Gitlab: https://github.com/GANESHARAVIND-124/AWS_S3_Bucket_Terraform.git
Deploying a static website on AWS S3 is easy, but making it secure, scalable, and highly available requires additional configurations. This guide will show you how to build a production-ready static website using Terraform while ensuring:
Security— Restrict direct S3 access, enforce HTTPS, and follow best IAM practices.
Performance— Use CloudFront CDN for fast, global content delivery.
Reliability— Integrate Route 53 for domain management and DNS resolution.
By the end of this tutorial, you will have a fully automated Terraform setup to launch a secure and optimized static website on AWS.
Introduction
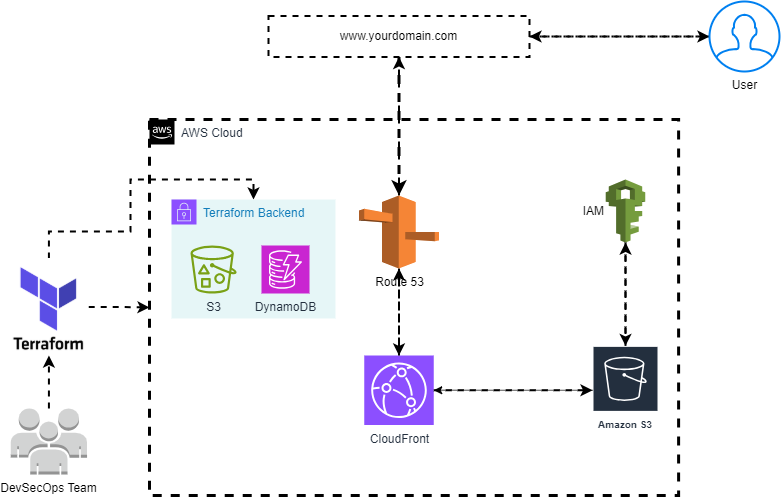
In this blog, we will learn how to securely host a static website on AWS S3 using Terraform, while ensuring performance and security with CloudFront, Route 53, and IAM policies. This setup enables global content delivery, custom domain integration, and restricted S3 access via CloudFront Origin Access Control (OAC).
Why Use AWS S3 for Static Websites?
AWS S3 provides a highly available and scalable way to host static websites. However, to ensure security and performance, we integrate:
- CloudFront (CDN) — Improves global performance and security.
- Route 53 (DNS) — Configures a custom domain for easy access.
- IAM Policies — Restricts direct access to S3, allowing only CloudFront.
Project Tech Stack
AWS S3 — Static website hosting
AWS CloudFront— Content Delivery Network (CDN)
AWS Route 53 — Domain Name System (DNS)
AWS IAM — Security policies
Project Structure
3-tier-webapp/
│
├── .terraform/ # Terraform’s internal files and state
│ ├── .terraform.lock.hcl # Lock file for provider versions
│ ├── terraform.tfstate # Current state of your infrastructure
│ └── modules/ # Cached modules
│
├── backend.tf # Backend configuration for state management
├── main.tf # Main configuration file for resources
├── providers.tf # Provider configuration (e.g., AWS)
├── terraform.tfvars # Variable values for the Terraform configuration
├── variables.tf # Variable definitions
│
├── modules/ # Custom modules for organizing resources
│ ├── compute/ # Module for compute resources (EC2, ALB, etc.)
│ │ ├── alb.tf # ALB configuration
│ │ ├── autoscaling.tf # Auto Scaling configuration
│ │ ├── ec2.tf # EC2 instance configuration
│ │ ├── outputs.tf # Outputs for the compute module
│ │ └── variables.tf # Variables for the compute module
│ │
│ ├── database/ # Module for database resources (RDS, etc.)
│ │ ├── rds.tf # RDS configuration
│ │ ├── outputs.tf # Outputs for the database module
│ │ └── variables.tf # Variables for the database module
│ │
│ └── networking/ # Module for networking resources (VPC, subnets, etc.)
│ ├── vpc.tf # VPC configuration
│ ├── subnets.tf # Subnet configuration
│ ├── nat.tf # NAT Gateway configuration
│ ├── security_groups.tf # Security Groups configuration
│ ├── outputs.tf # Outputs for the networking module
│ └── variables.tf # Variables for the networking module
│
└── README.md
Step 1: Configure S3 for Static Website Hosting
Terraform Code (S3 Module)
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "static_site" {
bucket = var.bucket_name
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket_website_configuration" "website" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.static_site.id
index_document {
suffix = "index.html"
}
}resource "aws_s3_bucket_policy" "allow_cloudfront" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.static_site.id
policy = jsonencode({
Statement = [{
Effect = "Allow"
Principal = { Service = "cloudfront.amazonaws.com" }
Action = "s3:GetObject"
Resource = "${aws_s3_bucket.static_site.arn}/*"
}]
})
}
📌 Key Features:
✔ Enables static website hosting on S3
✔ Restricts public access & only allows CloudFront
🚀 Step 2: Secure Content Delivery with CloudFront
CloudFront will accelerate content delivery and enforce HTTPS for security.
Terraform Code (CloudFront Module)
resource "aws_cloudfront_distribution" "cdn" {
origin {
domain_name = aws_s3_bucket.static_site.bucket_regional_domain_name
origin_access_control_id = aws_cloudfront_origin_access_control.s3_oac.id
}
enabled = true
default_root_object = "index.html"
viewer_certificate {
cloudfront_default_certificate = true
}
}
📌 Key Features:
✔ Uses Origin Access Control (OAC) — S3 is accessible only via CloudFront
✔ Enforces HTTPS — All traffic is securely encrypted
🌐 Step 3: Configure Route 53 for Custom Domain
If you have a custom domain, set up Route 53 to map it to CloudFront.
Terraform Code (Route 53 Module)
resource "aws_route53_record" "www" {
zone_id = var.hosted_zone_id
name = var.domain_name
type = "A"
alias {
name = aws_cloudfront_distribution.cdn.domain_name
zone_id = aws_cloudfront_distribution.cdn.hosted_zone_id
evaluate_target_health = false
}
}
📌 Key Features:
✔ Maps a custom domain to the CloudFront distribution
✔ Improves website accessibility via user-friendly URLs
🔒 Step 4: Secure Access with IAM Policies
IAM policies help restrict access and follow least privilege principles.
Terraform Code (IAM Module)
resource "aws_iam_policy" "s3_readonly" {
name = "S3ReadOnlyPolicy"
description = "Policy to allow read-only access to S3"
policy = jsonencode({
Statement = [{
Effect = "Allow"
Action = ["s3:GetObject"]
Resource = "${aws_s3_bucket.static_site.arn}/*"
}]
})
}
📌 Key Features:
✔ Prevents unauthorized access to S3 files
✔ Restricts permissions to only what’s necessary
📌 Deployment Guide
🔹 Step 1: Initialize Terraform
terraform init
🔹 Step 2: Validate Configuration
terraform validate
🔹 Step 3: Deploy Infrastructure
terraform apply -auto-approve
🔹 Step 4: Verify the Website
Check the Route 53 DNS records:
aws route53 list-resource-record-sets --hosted-zone-id <HOSTED_ZONE_ID>
Visit the website in your browser:
🔗 yourdomain.com
✅ Key Security Measures Implemented
🔒 CloudFront OAC — Restricts S3 access to CloudFront only.
🔒 HTTPS via CloudFront — Ensures encrypted traffic.
🔒 IAM Policies — Follows least privilege access control.
🚀 Future Enhancements
🔹 Automate deployments with CI/CD pipelines (GitHub Actions, AWS CodePipeline)
🔹 Add AWS WAF for DDoS protection & firewall rules
🔹 Implement logging & monitoring with AWS CloudWatch
🎯 Final Thoughts
This Terraform-based AWS static website hosting ensures:
✔ Security— Only CloudFront can access S3
✔ Performance— Global content delivery via CloudFront
✔ Scalability— Easily extendable with automation
With this setup, you have a secure, scalable, and high-performing static website hosted on AWS! 🚀
🔥 Have questions or improvements? Let’s discuss in the comments!


Top comments (0)