A Practical Tour of Key Amazon SageMaker Services
Amazon SageMaker is a managed platform that helps teams build, train, and run machine learning (ML) workloads without stitching together separate tools. Instead of maintaining custom infrastructure for every stage of the ML lifecycle, you can rely on SageMaker components for data prep, training, deployment, monitoring, and governance. This article walks through several important SageMaker capabilities and how they fit into a modern ML workflow.
1. SageMaker Automatic Model Tuning
SageMaker Automatic Model Tuning runs many training jobs with different hyperparameter settings and searches for the configuration that yields the best objective metric. It uses Bayesian optimization under the hood to decide which combination of hyperparameters to try next, so you do not have to manually run dozens of experiments yourself.
Key benefits:
- Cuts down on manual hyperparameter search effort.
- Often improves model quality by efficiently exploring the search space.
- Works with built‑in, marketplace, and custom algorithms.
2. SageMaker Deployment and Inference
SageMaker provides managed infrastructure to host trained models and expose them as endpoints or batch jobs, so you can serve predictions at scale without managing servers directly. It supports real‑time, batch, asynchronous, and serverless inference options, along with traffic‑splitting for A/B testing and safe rollouts.
Common deployment patterns:
- Real‑time endpoints for low‑latency prediction APIs.
- Batch transform for large, offline scoring jobs.
- Asynchronous inference for long‑running requests.
- Serverless inference for spiky or low‑throughput workloads.
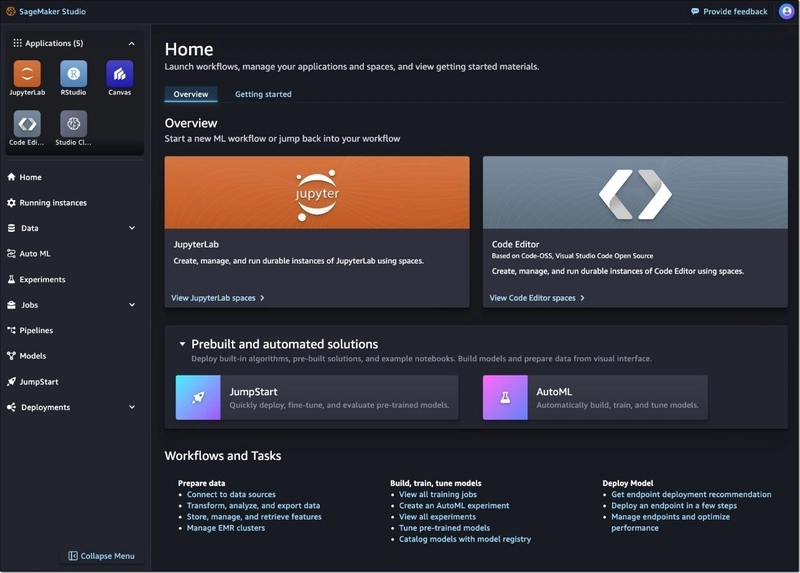
3. SageMaker Studio
SageMaker Studio is a web‑based integrated development environment that centralizes many ML activities in a single visual interface.
Within Studio, you can launch notebooks, run experiments, debug models, and monitor performance without constantly switching tools.
Main capabilities:
- Managed notebooks for exploration and prototyping.
- Experiment tracking to organize and compare runs.
- Debugging tools to inspect training behavior.
- Built‑in monitoring views for deployed models.
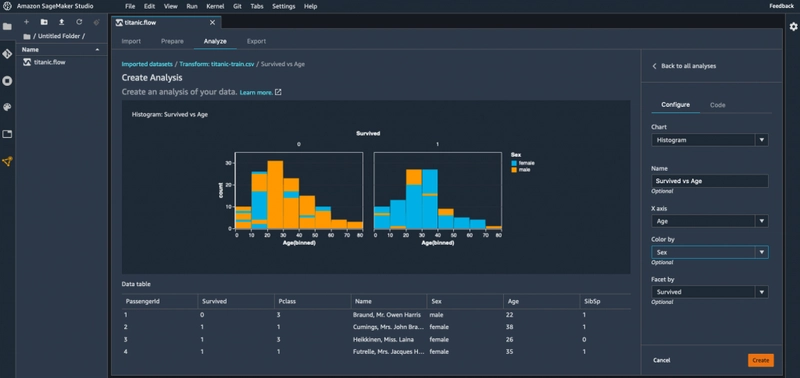
4. SageMaker Data Wrangler
Data Wrangler is designed to shorten the “data cleaning and feature engineering” phase by providing a visual workspace for data preparation. You can connect to data sources, explore data distributions, apply transformations, and then export the prepared dataset into downstream SageMaker workflows.
What you can do:
- Apply hundreds of built‑in data transformations and feature ops.
- Visualize data quality and distributions as you iterate.
- Engineer features and send them into SageMaker Pipelines.
5. SageMaker Clarify
SageMaker Clarify provides bias and explainability tooling for your ML models, helping you understand both how they behave and how they might impact different user groups. It analyzes training data and predictions to surface fairness metrics and generate feature‑importance explanations.
Key features:
- Bias detection metrics on datasets and model outputs.
- Model explainability reports for stakeholders.
- Feature importance for both global and local explanations.
- Support for compliance and responsible‑AI requirements.
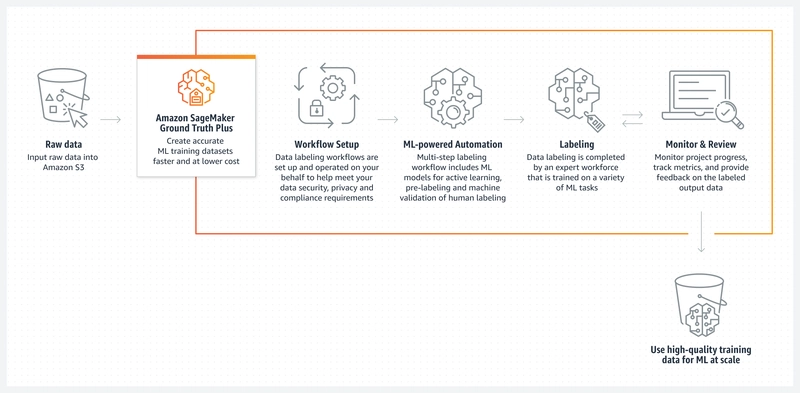
6. SageMaker Ground Truth
Ground Truth helps you build labeled datasets by managing annotation workflows and integrating with human labelers. You can use Amazon’s own workforce, third‑party vendors, or your internal team, depending on the data sensitivity and scale requirements.
Labeling options:
- Public workforce through Amazon Mechanical Turk.
- Vendor workforces managed by AWS partners.
- Private labeling teams within your organization.
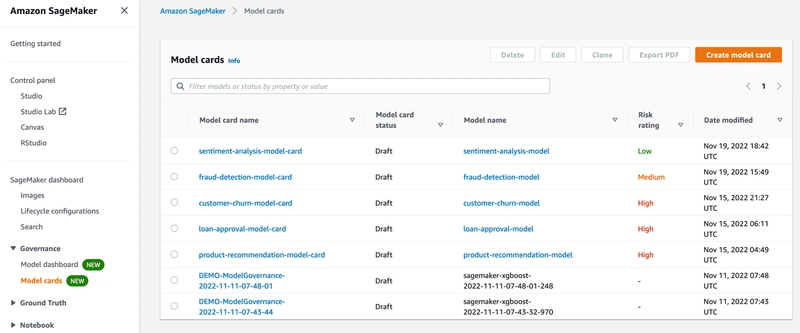
7. SageMaker Model Cards
Model Cards in SageMaker provide a structured template for documenting important details about each model, which is critical for governance and audits. They centralize context like intended use, training data characteristics, and evaluation metrics in a standardized format.
Typical sections include:
- High‑level model description and owners.
- Expected use cases and known limitations.
- Training data sources and configuration.
- Evaluation methodology and performance results.
8. SageMaker Model Dashboard
SageMaker Model Dashboard offers a unified view across models that are running in production so teams can track health and risk in one place. It aggregates information from monitoring tools to help you see which models might require retraining or investigation.
Core capabilities:
- Tracking model performance indicators over time.
- Detecting data and prediction drift patterns.
- Configuring alerts and notifications for issues.
9. SageMaker Model Monitor
Model Monitor continuously evaluates the quality of models deployed in SageMaker by comparing live traffic to a defined baseline. When it detects drift or quality issues, it can surface alerts so you can decide whether to retrain, roll back, or adjust the model.
Things it can monitor:
- Input data quality and schema consistency.
- Prediction quality and performance metrics.
- Bias drift over time on key attributes.
- Changes in feature attribution patterns.
10. SageMaker Model Registry
The Model Registry is a catalog for your trained models, enabling controlled promotion from experimentation to production. It tracks versions, metadata, and approval states so that ML and MLOps teams can coordinate deployments more safely.
Key capabilities:
- Versioning of model artifacts and metadata.
- Approval workflows for moving models between stages.
- Lineage tracking across training, evaluation, and deployment.
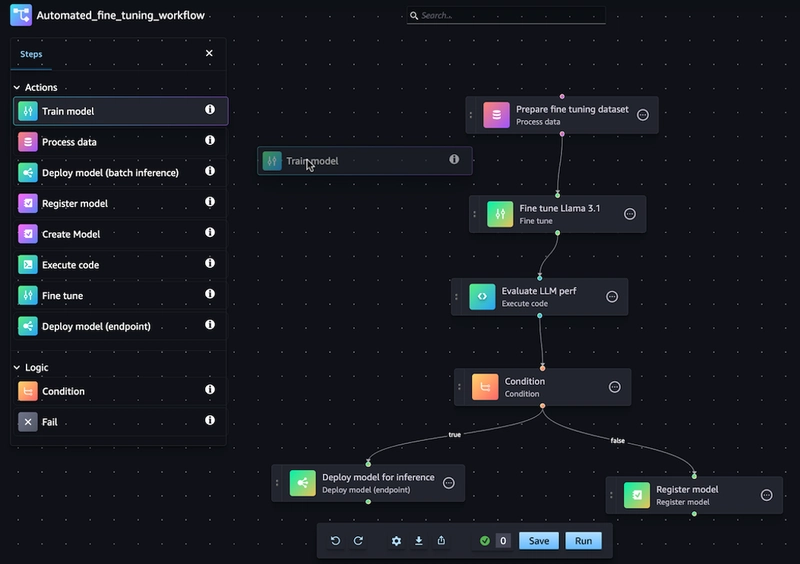
11. SageMaker Pipelines
SageMaker Pipelines is a purpose‑built workflow engine for ML that lets you define and automate multi‑step pipelines, from preprocessing to training to deployment. Pipelines make ML workflows reproducible, repeatable, and easier to integrate with CI/CD systems.
Advantages:
- Ensures reproducible runs with versioned definitions.
- Encourages reusability of standardized pipeline steps.
- Integrates with DevOps tooling for automated releases.
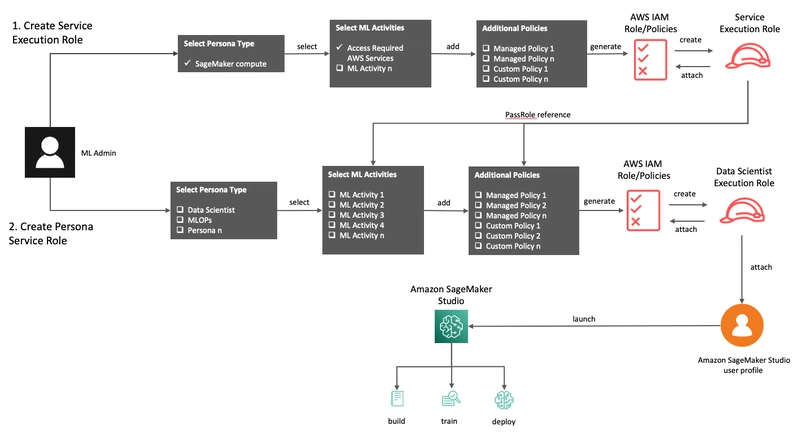
12. SageMaker Role Manager
Role Manager simplifies the process of configuring permissions for SageMaker resources by offering templates and guided workflows. Instead of manually writing complex IAM policies, you can start from predefined roles and then adjust them as needed.
Highlights:
- Curated roles for common SageMaker usage patterns.
- Fine‑grained permission controls for security teams.
- Tight integration with AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM).
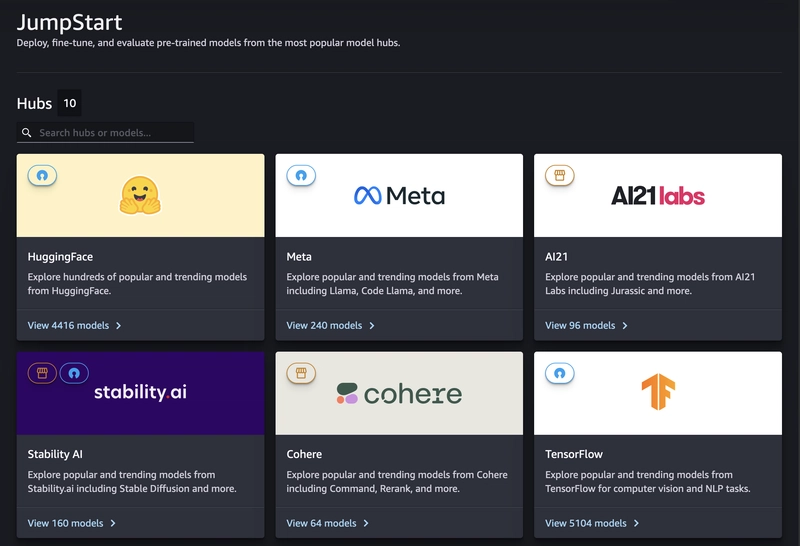
13. SageMaker JumpStart
JumpStart provides a gallery of pre‑built solutions, pre‑trained models, and example notebooks that you can deploy or customize with just a few steps. It is particularly useful when you want to quickly prototype a use case like classification, forecasting, or computer vision without building everything from scratch.
What JumpStart offers:
- Ready‑to‑use pre‑trained models for common tasks.
- End‑to‑end solution templates with infrastructure code.
- Example notebooks you can open directly in Studio.
14. SageMaker Canvas
SageMaker Canvas targets business users who want to generate predictions without writing code or managing infrastructure. It provides a visual interface where users can connect data, build ML models with AutoML, and explore predictions interactively.
Key traits:
- Drag‑and‑drop interface for non‑technical users.
- Automatic model building and selection behind the scenes.
- Focus on business‑friendly workflows and collaboration.
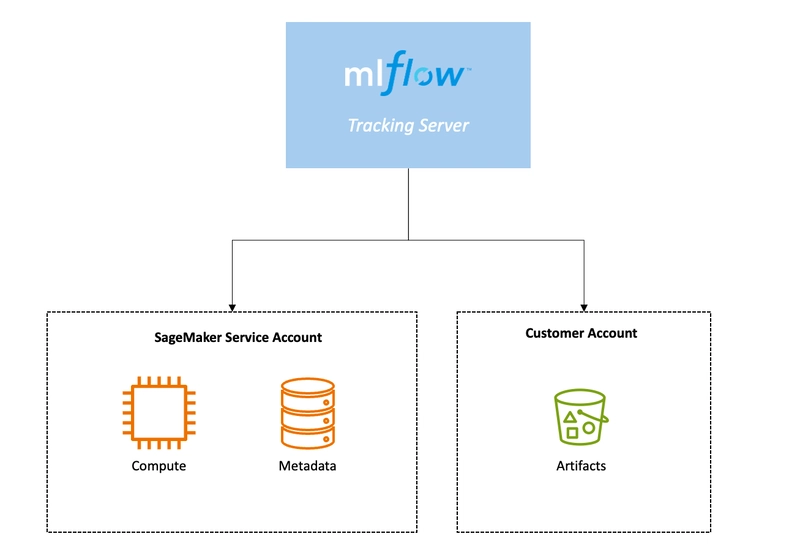
15. SageMaker MLflow Integration
SageMaker integrates with the open‑source MLflow ecosystem so that teams already using MLflow for experiment tracking and model management can tie those workflows into SageMaker services. This integration lets you log runs, track artifacts, and manage model versions while still deploying on SageMaker.
You can use it to:
- Track experiments and metrics in MLflow while training on SageMaker.
- Register models in an MLflow registry and connect them to SageMaker deployments.
- Store training artifacts in a centralized and queryable location.
Wrapping up
AWS SageMaker brings together many specialized services that collectively cover data preparation, experimentation, deployment, monitoring, and governance for ML workloads. By adopting the right mix of these tools, teams can shorten development cycles and operate ML systems more reliably at scale.
For deeper dives into specific features, see the official SageMaker documentation.
References
- AWS SageMaker Documentation.
- AWS Machine Learning Blog.
- AWS re:Invent sessions and technical talks.





Top comments (0)