Does the Programming Environment Affect Rotation Accuracy? A 90° Test Using the Gyro Sensor
When using LEGO SPIKE Prime in robotics competitions, how much does the choice of programming environment affect rotation accuracy?
To investigate this, I conducted an experiment comparing different programming environments.
Tested Programming Environments
I compared the following four environments:
- Word Blocks (SPIKE App 3) → Download here
- Python (SPIKE App 3) → Download here
- Python (Pybricks) → More info
- C Language (spike-rt) → GitHub repository
Robot Configuration
For the test, I used a car-type robot with the following setup:
- Left motor: Port A
- Right motor: Port B
Test Method
To compare the environments, I conducted the following test:
- Use the hub’s gyro sensor to rotate the robot 90°
- Measure the difference between the target angle (90°) and the actual rotation
- Perform 10 trials for each environment and calculate the average error
Program Code:
Word Blocks
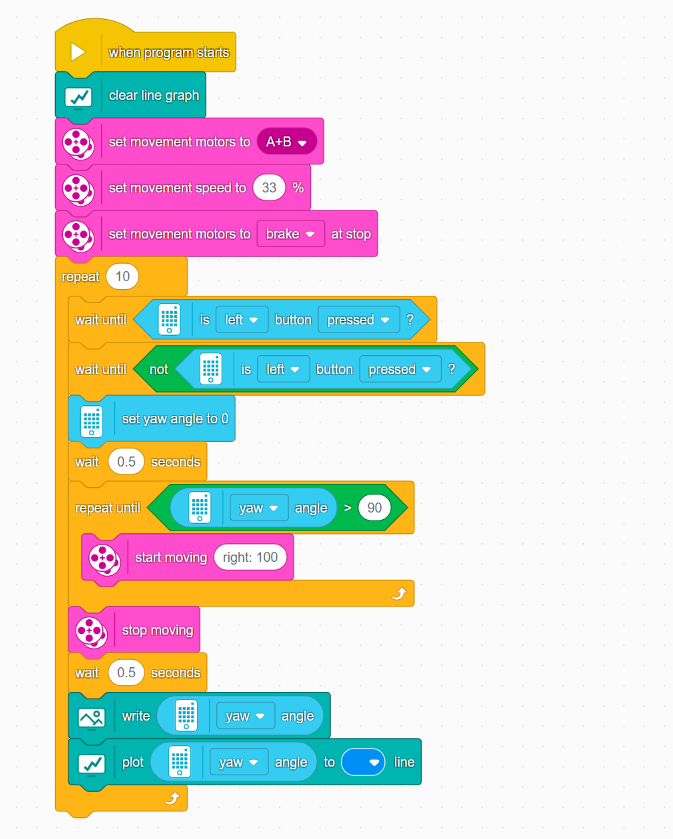
Python (SPIKE App 3)
import motor, motor_pair, time
from hub import motion_sensor, port, button
motor_pair.pair(motor_pair.PAIR_1, port.A, port.B)
motion_sensor.up_face()
for i in range(10):
# Wait for the left button to be pressed
while not button.pressed(button.LEFT):
pass
while button.pressed(button.LEFT):
pass
# Reset yaw
motion_sensor.reset_yaw(0)
time.sleep_ms(50) # Wait for yaw angle to reset
start = motion_sensor.tilt_angles()[0]*0.1
# Turn right
while (abs(motion_sensor.tilt_angles()[0]*0.1) < 90):
motor_pair.move_tank(motor_pair.PAIR_1, 300, -300)
# Stop turning
motor_pair.stop(motor_pair.PAIR_1,stop=motor.BRAKE)
time.sleep_ms(500)
stop = abs(motion_sensor.tilt_angles()[0]*0.1)
print("start:", start, "stop:", stop)
Python (Pybricks)
from pybricks.hubs import PrimeHub
from pybricks.pupdevices import Motor, ColorSensor, UltrasonicSensor, ForceSensor
from pybricks.parameters import Button, Color, Direction, Port, Side, Stop
from pybricks.robotics import DriveBase
from pybricks.tools import wait, StopWatch
hub = PrimeHub()
left_motor = Motor(Port.A, Direction.COUNTERCLOCKWISE)
right_motor = Motor(Port.B, Direction.CLOCKWISE)
for i in range(10):
# Wait until button is pressed
while not any(hub.buttons.pressed()):
wait(10)
# Wait for all buttons to be released.
while any(hub.buttons.pressed()):
wait(10)
while not hub.imu.ready():
wait(10)
# Reset the IMU
hub.imu.reset_heading(0)
wait(500)
start_heading = hub.imu.heading()
# Turn right
while abs(start_heading - hub.imu.heading()) < 90:
left_motor.run(300)
right_motor.run(-300)
# Stop turning
left_motor.brake()
right_motor.brake()
wait(500)
stop_heading = round(hub.imu.heading(), 1)
print("start:", start_heading, "stop:", stop_heading)
C Language (spike-rt)
#include <t_syslog.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <kernel.h>
#include <spike/hub/system.h>
#include <gyro_turn.h>
#include "spike/pup/motor.h"
#include "spike/pup/colorsensor.h"
#include "spike/pup/forcesensor.h"
#include "spike/pup/ultrasonicsensor.h"
#include "spike/hub/battery.h"
#include "spike/hub/button.h"
#include "spike/hub/display.h"
#include "spike/hub/imu.h"
#include "spike/hub/light.h"
#include "spike/hub/speaker.h"
#include <pbio/color.h>
#include "kernel_cfg.h"
#include "syssvc/serial.h"
#include "math.h"
pup_motor_t *motorA;
pup_motor_t *motorB;
pup_device_t *ColorSensor;
pup_device_t *ForceSensor;
pup_device_t *UltraSonicSensor;
// 0:roll(x) 1:pitch(y) 2:yaw(z)
float ang_v[3] = {0};
float imu_offset[3] = {0};
float start_value; // Gyro value at start
float stop_value; // Gyro value at stop
void Main(intptr_t exinf)
{
motorA = pup_motor_init(PBIO_PORT_ID_A, PUP_DIRECTION_COUNTERCLOCKWISE);
motorB = pup_motor_init(PBIO_PORT_ID_B, PUP_DIRECTION_CLOCKWISE);
imu_setup(imu_offset); // Offset calibration
int8_t i;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// Wait for left button to be pressed
hub_button_t pressed;
while(!(pressed&HUB_BUTTON_LEFT)){
hub_button_is_pressed(&pressed);
hub_light_on_color(PBIO_COLOR_GREEN);
}
// Wait for the left button to be released
while (pressed & HUB_BUTTON_LEFT) {
hub_button_is_pressed(&pressed);
hub_light_on_color(PBIO_COLOR_BLUE);
}
dly_tsk(500*1000);
sta_cyc(CYC_HDR); // Start gyro sensor monitoring
hub_imu_init(); // Initializing the IMU
// Reset yaw
ang_v[2] = 0;
start_value = ang_v[2];
// Turn right
while (fabs(ang_v[2]) < 90) {
pup_motor_set_power(motorA, 30);
pup_motor_set_power(motorB, -30);
}
// Stop turning
pup_motor_brake(motorA);
pup_motor_brake(motorB);
dly_tsk(500000);
stop_value = ang_v[2];
syslog(LOG_NOTICE, "start: %d.%02d stop: %d.%02d",
(int)start_value, (int)((start_value - (int)start_value) * 100),
(int)stop_value, (int)(fabs(stop_value - (int)stop_value) * 100));
}
stp_cyc(CYC_HDR); // Stop gyro sensor monitoring
}
void gyro_monitor(intptr_t exinf)
{
float ang_raw[3]; // IMU angular acceleration
hub_imu_get_angular_velocity(ang_raw);
// Offset Correction
ang_v[0] += (ang_raw[0] - imu_offset[0]) * 0.001;
ang_v[1] += (ang_raw[1] - imu_offset[1]) * 0.001;
ang_v[2] += (ang_raw[2] - imu_offset[2]) * 0.001;
}
void imu_setup(float offset[3]){
dly_tsk(3*1000*1000);
hub_light_on_color(PBIO_COLOR_ORANGE);
hub_imu_init(); // Initializing IMU
float ang_raw[3]; // Raw IMU angular velocity
// Offset calibration
for(int i=0; i<1000; i++){
hub_imu_get_angular_velocity(ang_raw);
offset[0] += ang_raw[0];
offset[1] += ang_raw[1];
offset[2] += ang_raw[2];
dly_tsk(1*1000);
}
offset[0] /= 1000;
offset[1] /= 1000;
offset[2] /= 1000;
}
Results: Which Environment Was Most Accurate?
Here are the average rotation errors (smaller is better):
1️⃣ 6.4° - C Language (spike-rt) 🏆
2️⃣ 8.6° - Python (Pybricks)
3️⃣ 9.6° - Python (SPIKE App 3)
4️⃣ 17.1° - Word Blocks (SPIKE App 3)
Additionally, I measured the error fluctuation range (stability):
1️⃣ 0.8° - C Language (spike-rt) 🏆
2️⃣ 0.9° - Word Blocks (SPIKE App 3)
3️⃣ 1.0° - Python (Pybricks)
4️⃣ 1.2° - Python (SPIKE App 3)
Key Takeaways:
- C Language (spike-rt) had the most accurate rotation (smallest error)
- C Language (spike-rt) also had the most stable results (smallest variation) ________________________________________
Want to Try C Programming on LEGO SPIKE Prime?
If you’re interested in trying C on SPIKE Prime, there are beginner-friendly learning materials available. As of March 2025, a trial version is also accessible—give it a try!
Related Articles
- Testing LEGO SPIKE Prime with C: Line Follower Speed & Stability
- Introducing SPIKE-RT: the C Language Software Platform for LEGO SPIKE Prime
- Comparing LEGO SPIKE Prime Programming: Which is Best for Robotics Competitions? - 1
- Comparing LEGO SPIKE Prime Programming: Which is Best for Robotics Competitions? - 2
- Comparing LEGO SPIKE Prime Programming: Which is Best for Robotics Competitions? - 4
🔹 More tests are planned, including further evaluations for robotics competitions. Stay tuned for future updates! 🚀



Top comments (0)