Overview of My Submission
https://github.com/SoftMaple/github-insights-view
Submission Category:
Action Star
Link to Code
Context
Recently, I made a project to generate
sourcecode for better paper typesetting:
For old version, please check out the repo: Eorg.
Documentation
For details, check out our documentation.
Features
Using draftjs-to-latex for generating LaTeX source code.
Issues and Pitfalls
See more details at here: https://draftjs.org/docs/advanced-topics-issues-and-pitfalls
Development
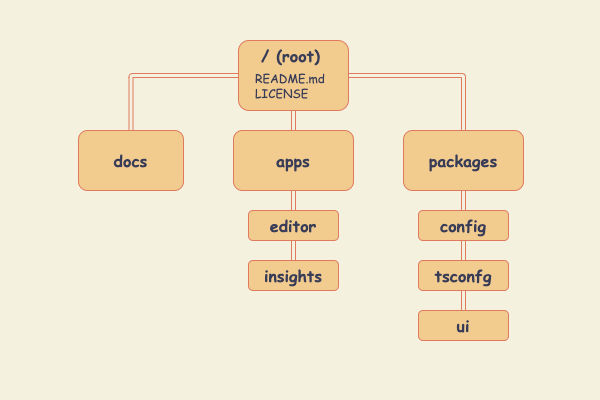
Turborepo Architecture:
-
docs - built with Docusaurus 2
-
apps
-
packages
We use pnpm for package management, if you never used it, see pnpm for installation.
pnpm install
pnpm dev
What if I just want to check out Editor app source code?
git clone --no-checkout https://github.com/softmaple/softmaple
cd softmaple
git sparse-checkout init --cone --sparse-index
git sparse-checkout set apps/editor packages
git checkout main
Read more: sparse-checkout and sparse index.
Community
The SoftMaple community can be found on GitHub Discussions, where you can ask questions and voice…
The situation is that the github just saves the latest 14 days repo clones and views. So I want to make a dashboard to view all the data per day. For me, CRON job is better.
I attempted github actions at the first time,
 softmaple
/
insights-cronjob
softmaple
/
insights-cronjob
Just a cronjob for tracking github insights related to Softmaple
It delayed about 1 hour, so I think there is a better way to trigger the event precisely.
Thanks for MongoDB Atlas Hackathon on DEV, it give me a new approache to schedule CRON job, that's Atlas Triggers.
Implementation
Firstly, to store the data, we need to call github API to retrieve clones and views. we will use an npm dependency called @octokit/core. Before using it, add it to dependencies:

const { Octokit } = require("@octokit/core"); // do not forget this.
async function callOctokit(route, owner, repo) {
const octokit = new Octokit({ auth: OCTOKIT_TOKEN });
return await octokit.request(route, { owner, repo });
}
async function getClones(collection, owner, repo) {
try {
const { status, data } = await callOctokit(
"GET /repos/{owner}/{repo}/traffic/clones",
owner,
repo
);
const { clones } = data;
// console.log(clones);
} catch(err) {
throw new Error("Error fetching clones: ", err.message, owner, repo);
}
}
async function getViews(collection, owner, repo) {
try {
const { status, data } = await callOctokit(
"GET /repos/{owner}/{repo}/traffic/views",
owner,
repo
);
const { views } = data;
// console.log(views);
} catch(err) {
throw new Error("Error fetching views: ", err.message, owner, repo);
}
}
It works.
Next, we need to store the data, but which should we store?
I want to update the data in Front End per day, so we just trigger it and store the 'yesterday' clones and views, so we need to implement a util function to get yesterday's data.
There is an example at MongoDB Atlas: scheduled-triggers
Notice:
dayjsis also a way to determine whether a date is yesterday.
But we need to set the date hour from '7' to '0' for comparing with github response data timestamp, see more details here: https://docs.github.com/en/rest/reference/repository-metrics#traffic
function getToday() {
return setDaybreak(new Date());
}
function getYesterday() {
const today = getToday();
const yesterday = new Date(today);
yesterday.setDate(today.getDate() - 1);
// console.log(yesterday);
// we just need the timestamp as this format: YYYY-MM-DD
return yesterday.toISOString().split('T')[0];
}
function setDaybreak(date) {
date.setHours(0); // modified original '7'.
date.setMinutes(0);
date.setSeconds(0);
date.setMilliseconds(0);
return date;
}
and then modify getClones and getViews functions.
async function getClones(collection, owner, repo) {
try {
const { status, data } = await callOctokit(
"GET /repos/{owner}/{repo}/traffic/clones",
owner,
repo
);
const { clones } = data;
// console.log(clones);
const latestData = clones[clones.length - 1];
const shouldUpdate = latestData.timestamp.split("T")[0] === getYesterday();
if (shouldUpdate) {
await collection.insertOne({ name: repo, ...latestData });
console.log("getClones: ", repo);
} else { // Notice: if clones count is 0, it will not be returned from the api.
await collection.insertOne({ name: repo, timestamp: new Date().toISOString(), count: 0, uniques: 0 });
}
} catch(err) {
throw new Error("Error fetching clones: ", err.message, owner, repo);
}
}
async function getViews(collection, owner, repo) {
try {
const { status, data } = await callOctokit(
"GET /repos/{owner}/{repo}/traffic/views",
owner,
repo
);
const { views } = data;
// console.log(views);
const latestData = views[views.length - 1];
// console.log(latestData.timestamp.split("T")[0], getYesterday());
const shouldUpdate = latestData.timestamp.split("T")[0] === getYesterday();
if (shouldUpdate) {
await collection.insertOne({ name: repo, ...latestData });
console.log("getViews: ", repo);
} else { // Notice: if views count is 0, it will not be returned from the api.
await collection.insertOne({ name: repo, timestamp: new Date().toISOString(), count: 0, uniques: 0 });
}
} catch(err) {
throw new Error("Error fetching views: ", err.message, owner, repo);
}
}
Finally, call the two functions as below:
exports = async function trigger() {
/*
A Scheduled Trigger will always call a function without arguments.
Documentation on Triggers: https://docs.mongodb.com/realm/triggers/overview/
Functions run by Triggers are run as System users and have full access to Services, Functions, and MongoDB Data.
Access a mongodb service:
const collection = context.services.get(<SERVICE_NAME>).db("db_name").collection("coll_name");
const doc = collection.findOne({ name: "mongodb" });
Note: In Atlas Triggers, the service name is defaulted to the cluster name.
Call other named functions if they are defined in your application:
const result = context.functions.execute("function_name", arg1, arg2);
Access the default http client and execute a GET request:
const response = context.http.get({ url: <URL> })
Learn more about http client here: https://docs.mongodb.com/realm/functions/context/#context-http
*/
const db = context.services.get("Insights").db("insights");
const clones = db.collection("clones");
const views = db.collection("views");
let success = true,
error = null;
try {
await getClones(clones, "SoftMaple", "Editor");
await getViews(views,"SoftMaple", "Editor");
} catch(err) {
error = err.message;
success = false;
}
return {
success,
error
};
}
The last step: do not forget to set CRON time

Final Result
Thanks MongoDB Atlas Hackathon on DEV again!












Top comments (0)