What is PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is a free, object-relational database management system whose development began in the 1980s and was first used in a public CVS server in July 1996. PostgreSQL was initiated by Michael Stonebraker, who researched and developed databases at the University of California. From his time at Berkeley, the database management system known today as PostgreSQL emerged.
PostgreSQL has been known by this name since the mid-1990s and has been available to all developers as open-source technology and has been continuously developed ever since. PostgreSQL is one of the most popular database management systems, which of course has to do with the fact that it has existed for so long, and the many competent developers have made the open-source project quite practical for a long time.
According to the StackOverflow “2021 Developers Survey” linked above, PostgreSQL is the second most-used database technology behind MySQL – and it’s rising steadily. Because while only about 26% of developers used it in 2017, it was already 34% in 2019 and by 2021 it was even more than 40%.
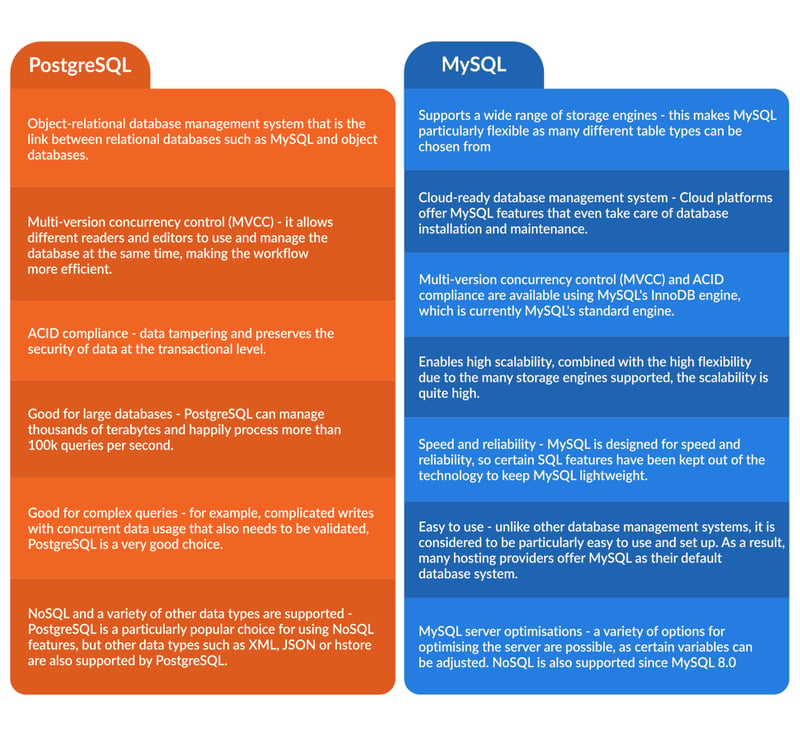
**** PostgreSQL vs MySQL: Features and Functions ***
SQL Commands in PostgreSQL:-
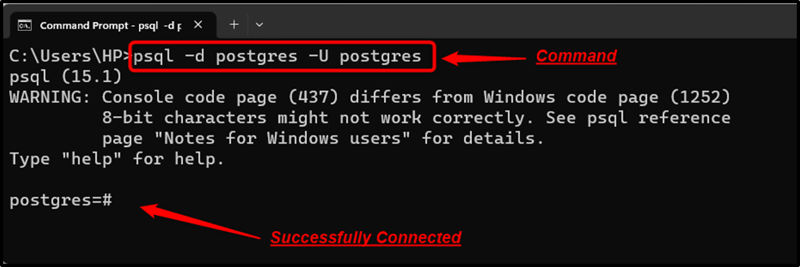
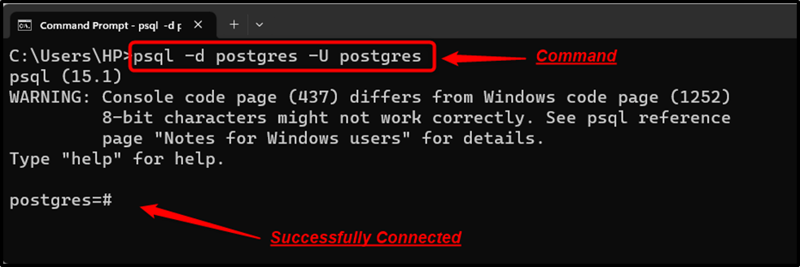
Example 1: Connecting to a Database
Open the CMD and execute the below-provided psql command to establish a connection to a particular database:
Example 2: Checking Postgres Version
Executing the “SELECT VERSION();” command will retrieve the currently installed Postgres version:
****Example 3: Listing All Databases
Listing available databases is a very common task in Postgres that can be accomplished via the “\l” command:
\l
The “\l” successfully retrieves the list of available databases.
****Example 4: Accessing/Switching a Database
Performing any operation on a database object requires accessing that database. To accomplish this task, execute the “\c” command from the “SQL Shell”:
\c sample_db;
The connection with the “sample_db” database has been established successfully.
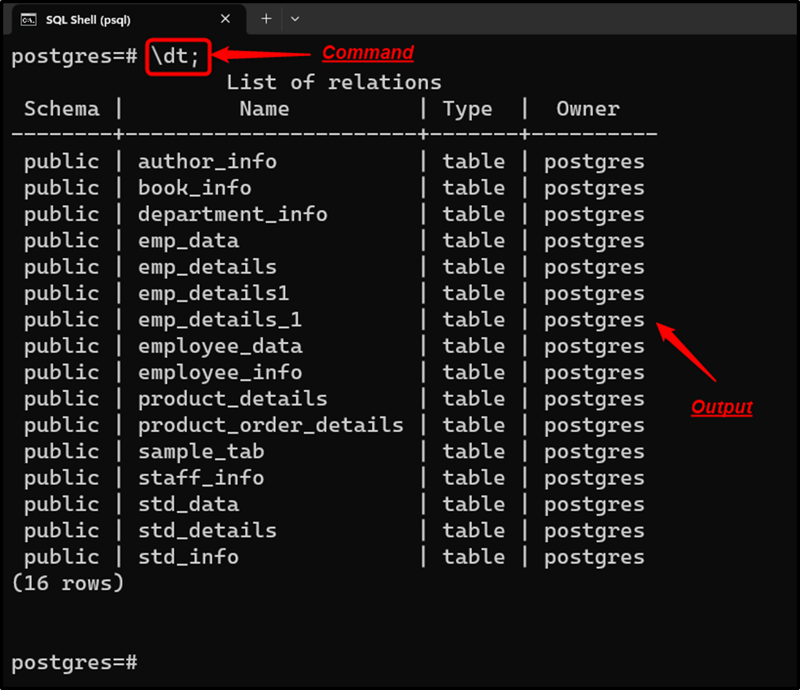
***Example 5: Listing All Available Tables
In Postgres, the tables are used to represent the data elements in a well-organized format. Run the “\dt” command from SQL Shell to fetch the list of available tables/relations:
The stated command returns all the tables available in the selected database.
**Example 6: Describing All Tables
Postgres users can use the “\d” command to get the list of relations, including sequences, views, etc.
\d
The “\d” command successfully retrieves the “schema name”, “table name”, “relation type”, and owner.
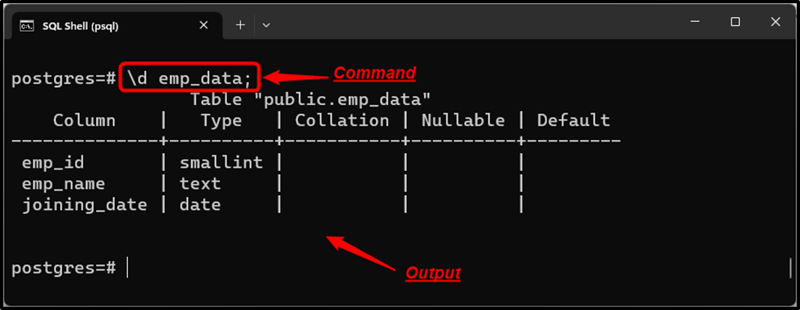
**Example 7: Describing a Specific Table
Execute the “\d” command followed by the table name to describe a specific table in Postgres:
\d emp_data;
The above-stated command will describe the “emp_data” table:
The stated command retrieves all the details regarding the “emp_data” table, such as column names, column types, columns’ default values, etc.
Basic Query
Select all columns from a table:
SELECT * FROM table_name;
Selecting Specific Columns
Select specific columns:
SELECT column1, column2 FROM table_name;
Filtering Data (Using WHERE Clause)
Select rows where a column matches a specific value:
SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE column_name = 'value';
Select rows where a column matches multiple values:
SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE column_name IN ('value1', 'value2');
Select rows based on conditions:
SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE column_name > 100;
Using AND/OR for multiple conditions:
SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE column1 = 'value1' AND column2 > 50;


Top comments (0)