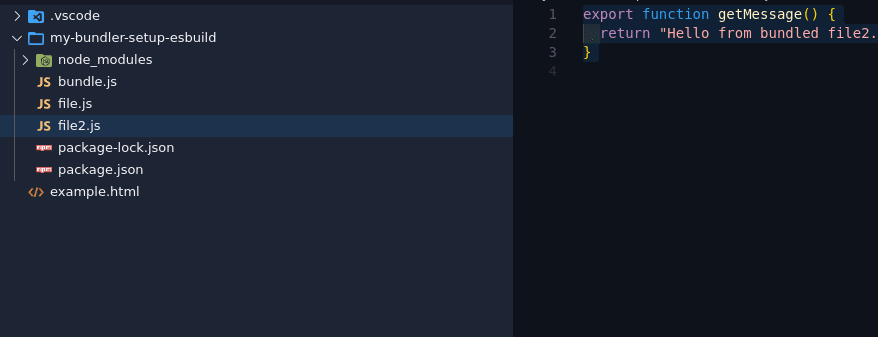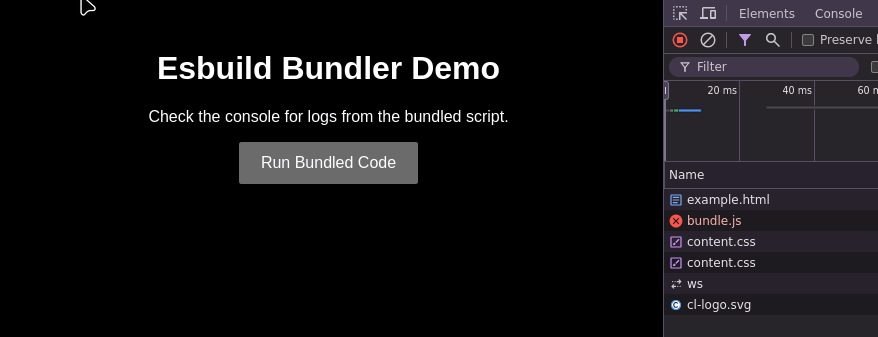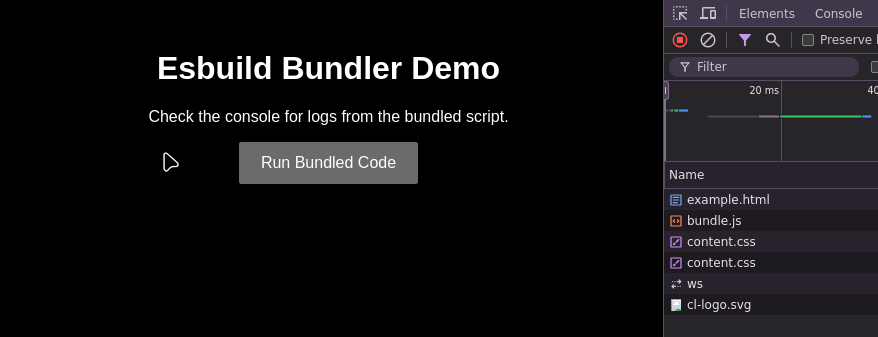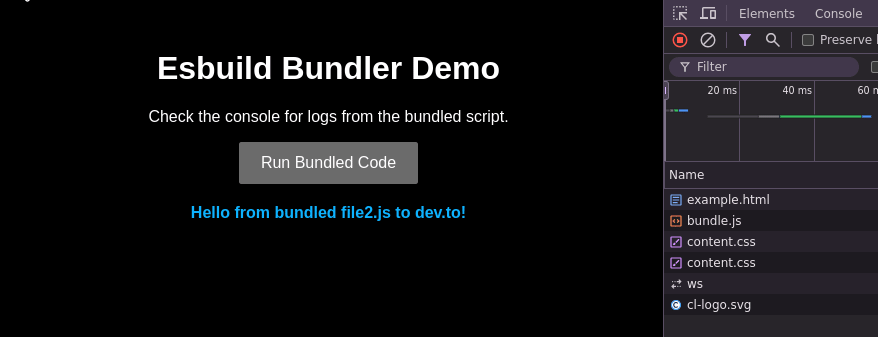
Now, open http://localhost:3000 in your browser.
Click the Run Bundled Code button and check the output!
🎯 Where Can This Be Used?
This simple bundler setup can be useful for:
- Small web projects needing modular JavaScript
- Quick prototyping without Webpack complexity and npm publishing
- Lightweight projects where frameworks aren’t required
- Experimenting with modern JavaScript features in the browser
- Educational purposes (learning ES6 modules, bundling, serving static files)
Wrapping Up
This is just the beginning—Esbuild can do much more! Stay tuned for future optimizations like minification, live-reloading, and more. 🚀
💡 What do you think? Would you use Esbuild for quick bundling? or a much faster one Rsbuild? Drop a comment below! 🎯
A collection of UI/UX-focused tools crafted to simplify workflows, save time, and reduce friction in searching tools/materials.
Any feedback or contributors are welcome!
It’s online, open-source, and ready for anyone to use.
👉 Check it out: ⭐ Star it on GitHub: Let’s make it even better together.

*AI agents write code fast. They also silently remove logic, change behavior, and introduce bugs -- without telling you. You often find out in production.
git-lrc fixes this. It hooks into git commit and reviews every diff before it lands. 60-second setup. Completely free.*
Any feedback or contributors are welcome! It's online, source-available, and ready for anyone to use.
⭐ Star it on GitHub:
 HexmosTech
/
git-lrc
HexmosTech
/
git-lrc
Free, Unlimited AI Code Reviews That Run on Commit
AI agents write code fast. They also silently remove logic, change behavior, and introduce bugs -- without telling you. You often find out in production.
git-lrc fixes this. It hooks into git commit and reviews every diff before it lands. 60-second setup. Completely free.
See It In Action
See git-lrc catch serious security issues such as leaked credentials, expensive cloud operations, and sensitive material in log statements
git-lrc-intro-60s.mp4
Why
- 🤖 AI agents silently break things. Code removed. Logic changed. Edge cases gone. You won't notice until production.
- 🔍 Catch it before it ships. AI-powered inline comments show you exactly what changed and what looks wrong.
- 🔁 Build a habit, ship better code. Regular review → fewer bugs → more robust code → better results in your team.
- 🔗 Why git? Git is universal. Every editor, every IDE, every AI…





Top comments (4)
Nice article! My favorite bundler is
bunbuild, because it's so fast!Thanks :)
Yeah, I've heard about that, will try it.
Extra points for the memes.
Thanks hehe :)