In this post, I'll show you how to create a simple MCP Server and test it in Cursor.
For this tutorial, I'm using the official csharp-sdk, which is still in its early stages:
1. Create a simple project
First, create an empty console project:
dotnet new console -n Tutorial.McpTimeServer
2. Install packages
Install these 2 packages:
dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting
dotnet add package ModelContextProtocol --prerelease
3. Write the code
Replace the Program.cs content with this:
using System.ComponentModel;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using ModelContextProtocol;
using ModelContextProtocol.Server;
Console.WriteLine("Hello MCP World!");
var builder = Host.CreateEmptyApplicationBuilder(settings: null);
builder.Services
.AddMcpServer()
.WithStdioServerTransport()
.WithTools();
var host = builder.Build();
await host.RunAsync();
[McpToolType]
public static class TimeTool
{
[McpTool, Description("Gets the current time.")]
public static string GetCurrentTime() => DateTimeOffset.Now.ToString();
}
4. Run the project
If you run the project using dotnet run, you will see Hello MCP World! and the program will remain open as it's listening to stdin.
5. Test it on Cursor
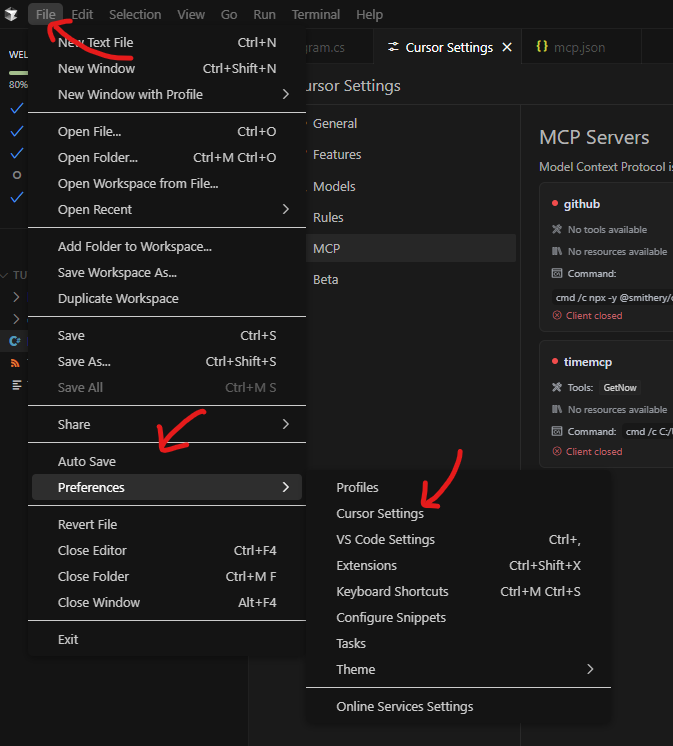
Now it's time to configure it on Cursor. Go to File -> Preferences -> Cursor Settings.
Click on "Add new global MCP Server" or open .cursor/mcp.json and add your MCP Server information like this:
{
"mcpServers": {
"timemcp": {
"command": "cmd",
"args": [
"/c",
"C:/Users/Mehran/source/repos/Tutorial.McpTimeServer/bin/Debug/net9.0/Tutorial.McpTimeServer.exe"
]
}
}
}
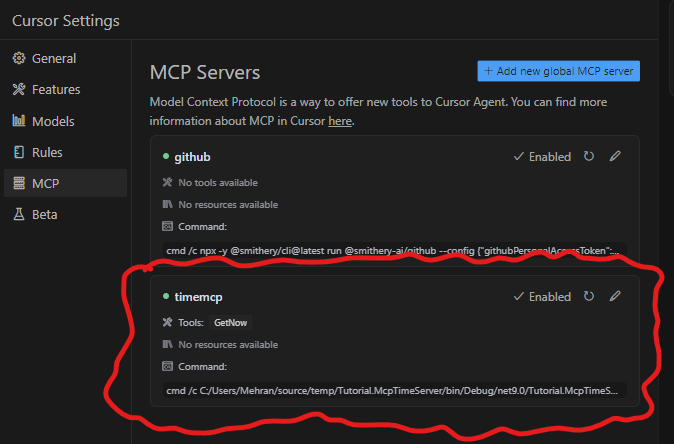
Now your MCP Servers page should look like this:
5. Test your MCP Server
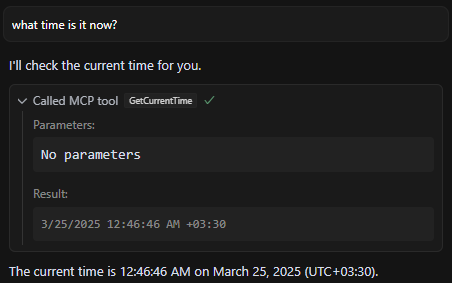
Now ask about the time, and it will use your tool.
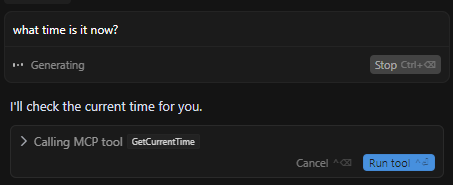
And if you click on "Run tool," it displays the time when the MCP tool we created was called.
6. Find the code
You can find the complete code on my GitHub:


Top comments (1)
Thank you