- Microservices are built in multiple programming languages
- Containers simplify deployment of microservices:
- Step 1 : Create a self contained Docker image
- Application Runtime (JDK or Python), Application code and Dependencies
- Step 2 : Run it as a container any where Local machine OR Corporate data center OR Cloud
- Use On-Demand instances or Spot instances
- Launch type: EC2 or Fargate
- Data volumes attached to containers
- Deployment type:
- Rolling update
- Blue/green deployment (powered by AWS CodeDeploy)
- Task Placement Strategies:
- binpack - Leave least amount of unused CPU or memory. Minimizes number of container instances in use
- random - Random task placement
- spread - Based on specified values:
- Host (instanceId)
- (OR) Availability Zone(attribute:ecs.availability-zone)
- (Alowed) Combine strategies and prioritize
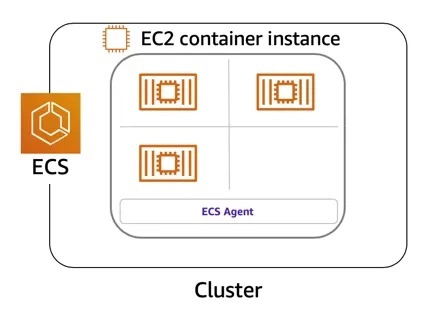
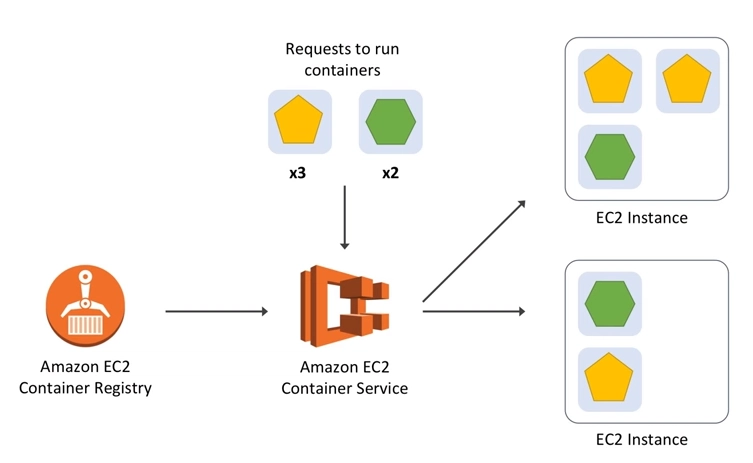
- How do you manage 100s of containers?
- ECS - Fully managed service for container orchestration
- Step 1 : Create a Cluster (Group of one or more EC2 instances)
- Step 2: Deploy your microservice containers
- AWS Fargate: Serverless ECS. DON'T worry about EC2 instances.
- Cloud Neutral: Kubernetes
- AWS - AWS Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)
- Load balancing:
- Performed using Application Load Balancers
- Dynamic host port mapping: Multiple tasks from the same service are allowed per EC2 (container) instance
- Path-based routing: Multiple services can use the same listener port on same ALB and be routed based on path (www.myapp.com/microservice-a and www.myapp.com/microservice-b)
For further actions, you may consider blocking this person and/or reporting abuse


Top comments (0)