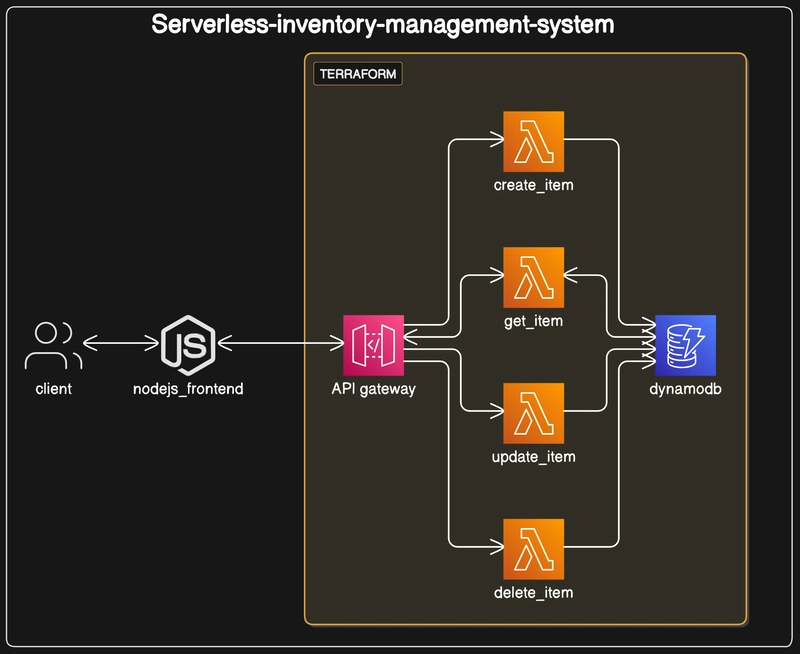
This project demonstrates how to build a clean and scalable full-stack inventory management system using pure AWS serverless components. With React on the frontend and Terraform on the backend, it’s cloud-native and production-ready.
📁 Project Architecture
This project is a fully serverless full-stack inventory management system built using:
- AWS Lambda for serverless backend logic
- Amazon API Gateway for HTTP endpoints
- Amazon DynamoDB as the NoSQL database
- React.js for the frontend
- Terraform for infrastructure as code
🔧 Tech Stack
- Frontend: React.js (calls API Gateway endpoints)
- Backend: AWS Lambda (Python) + API Gateway
- Database: Amazon DynamoDB
- Infrastructure: Terraform
- API Testing: Postman
Frontend Implementation
The React frontend provides an intuitive interface for inventory operations.The frontend communicates with backend services via API calls.
// src/App.jsx
import Header from './components/Header';
import InventoryList from './components/InventoryList';
import InventoryForm from './components/InventoryForm';
import InventoryDetails from './components/InventoryDetails';
import { fetchItems, fetchItem, createItem, updateItem, deleteItem } from './services/api';
import './App.css';
function App() {
const [items, setItems] = useState([]);
const [selectedItem, setSelectedItem] = useState(null);
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(false);
const [error, setError] = useState(null);
const [isFormOpen, setIsFormOpen] = useState(false);
const [isEditing, setIsEditing] = useState(false);
// Fetch all inventory items on component mount
useEffect(() => {
fetchInventoryItems();
}, []);
const fetchInventoryItems = async () => {
setIsLoading(true);
setError(null);
try {
const data = await fetchItems();
setItems(data.items || []);
} catch (err) {
setError('Failed to fetch inventory items. Please try again.');
console.error(err);
} finally {
setIsLoading(false);
}
};
Backend Services
Lambda functions handle the core business logic of the application.
✅ CRUD Lambda Functions (Python)
create_item.py
import json
import boto3
import os
import uuid
from datetime import datetime
from decimal import Decimal
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# Initialize DynamoDB
dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb')
table = dynamodb.Table(os.environ.get('DYNAMODB_TABLE'))
try:
# Parse request body
body = json.loads(event.get('body', '{}'), parse_float=Decimal) # Convert floats to Decimal
# Generate unique itemId and timestamps
item_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
timestamp = datetime.utcnow().isoformat()
# Create item object
item = {
'itemId': item_id,
'name': body.get('name'),
'description': body.get('description'),
'quantity': int(body.get('quantity', 0)), # Ensure quantity is integer
'price': Decimal(str(body.get('price', 0))), # Convert price to Decimal
'category': body.get('category'),
'imageUrl': body.get('imageUrl'),
'createdAt': timestamp,
'updatedAt': timestamp
}
Other functions follow a similar pattern for GET, PUT, and DELETE using event['pathParameters'] and event['body'].
API Gateway Routes
These routes define the RESTful endpoints for the Inventory Management System. Each route is connected to an AWS Lambda function:
| Method | Path | Lambda |
|---|---|---|
| POST | /items | create_item.py |
| GET | /items | get_items.py |
| PUT | /items/{id} | update_item.py |
| DELETE | /items/{id} | delete_item.py |
DynamoDB Data Model
DynamoDB provides a flexible, high-performance database solution. Access patterns are optimized through careful index design to support common inventory operations.
{
"itemId": "item-123",
"name": "Wireless Headphones",
"description": "WH-2023-BLK",
"category": "electronics",
"quantity": 157,
"imageUrl": "supplier-456",
"price": 45.99,
"createdAt": "timestamp",
"updatedAt": "timestamp"
Deploying the Backend with Terraform
Terraform enables infrastructure as code, making deployment consistent and repeatable. Here's a step-by-step guide to deploying the backend infrastructure:
1. Prerequisites
Before starting, ensure you have:
- AWS CLI installed and configured with appropriate permissions
- Terraform CLI installed
- Git installed for repository access
2. Clone the Repository
First, clone the project repository containing the Terraform configuration:
git clone https://github.com/OjoOluwagbenga700/serverless-inventory-management-system.git
cd backend/terraform
3. Initialize Terraform
Initialize the Terraform working directory:
terraform init
This command downloads the necessary provider plugins and sets up the backend configuration.
4. Review the Execution Plan
Generate and review the execution plan:
terraform plan
This shows you what resources will be created, modified, or destroyed.
5. Apply the Configuration
Apply the Terraform configuration to provision the infrastructure:
terraform apply --auto-approve
Terraform will create all the necessary AWS resources:
- DynamoDB tables
- IAM roles and policies
- Lambda functions
- API Gateway endpoints
- CloudWatch log groups
6. Verify Deployment
After successful application, Terraform will output the API Gateway endpoint URL
api_gateway_url = "https://i5mmj6bhw1.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com"
7. Update Frontend Configuration
Use the output values to update your frontend environment configuration.
// src/services/api.js
// API Gateway integration layer
const API_ENDPOINT = 'https://i5mmj6bhw1.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com';
// Fetch all inventory items
export async function fetchItems() {
try {
const response = await fetch(`${API_ENDPOINT}/items`);
if (!response.ok) {
const errorData = await response.json();
throw new Error(errorData.message || `API error: ${response.status}`);
}
return await response.json();
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error fetching items:', error);
throw error;
}
}
7. Run frontend Application
Navigate to the frontend directory
cd frontend/inventory-management-system
Run the following npm commands
npm install
npm start
Testing CRUD Operations with Postman
You can test all CRUD operations by:
- Setting method and endpoint (e.g.,
POST /items) - Sending appropriate JSON body
- Checking responses
Conclusion
By leveraging AWS serverless technologies, React, and Terraform, businesses can implement a powerful inventory management system that scales with their needs while minimizing operational overhead. This cloud-native approach provides the flexibility to adapt quickly to changing business requirements while maintaining robust security and performance.
Feel free to clone, fork, or build on top of it!









Top comments (0)