Introduction
Have you ever wondered how websites collect visitor information through those neat contact forms? Whether it's a simple feedback form or a comprehensive job application, HTML forms are the backbone of interactive web experiences. In this guide, we'll walk through creating your very own contact form from scratch—no previous coding experience required!
By the end of this tutorial, you'll have built a fully functional contact form and gained an understanding of the essential HTML elements that make forms work. So let's dive in and start building!
What Are HTML Forms?
At their core, HTML forms are the primary way websites collect information from visitors. Every time you fill out an online survey, submit a comment on a blog, or make an online purchase, you're interacting with an HTML form.
The Basic Structure
All HTML forms are built using the <form> element, which serves as a container for various input elements:
<form action="/submit-form" method="post">
<!-- Input elements go here -->
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
Let's break down the key attributes:
-
action: Specifies where the form data should be sent when submitted -
method: Defines how the data is sent (usuallygetorpost)
Planning Your Contact Form
Before writing any code, let's decide what information we want to collect. A typical contact form includes:
- Name
- Email address
- Subject
- Message
- Submit button
We might also want to include optional fields like phone number or a dropdown for the type of inquiry.
Building the Form Step by Step
Let's create our contact form piece by piece:
Step 1: Set Up the Basic Form Structure
First, we'll create the container for our form:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Contact Us</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Contact Us</h1>
<form action="#" method="post">
<!-- We'll add our input fields here -->
<button type="submit">Send Message</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>
The action="#" is a placeholder. In a real website, this would be replaced with the URL of a server-side script that processes the form data.
Step 2: Add Text Input Fields
Now, let's add input fields for name, email, and subject:
<form action="#" method="post">
<div>
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<input type="text" id="name" name="name" required>
</div>
<div>
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email" required>
</div>
<div>
<label for="subject">Subject:</label>
<input type="text" id="subject" name="subject" required>
</div>
<button type="submit">Send Message</button>
</form>
Step 3: Add a Textarea for the Message
The message requires a multi-line input field, so we'll use a <textarea> element:
<div>
<label for="message">Message:</label>
<textarea id="message" name="message" rows="5" required></textarea>
</div>
Step 4: Add a Dropdown Menu for Inquiry Type
Let's add a dropdown menu to categorize the type of inquiry:
<div>
<label for="inquiry">Inquiry Type:</label>
<select id="inquiry" name="inquiry">
<option value="general">General Question</option>
<option value="support">Technical Support</option>
<option value="billing">Billing Issue</option>
<option value="other">Other</option>
</select>
</div>
Step 5: Add a Checkbox for Newsletter Subscription
We can also add a checkbox to ask if the user wants to subscribe to a newsletter:
<div>
<input type="checkbox" id="newsletter" name="newsletter" value="yes">
<label for="newsletter">Subscribe to our newsletter</label>
</div>
The Complete Contact Form
Putting it all together, here's our complete contact form:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Contact Us</title>
<style>
/* Basic styling to make the form look better */
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
line-height: 1.6;
max-width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 20px;
}
form div {
margin-bottom: 15px;
}
label {
display: block;
margin-bottom: 5px;
}
input[type="text"],
input[type="email"],
select,
textarea {
width: 100%;
padding: 8px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 4px;
}
button {
background-color: #4CAF50;
color: white;
padding: 10px 15px;
border: none;
border-radius: 4px;
cursor: pointer;
}
button:hover {
background-color: #45a049;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Contact Us</h1>
<p>Please fill out this form to get in touch with our team. We'll respond as soon as possible!</p>
<form action="#" method="post">
<div>
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<input type="text" id="name" name="name" placeholder="Your full name" required>
</div>
<div>
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email" placeholder="your.email@example.com" required>
</div>
<div>
<label for="phone">Phone (optional):</label>
<input type="tel" id="phone" name="phone" placeholder="Your phone number">
</div>
<div>
<label for="inquiry">Inquiry Type:</label>
<select id="inquiry" name="inquiry">
<option value="general">General Question</option>
<option value="support">Technical Support</option>
<option value="billing">Billing Issue</option>
<option value="other">Other</option>
</select>
</div>
<div>
<label for="subject">Subject:</label>
<input type="text" id="subject" name="subject" placeholder="Brief subject of your message" required>
</div>
<div>
<label for="message">Message:</label>
<textarea id="message" name="message" rows="5" placeholder="Your message here..." required></textarea>
</div>
<div>
<input type="checkbox" id="newsletter" name="newsletter" value="yes">
<label for="newsletter" style="display: inline;">Subscribe to our newsletter</label>
</div>
<button type="submit">Send Message</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>
I've added some basic CSS styling to make the form look better, but the functionality comes from the HTML elements.
Understanding Form Input Types
HTML5 introduced several specialized input types that make forms more user-friendly and validate data automatically:
Text Inputs
<!-- Basic text input -->
<input type="text">
<!-- Email input (validates email format) -->
<input type="email">
<!-- Password input (hides characters) -->
<input type="password">
<!-- Number input (only allows numbers) -->
<input type="number">
<!-- Phone number input -->
<input type="tel">
<!-- URL input (validates URL format) -->
<input type="url">
Other Input Types
<!-- Date picker -->
<input type="date">
<!-- Color picker -->
<input type="color">
<!-- Range slider -->
<input type="range" min="0" max="100">
<!-- File upload -->
<input type="file">
Form Validation
HTML5 provides built-in form validation through attributes:
Required Fields
The required attribute ensures the user fills out a field before submitting the form:
<input type="text" required>
Pattern Validation
The pattern attribute lets you validate input using regular expressions:
<!-- Only accepts 5-digit zip codes -->
<input type="text" pattern="[0-9]{5}" title="Five digit zip code">
Min/Max Values
For number inputs, you can set minimum and maximum values:
<input type="number" min="1" max="100">
Min/Max Length
Control the length of text inputs:
<input type="text" minlength="3" maxlength="50">
Enhancing User Experience
Let's look at some ways to make your form more user-friendly:
Placeholder Text
Placeholder text provides hints about what to enter in each field:
<input type="text" placeholder="Your full name">
Autofocus
The autofocus attribute puts the cursor in a specific field when the page loads:
<input type="text" autofocus>
Tabindex
The tabindex attribute controls the order of elements when users navigate with the Tab key:
<input type="text" tabindex="1">
<input type="email" tabindex="2">
Fieldsets and Legends
For longer forms, you can group related fields using <fieldset> and <legend>:
<fieldset>
<legend>Personal Information</legend>
<!-- Name, email, etc. -->
</fieldset>
<fieldset>
<legend>Message Details</legend>
<!-- Subject, message, etc. -->
</fieldset>
Styling Your Form
While we've included basic styling in our example, here are some CSS tips for making your form look even better:
Consistent Field Sizes
input, select, textarea {
width: 100%;
padding: 12px;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
Focus States
input:focus, select:focus, textarea:focus {
border-color: #4CAF50;
box-shadow: 0 0 5px rgba(76, 175, 80, 0.5);
outline: none;
}
Mobile Responsiveness
@media (max-width: 600px) {
form {
padding: 10px;
}
button {
width: 100%;
}
}
Form Handling
While HTML can create the form, you'll need additional technologies to process the submitted data:
Client-Side Options
- JavaScript can validate and manipulate form data before submission
- AJAX can submit the form without refreshing the page
Server-Side Options
- PHP, Node.js, Python, etc. can process form submissions
- Form services like Formspree or Netlify Forms can handle submissions without server-side code
For beginners without server-side knowledge, here's how to use a free service like Formspree:
<form action="https://formspree.io/your-email@example.com" method="POST">
<!-- Your form fields -->
</form>
Just replace "your-email@example.com" with your actual email address.
Accessibility Considerations
To make your form accessible to all users:
- Always use labels with each form control
- Group related fields with fieldsets and legends
- Provide clear error messages for validation failures
- Use ARIA attributes when necessary:
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<input type="text" id="name" name="name" aria-required="true" aria-describedby="name-help">
<span id="name-help">Please enter your full name as it appears on official documents.</span>
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Forgetting the "name" attribute: Without this, the server can't identify the data
- Not using appropriate input types: Use "email" for emails, "tel" for phone numbers, etc.
- Neglecting mobile users: Test your form on small screens
- Making forms too long: Only ask for information you truly need
- Not providing feedback: Users should know if their submission was successful
Putting It All Together: A Real-World Example
Here's a more stylized version of our contact form that applies all the best practices we've discussed:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Contact Us | My Website</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: 'Segoe UI', Tahoma, Geneva, Verdana, sans-serif;
line-height: 1.6;
color: #333;
max-width: 800px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 20px;
background-color: #f9f9f9;
}
h1 {
color: #2c3e50;
border-bottom: 2px solid #3498db;
padding-bottom: 10px;
}
.form-container {
background: white;
padding: 25px;
border-radius: 8px;
box-shadow: 0 2px 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
.form-group {
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
label {
display: block;
margin-bottom: 8px;
font-weight: 600;
color: #2c3e50;
}
input[type="text"],
input[type="email"],
input[type="tel"],
select,
textarea {
width: 100%;
padding: 12px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 4px;
font-size: 16px;
transition: border-color 0.3s, box-shadow 0.3s;
}
input:focus,
select:focus,
textarea:focus {
border-color: #3498db;
box-shadow: 0 0 8px rgba(52, 152, 219, 0.2);
outline: none;
}
.checkbox-group {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
}
.checkbox-group label {
margin: 0 0 0 10px;
font-weight: normal;
}
button {
background-color: #3498db;
color: white;
border: none;
padding: 12px 20px;
font-size: 16px;
border-radius: 4px;
cursor: pointer;
transition: background-color 0.3s;
}
button:hover {
background-color: #2980b9;
}
.required-field::after {
content: "*";
color: #e74c3c;
margin-left: 5px;
}
.form-footer {
margin-top: 15px;
font-size: 14px;
color: #7f8c8d;
}
@media (max-width: 600px) {
.form-container {
padding: 15px;
}
button {
width: 100%;
}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Get In Touch</h1>
<p>Have questions or feedback? We'd love to hear from you. Fill out the form below, and our team will get back to you as soon as possible.</p>
<div class="form-container">
<form action="https://formspree.io/your-email@example.com" method="POST">
<fieldset style="border: none; padding: 0; margin: 0;">
<legend style="font-weight: bold; font-size: 18px; margin-bottom: 15px; color: #2c3e50;">Personal Information</legend>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="name" class="required-field">Name</label>
<input type="text" id="name" name="name" placeholder="Your full name" required autofocus>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="email" class="required-field">Email</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email" placeholder="your.email@example.com" required>
</div>
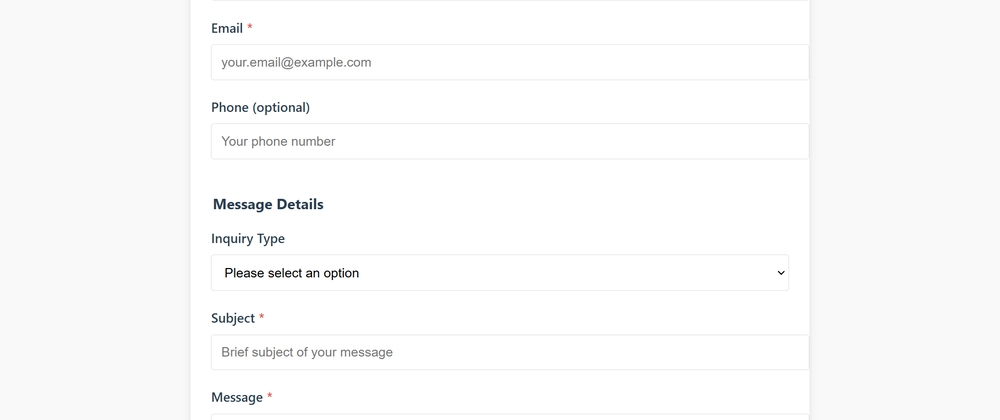
<div class="form-group">
<label for="phone">Phone (optional)</label>
<input type="tel" id="phone" name="phone" placeholder="Your phone number">
</div>
</fieldset>
<fieldset style="border: none; padding: 0; margin: 20px 0 0 0;">
<legend style="font-weight: bold; font-size: 18px; margin-bottom: 15px; color: #2c3e50;">Message Details</legend>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="inquiry">Inquiry Type</label>
<select id="inquiry" name="inquiry">
<option value="">Please select an option</option>
<option value="general">General Question</option>
<option value="support">Technical Support</option>
<option value="billing">Billing Issue</option>
<option value="other">Other</option>
</select>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="subject" class="required-field">Subject</label>
<input type="text" id="subject" name="subject" placeholder="Brief subject of your message" required>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="message" class="required-field">Message</label>
<textarea id="message" name="message" rows="6" placeholder="Your message here..." required></textarea>
</div>
<div class="form-group checkbox-group">
<input type="checkbox" id="newsletter" name="newsletter" value="yes">
<label for="newsletter">Subscribe to our newsletter for updates and tips</label>
</div>
</fieldset>
<button type="submit">Send Message</button>
<div class="form-footer">
<p>Fields marked with <span style="color: #e74c3c;">*</span> are required.</p>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Conclusion
Congratulations! You've learned how to create a fully functional HTML contact form from scratch. We've covered everything from basic structure to validation, styling, and accessibility best practices.
Remember these key takeaways:
- Start with the basics: A good form begins with the right HTML structure
- Use appropriate input types: They provide built-in validation and better user experience
- Add validation: Help users submit correct information the first time
- Style thoughtfully: A well-designed form encourages completion
- Consider accessibility: Make sure all users can interact with your form
- Keep it simple: Only ask for information you truly need
With these skills, you can create effective contact forms for your website or continue learning about more complex form implementations. As you grow more comfortable with HTML, you can explore CSS for more advanced styling and JavaScript for interactive form features.
Next Steps
Ready to expand your web development skills? Consider learning about:
- CSS Grid and Flexbox for advanced layout control
- JavaScript form validation for custom validation logic
- AJAX form submission for submitting forms without page reloads
- PHP or Node.js for processing form data on the server
Follow Me
If you found this guide helpful, please consider following me for more web development content:
- GitHub: Abdelhakim-Baalla
- LinkedIn: Abdelhakim Baalla
- Twitter (X): @Abdelhakim99891
- Instagram: @abdelhakim.baalla
Have questions about HTML forms or web development in general? Feel free to reach out! I'm always happy to help fellow developers on their coding journey.


Top comments (0)