Triggered Questions 2
🚀 The Question That Triggered It All
During my Java practice, I came across this code:
public class Check {
static int a = 10;
int b = 20;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Check obj1 = new Check();
Check obj2 = new Check();
obj1.b = 30;
obj2.a = 40;
System.out.println(obj1.a + " " + obj2.b);
}
}
At first glance, I thought the output would be:
10 30
But the actual output was:
40 20
😮 Wait… What?! We just changed
obj1.b = 30;, then why did it print20?
This made me stop, dig deep, and finally understand how Java handles memory for static and non-static variables.
🧩 What’s Happening Here?
Let’s break it down:
✅ static int a = 10;
- This is a class-level variable.
- Stored in the Method Area (shared memory).
- Shared across all objects of the class.
✅ int b = 20;
- This is an instance variable.
- Stored in heap memory, separately for each object.
- Each object gets its own copy of
b.
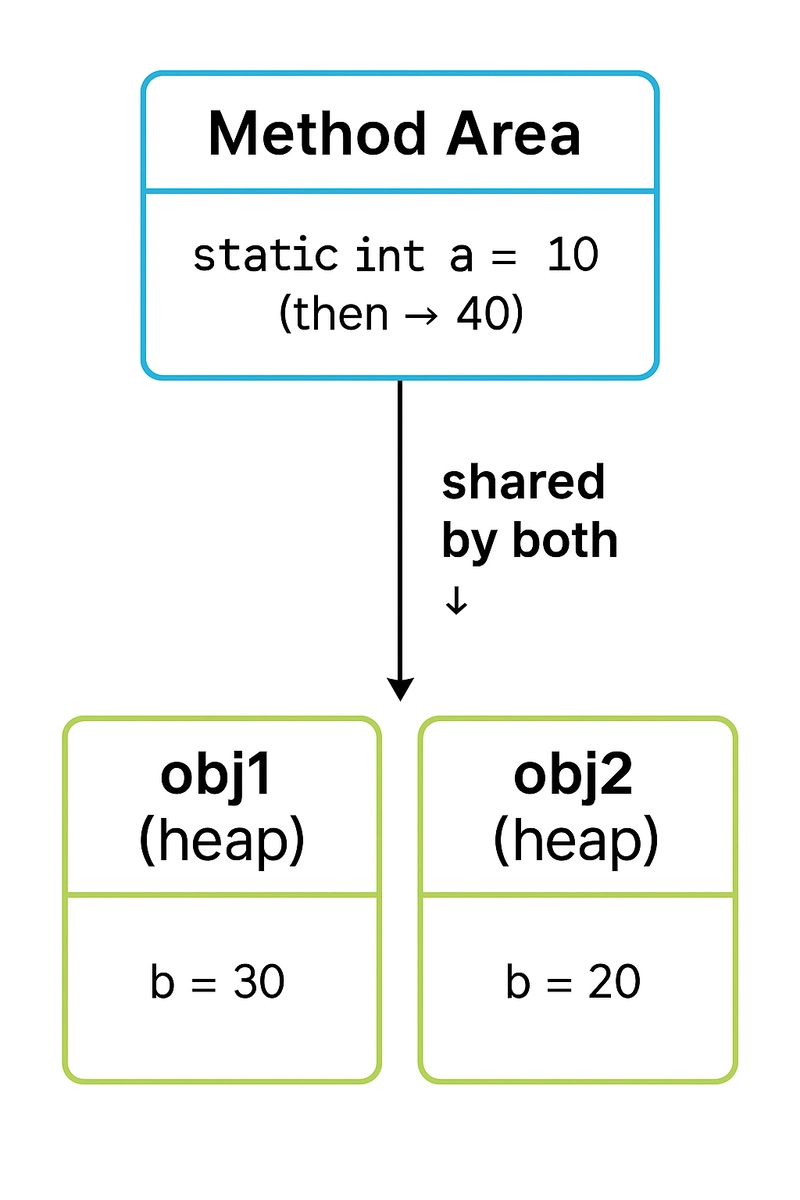
🧠 Visual Representation (with Diagram)
Explanation of Diagram:
-
Method Area (top) holds the
staticvariablea. -
Heap Memory (bottom) contains
obj1andobj2, each with its ownb. - When
obj1.b = 30;, only obj1’sbis affected. - When
obj2.a = 40;, it updates the shareda, soobj1.aalso becomes 40. -
obj2.bwas never changed, so it remains 20.
✅ Step-by-Step Execution:
-
ais set to 10 → lives in Method Area. -
obj1andobj2are created → each has their own copy ofb = 20. -
obj1.b = 30;→ changes only obj1’sb. -
obj2.a = 40;→ changes shareda. - Output:
System.out.println(obj1.a + " " + obj2.b);
-
obj1.a→ 40 (shared) -
obj2.b→ 20 (not changed)
🧠 Lesson Learned:
Static = shared across objects
Instance = unique to each object
This lesson not only helped me crack this question but also made Java’s memory model crystal clear.
THANK YOU !
I was confused about memory areas, but now everything is clear. Big thanks to Vijay sir and Vassu bro!


Top comments (0)