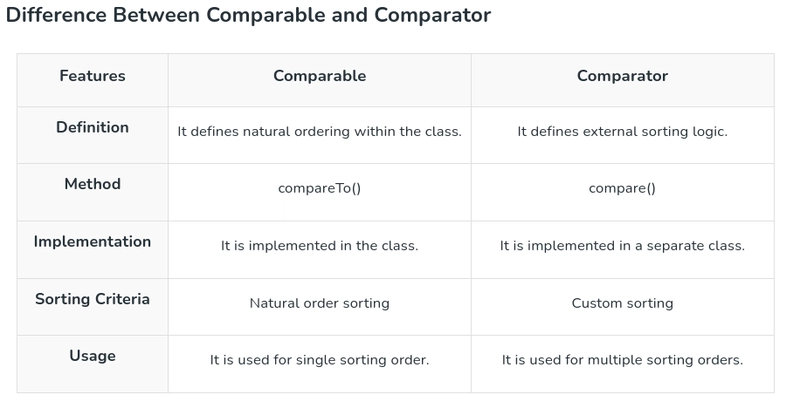
Comparable: It is used to define the natural ordering of the objects within the class.--->method..compareTo()
Comparator:(TBD) It is used to define custom sorting logic externally.method..compare()
package collections;
public class mobile implements Comparable<Object> {
String brand;
int price;
int ram;
double weigth;
mobile(String brand, int price, int ram, double weigth) {
this.brand = brand;
this.price = price;
this.ram = ram;
this.weigth = weigth;
}
public String toString() {
return this.brand + " " + this.price + " " + this.ram + " " + this.weigth;
}
public int compareTo(Object o) // call compareTo as m1 and passes parameters as m2
{
// System.out.println("First "+ this.price);//m1(print and see how compare happen)
mobile m = (mobile) o;// converting mobile class object
// System.out.println("second "+ m.price);//m2(print and see how compare happen)
if (this.price > m.price) {
return 1;// ascending
} else if (this.price < m.price) {
return -1;// decending
}
return 0;//equal
}
}
package collections;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class mobshop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
mobile m1 = new mobile("samsang", 15000, 12, 5.0);
mobile m2 = new mobile("vivo", 10000, 6, 7.0);
mobile m3 = new mobile("apple", 100000, 4, 5.0);
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();
al.add(m1);
al.add(m2);
al.add(m3);
System.out.println("Before Sorting: " + al);
Collections.sort(al);// use to sort in order
System.out.println("After Sorting: " + al);
int max_price = 0;
String brand = " ";
Iterator it = al.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
mobile mob = (mobile) it.next();
if (mob.price > max_price) {
max_price = mob.price;
brand = mob.brand;
}
}
System.out.println(max_price + " brand = " + brand);
}
}
Output:
Before Sorting: [samsang 15000 12 5.0, vivo 10000 6 7.0, apple 100000 4 5.0]
After Sorting: [vivo 10000 6 7.0, samsang 15000 12 5.0, apple 100000 4 5.0]
100000 brand = apple
Reference:https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/comparable-vs-comparator-in-java/
package collections;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Battery {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Mobile1> mobiles = new ArrayList<>();
mobiles.add(new Mobile1("Samsung Galaxy S22", 4500, 8, 65000));
mobiles.add(new Mobile1("iPhone 14", 3700, 6, 79000));
mobiles.add(new Mobile1("OnePlus 10", 5000, 12, 55000));
mobiles.add(new Mobile1("Redmi Note 12", 5000, 6, 18000));
mobiles.add(new Mobile1("Realme X7", 4300, 8, 22000));
mobiles.add(new Mobile1("Vivo V25", 4500, 8, 27000));
mobiles.add(new Mobile1("Oppo Reno 8", 4500, 8, 32000));
mobiles.add(new Mobile1("Poco F4", 4500, 8, 25000));
mobiles.add(new Mobile1("Motorola Edge 30", 4020, 8, 28000));
mobiles.add(new Mobile1("Asus ROG Phone 6", 6000, 16, 72000));
Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Choose sorting option:");
System.out.println("1. Price (Ascending)");
System.out.println("2. Battery (Descending)");
System.out.println("3. RAM (Descending)");
int ch=sc.nextInt();
Mobile1.sortType = ch;
Collections.sort( mobiles);
for(Mobile1 b:mobiles)
{
System.out.println(b);
}
}
}
package collections;
public class Mobile1 implements Comparable<Mobile1> {
public static int sortType = 1;
String name;
int battery;
int ram;
double price;
public String toString() {
return name + " - Battery: " + battery + "mAh, RAM: " + ram + "GB, Price: ₹" + price;
}
public Mobile1(String name, int battery, int ram, double price) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.battery = battery;
this.ram = ram;
this.price = price;
}
public int compareTo(Mobile1 other) {
switch (sortType) {
case 1:
if (this.price > other.price) {
return 1;
} else if (this.price < other.price) {
return -1;
} else {
return 0;
}
case 2: // Battery Descending
if (this.battery > other.battery)
return -1;
else if (this.battery < other.battery)
return 1;
else {
if (this.price > other.price) {
return 1;
} else if (this.price < other.price) {
return -1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
case 3: // RAM Descending
if (this.ram > other.ram)
return -1;
else if (this.ram < other.ram)
return 1;
else
return 0;
default:
return 0;
}
}
}
comparator
package Quantler;
public class Book {
String book;
String author;
Book(String book,String author)
{
this.book=book;
this.author=author;
}
}
package Quantler;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Bookcompare implements Comparator<Book> {
@Override
public int compare(Book b1, Book b2) {
return b1.book.compareTo(b2.book);
}
}
package Quantler;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class BookStorting {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Book> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Book("java","neel"));
list.add(new Book("python","sudhakar"));
list.add(new Book("c","vimal"));
Collections.sort(list,new Bookcompare());
for(Book b:list)
{
System.out.println(b.book+" "+b.author);
}
}
}


Top comments (0)