title: [Golang][Notion] How to Use Golang to Manipulate Notion DB as an Online Database
published: false
date: 2024-01-13 00:00:00 UTC
tags:
canonical_url: http://www.evanlin.com/til-golang-notion-db/
---

# Prerequisites
When writing many Side Projects, besides the web service server, the most troublesome thing is probably the database problem. Although my previous article [[Learning Experience][Golang] Using Github Issues as a Database](https://www.evanlin.com/go-github-issue/) once taught how to use the Github Golang API to put some simple data on Github Issues, but if the data format is more complex. It may be necessary to process it through a storage like a database format. However, many online databases are calculated by time and usage, which is not so friendly for those who want to write some interesting Side Projects.
This article will use [Notion Database](https://www.notion.so/help/guides/creating-a-database) as the data storage, and query and insert related data processing through Golang. This article will also teach you how to set up a [Notion Integration](https://developers.notion.com/docs/create-a-notion-integration) from the beginning, so that you can control [Notion Database](https://www.notion.so/help/guides/creating-a-database) through Golang without any pain.
#### This article will be explained through: [https://github.com/kkdai/linebot-smart-namecard](https://github.com/kkdai/linebot-smart-namecard).
# About Notion Database
<iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/O8qdvSxDYNY?si=HpjDcPf42mp5TqTR" title="YouTube video player" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share" allowfullscreen=""></iframe>
The above is a [Notion official tutorial video Notion Database](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O8qdvSxDYNY) which mentions how to create a Database, and explains a little:
- Create -> Select Database field -> Table
## Advantages of using Notion Database:
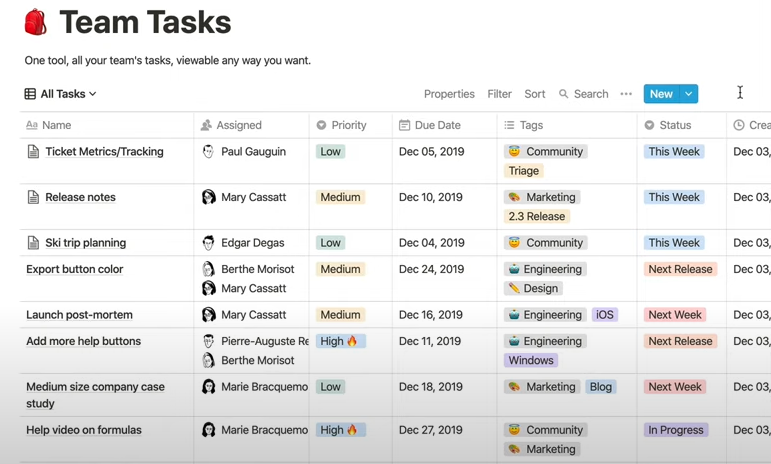
- Notion Database supports a very rich format and has a beautiful visual interface.
- And [Notion Database](https://www.notion.so/help/guides/creating-a-database) supports multiple formats: Table, Board, Calendar, List, and Gallery
- In addition to being convenient for coding, if there is a background administrator, they can directly view the results through the Notion UI.
# Create Notion Integration
You can first go to N[otion Developer](https://developers.notion.com/) to create the first [Notion Integration](https://www.notion.com/my-integrations):
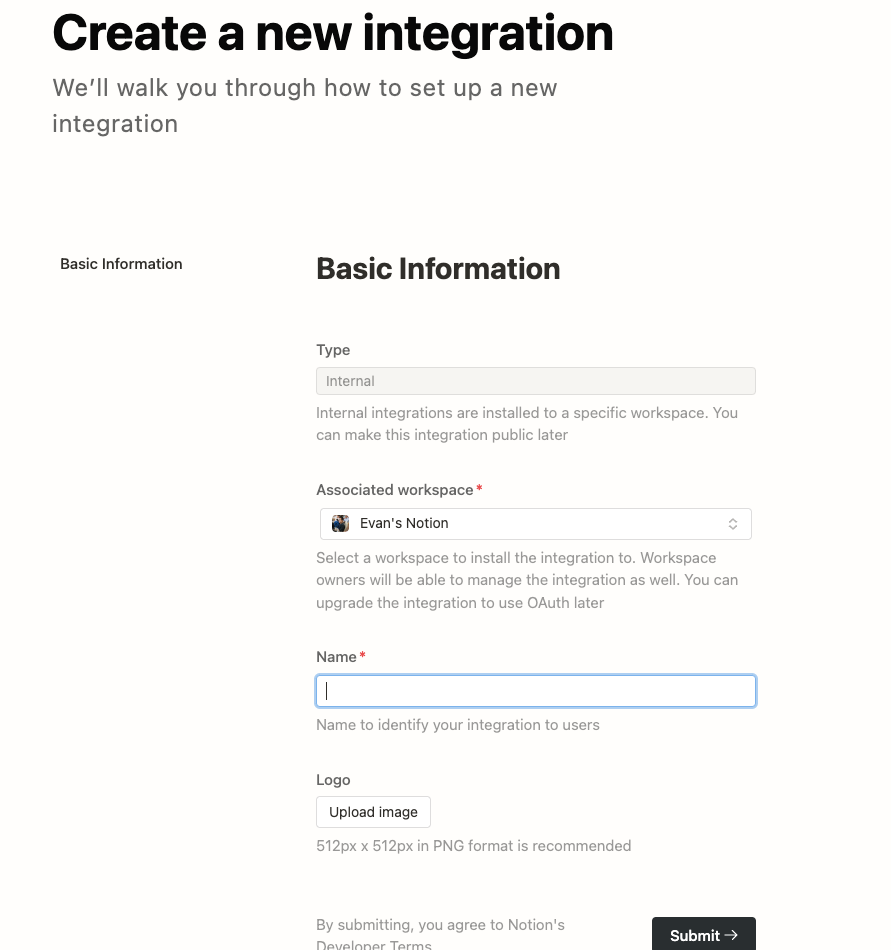
- **Type:** Internal, only you can use it, others cannot select it.
- **Name**: Just be able to identify it.
This way you can create an Integration and get the Internal Integration Secret (Notion API Key):
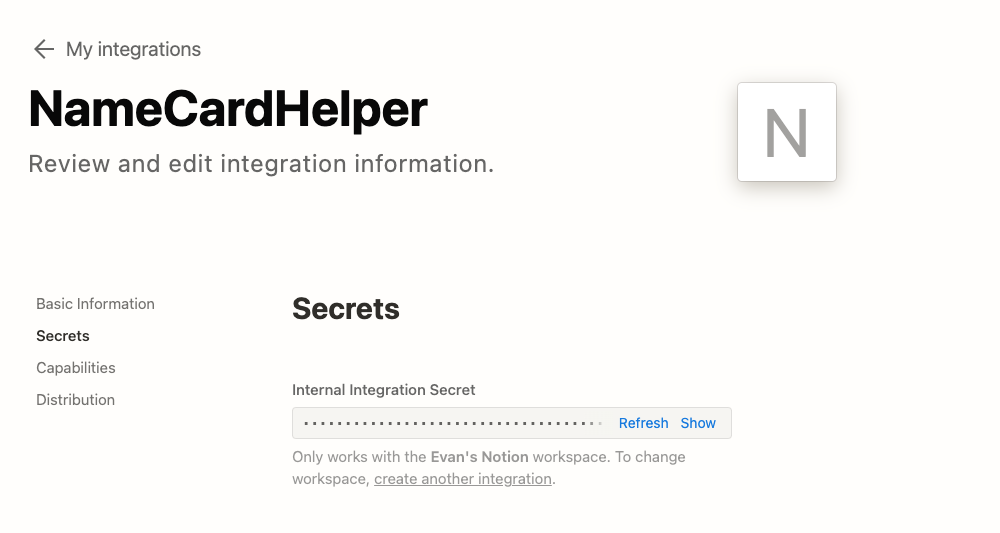
## Enable Notion Database to allow Notion Integration to access:
Remember to let the [Notion page get Integration permissions](https://developers.notion.com/docs/create-a-notion-integration#give-your-integration-page-permissions), refer to the following picture.
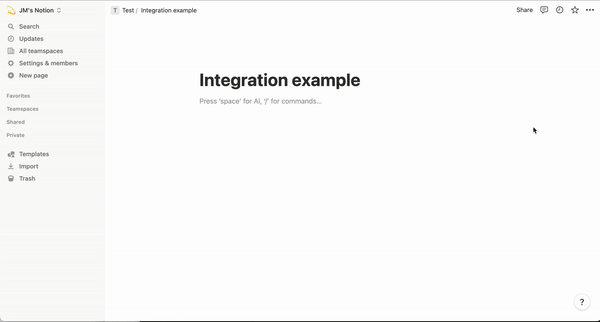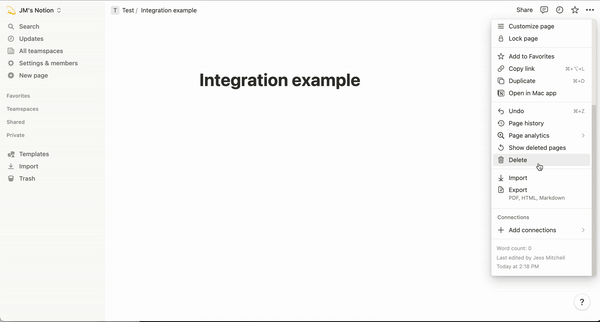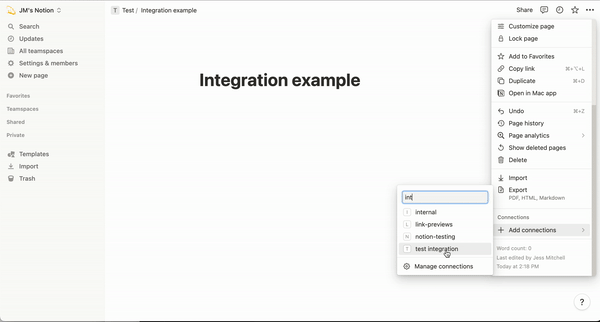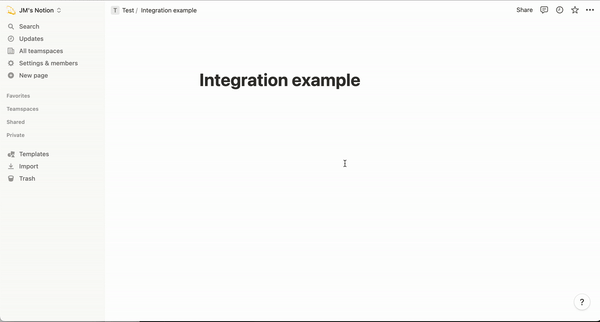
The GIF file given by the official is very clear, this is also the most important step. To allow your data to be accessed by Integration.
## Get Notion Database ID
This is also a very important thing, to use Golang to access your Notion Database, you need the following two pieces of information:
- **Notion Internal Integration Secret (API Key)**
- **Notion Page ID**
The Notion DB page URL should be `https://www.notion.so/b764xxxxxa?v=dexxxx1`, then `b764xxxxxa` is your DatabasePageId.
# Understand Notion Database Data Type:
When preparing to connect to [Notion Database](https://www.notion.so/help/guides/creating-a-database), you must first know the difference between each field.
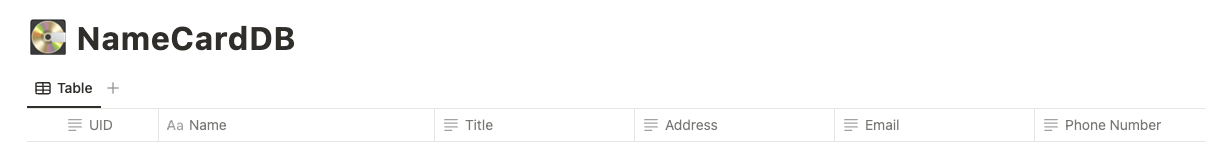
Taking my database as an example:
- **UID**: Stores LINE OA User UID, for identification purposes. The data format is: Text
- Others are Title, Address, Email, Phone Number.
- **Name**: Uses the Title data format, the difference is: Title can only have one field, and it will become the title of the new page.

# Start writing Golang Notion Database code:
#### The package used here is: [https://github.com/jomei/notionapi](https://github.com/jomei/notionapi)
## First, understand the data structure
// Person defines the structure of JSON data
type Person struct {
Name string json:"name"
Title string json:"title"
Address string json:"address"
Email string json:"email"
PhoneNumber string json:"phone_number"
}
// DatabaseEntry defines the structure of a Notion database entry.
type NotionDB struct {
DatabaseID string
Token string
}
- **Person**: From the JSON data of the business card scan, it also represents the data of each field here. Except for UID, which needs to be passed in through parameters.
- **NotionDB**: Data that needs to be known to start Notion:
- **Token**: is the Notion Integration Secret
- **DatabaseID**: can be obtained in the URL. The Notion DB page URL should be `https://www.notion.so/b764xxxxxa?v=dexxxx1`, then `b764xxxxxa` is your DatabasePageId.
## First, look at Query (search)
// QueryDatabase queries the Notion database based on the provided properties and values.
func (n *NotionDB) QueryDatabase(UId, property, value string) ([]Person, error) {
client := notionapi.NewClient(notionapi.Token(n.Token))
// Add UId to the filter conditions
// Build query filter conditions
filter := ¬ionapi.DatabaseQueryRequest{
Filter: notionapi.AndCompoundFilter{
notionapi.PropertyFilter{
Property: property,
RichText: ¬ionapi.TextFilterCondition{
Equals: value,
},
},
notionapi.PropertyFilter{
Property: "UID",
RichText: ¬ionapi.TextFilterCondition{
Equals: UId,
},
},
},
}
// Call the Notion API to query the database
result, err := client.Database.Query(context.Background(), notionapi.DatabaseID(n.DatabaseID), filter)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
var entries []Person
for _, page := range result.Results {
entry := n.createEntryFromPage(&page)
entries = append(entries, entry)
}
return entries, nil
}
What needs attention in this section is:
- The filter condition uses `AndCompoundFilter`, which means two conditions A && B.
- The `PropertyFilter` that needs attention, if the data format is different, needs to handle different data.
- Text: `TextFilterCondition`
- Title: `TitleFilterCondition`
- And so on.
## Then look at how to add data
// AddPageToDatabase adds a new page with the provided field values to the specified Notion database.
func (n *NotionDB) AddPageToDatabase(Uid string, name string, title string, address string, email string, phoneNumber string) error {
client := notionapi.NewClient(notionapi.Token(n.Token))
// Build Properties object to set page properties
properties := notionapi.Properties{
"UID": notionapi.RichTextProperty{
RichText: []notionapi.RichText{
{
PlainText: name,
Text: ¬ionapi.Text{Content: Uid},
},
},
},
"Name": notionapi.TitleProperty{
Title: []notionapi.RichText{
{
PlainText: name,
Text: ¬ionapi.Text{Content: name},
},
},
},
// Address, Email, Phone Number....
}
// Create a request for a new page
pageRequest := ¬ionapi.PageCreateRequest{
Parent: notionapi.Parent{
DatabaseID: notionapi.DatabaseID(n.DatabaseID),
},
Properties: properties,
}
// Call the Notion API to create a new page
_, err := client.Page.Create(context.Background(), pageRequest)
if err != nil {
log.Println("Error creating page:", err)
return err
}
log.Println("Page added successfully:", Uid, name, title, address, email, phoneNumber)
return nil
}
- Most of the code is similar, but according to the different fields. You need to adjust the following content:
"UID": notionapi.RichTextProperty{
RichText: []notionapi.RichText{
{
PlainText: name,
Text: ¬ionapi.Text{Content: Uid},
},
},
},
- The `name` in it is a fixed parameter and cannot be changed.
- Only the Content: `Uid` at the end can be changed.
- In addition, the `RichTextProperty` will also change according to the different fields. If it is incorrect, the data cannot be written correctly.
## Finally, the test example code:
func TestAddNotionDB(t *testing.T) {
token := os.Getenv("NOTION_INTEGRATION_TOKEN")
pageid := os.Getenv("NOTION_DB_PAGEID")
// If not set token and pageid , skip this test
if token == "" || pageid == "" {
t.Skip("NOTION_INTEGRATION_TOKEN or NOTION_DB_PAGEID not set")
}
db := &NotionDB{
DatabaseID: pageid,
Token: token,
}
err := db.AddPageToDatabase("uid", "name", "title", "address", "emai@email.com", "phone")
if err != nil {
t.Fatal(err)
}
}
# References:
- [[Learning Experience][Golang] Using Github Issues as a Database](https://www.evanlin.com/go-github-issue/)
- [Notion Database](https://www.notion.so/help/guides/creating-a-database)
- [Build your first Notion Integration](https://developers.notion.com/docs/create-a-notion-integration)
- [Notion official tutorial video Notion Database](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O8qdvSxDYNY)


Top comments (0)