Data Types in Java
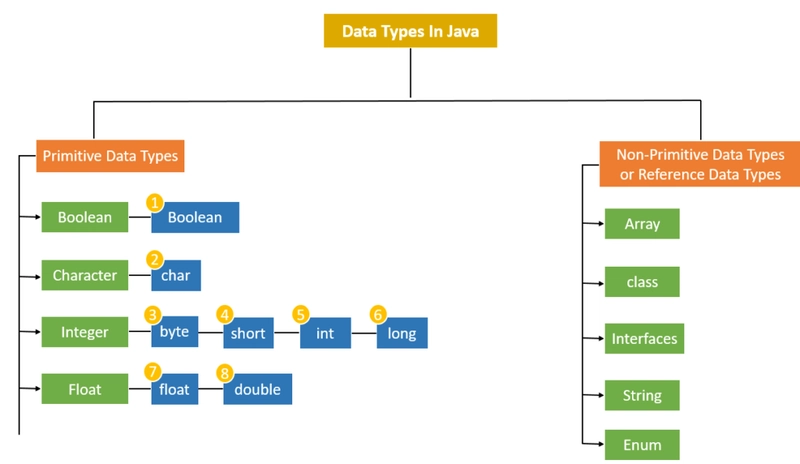
Java is a strongly typed language, which means every variable must be declared with a specific data type. Java data types are divided into two main categories:
1. Primitive Data Types
These are the most basic data types in Java and are built into the language. There are 8 primitive data types:
a) Integer Types (whole numbers)
-
byte
- Size: 8-bit (1 byte)
- Range: -128 to 127
- Default: 0
- Example:
byte b = 100;
-
short
- Size: 16-bit (2 bytes)
- Range: -32,768 to 32,767
- Default: 0
- Example:
short s = 10000;
-
int (most commonly used)
- Size: 32-bit (4 bytes)
- Range: -2³¹ to 2³¹-1 (-2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647)
- Default: 0
- Example:
int i = 100000;
-
long
- Size: 64-bit (8 bytes)
- Range: -2⁶³ to 2⁶³-1
- Default: 0L
- Example:
long l = 10000000000L;(Note the 'L' suffix)
b) Floating-Point Types (decimal numbers)
-
float
- Size: 32-bit (4 bytes)
- Range: approximately ±3.40282347E+38F
- Precision: 6-7 decimal digits
- Default: 0.0f
- Example:
float f = 3.14f;(Note the 'f' suffix)
-
double (default for decimal values)
- Size: 64-bit (8 bytes)
- Range: approximately ±1.79769313486231570E+308
- Precision: 15 decimal digits
- Default: 0.0d
- Example:
double d = 3.1415926535;
c) Character Type
-
char
- Size: 16-bit (2 bytes)
- Range: '\u0000' (0) to '\uffff' (65,535)
- Stores a single Unicode character
- Default: '\u0000'
- Example:
char c = 'A';orchar c = '\u0041';(Unicode for 'A')
d) Boolean Type
-
boolean
- Size: not precisely defined (typically 1 bit)
- Values: true or false
- Default: false
- Example:
boolean flag = true;
2. Non-Primitive Data Types (Reference Types)
These are objects that refer to memory locations where data is stored.
a) Classes
- Predefined classes like String, Scanner, etc.
- User-defined classes
- Example:
String s = "Hello";
b) Interfaces
- Example:
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
c) Arrays
- Example:
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3};
Key Differences Between Primitive and Non-Primitive Types
| Feature | Primitive Types | Non-Primitive Types |
|---|---|---|
| Storage | Store values directly | Store references to objects |
| Memory | Fixed size | Variable size |
| Default value | Have default values | Default is null |
| Performance | Faster | Slower |
| Methods | No methods | Have methods |
| Examples | int, char, boolean | String, Array, Classes |
Type Conversion
a) Widening (Implicit) Conversion
- Automatically done by compiler when converting smaller to larger types
- Example:
int i = 100; long l = i;
b) Narrowing (Explicit) Conversion
- Requires explicit cast and may lose data
- Example:
double d = 100.04; long l = (long)d;(l becomes 100)
Wrapper Classes
Java provides wrapper classes for each primitive type to use them as objects:
| Primitive | Wrapper Class |
|---|---|
| byte | Byte |
| short | Short |
| int | Integer |
| long | Long |
| float | Float |
| double | Double |
| char | Character |
| boolean | Boolean |
Example:
int primitiveInt = 42;
Integer wrapperInt = Integer.valueOf(primitiveInt); // Boxing
int unboxedInt = wrapperInt.intValue(); // Unboxing
// Autoboxing (automatic conversion since Java 5)
Integer autoBoxed = 42; // automatically converts to Integer
int autoUnboxed = autoBoxed; // automatically converts to int
Special Notes
-
Literals:
- Long: suffix with L (
long l = 123456789L;) - Float: suffix with F (
float f = 3.14F;) - Hexadecimal: prefix with 0x (
int hex = 0x1F;) - Binary: prefix with 0b (
int bin = 0b1010;)
- Long: suffix with L (
Underscores in Numeric Literals (Java 7+):
int million = 1_000_000;
long creditCard = 1234_5678_9012_3456L;
-
Default Values (for class fields):
- Numeric types: 0
- boolean: false
- char: '\u0000'
- Reference types: null
Understanding Java data types is fundamental to writing correct and efficient Java programs. The choice of data type affects memory usage, performance, and the range of values that can be stored.
Java Methods and Objects
1. Objects in Java
An object in Java is an instance of a class. It represents a real-world entity with:
- State (attributes/properties) – Represented by variables (fields)
- Behavior (actions) – Represented by methods
- Identity – Unique reference (memory address)
Creating an Object
Objects are created using the new keyword:
ClassName objectName = new ClassName();
Example:
public class Car {
// Fields (state)
String color;
String model;
int speed;
// Methods (behavior)
void accelerate() {
speed += 10;
}
void brake() {
speed -= 5;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating an object of Car
Car myCar = new Car();
// Assigning values to fields
myCar.color = "Red";
myCar.model = "Tesla";
myCar.speed = 0;
// Calling methods
myCar.accelerate();
System.out.println("Current Speed: " + myCar.speed); // Output: 10
}
}
2. Methods in Java
A method is a block of code that performs a specific task. It can take inputs (parameters) and return a result.
Method Syntax
accessModifier returnType methodName(parameters) {
// Method body
return value; // (if returnType is not void)
}
Types of Methods
- Instance Methods – Called on an object.
-
Static Methods – Called using the class name (
ClassName.methodName()). - Constructor Methods – Used to initialize objects.
Example of Different Methods
public class Calculator {
// Instance method
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
// Static method
public static int multiply(int a, int b) {
return a * b;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calculator calc = new Calculator();
// Calling instance method
int sum = calc.add(5, 3); // 8
// Calling static method
int product = Calculator.multiply(5, 3); // 15
System.out.println("Sum: " + sum);
System.out.println("Product: " + product);
}
}
3. Constructors in Java
A constructor is a special method used to initialize objects.
Types of Constructors
- Default Constructor (no-args) – Automatically created if no constructor is defined.
- Parameterized Constructor – Takes arguments to initialize fields.
Example of Constructors
public class Student {
String name;
int age;
// Default constructor
public Student() {
name = "Unknown";
age = 0;
}
// Parameterized constructor
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Using default constructor
Student student1 = new Student();
System.out.println(student1.name); // "Unknown"
// Using parameterized constructor
Student student2 = new Student("Alice", 20);
System.out.println(student2.name); // "Alice"
}
}
4. Method Overloading
Multiple methods can have the same name but different parameters (different types or number of parameters).
Example of Method Overloading
public class MathOperations {
// Method to add two integers
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
// Method to add three integers (overloading)
public int add(int a, int b, int c) {
return a + b + c;
}
// Method to add two doubles (overloading)
public double add(double a, double b) {
return a + b;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MathOperations math = new MathOperations();
System.out.println(math.add(5, 3)); // 8
System.out.println(math.add(5, 3, 2)); // 10
System.out.println(math.add(2.5, 3.5)); // 6.0
}
}
5. The this Keyword
- Refers to the current object.
- Used to distinguish between instance variables and parameters with the same name.
Example of this Keyword
public class Person {
String name;
int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name; // 'this.name' refers to the instance variable
this.age = age; // 'this.age' refers to the instance variable
}
}
6. Getters and Setters
Used to access (get) and modify (set) private fields.
Example of Getters & Setters
public class BankAccount {
private double balance;
// Getter
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
// Setter
public void setBalance(double balance) {
if (balance >= 0) {
this.balance = balance;
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BankAccount account = new BankAccount();
account.setBalance(1000.0);
System.out.println("Balance: " + account.getBalance());
}
}
Summary
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Object | Instance of a class with state & behavior. |
| Method | Block of code performing a task. |
| Constructor | Special method to initialize objects. |
| Method Overloading | Same method name, different parameters. |
this Keyword |
Refers to the current object. |
| Getters/Setters | Access and modify private fields. |
This covers the fundamentals of Java Methods and Objects.TBD


Top comments (0)