Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to computer systems or machines designed to simulate human-like intelligence, enabling them to perform tasks such as reasoning, problem-solving, learning, adaptation, perception, and decision-making.
AI systems use algorithms, data, and machine learning (a process of iterative improvement) to autonomously adapt, improve, and execute tasks. AI autonomy means an AI can operate, make decisions, and complete tasks with varying levels of human supervision .
Brief history of Artificial intelligence (AI)
The history of AI dates back to the early 1900s. From the birth of AI, its maturation, the AI boom, the AI winter, AI agents, and up to the present day, we have come a long way.
AI development experienced rises and falls multiple times; dozens of companies failed, and it was widely believed that the technologies were not viable. During this period, AI was primarily used behind the scenes.
The current buzz and success surrounding AI can be attributed to advanced technologies, powerful processors and hardware like GPUs, improved algorithms, and the availability of large datasets.
Narrow AI vs. General AI
There are various types of AI, but in this blog, we'll focus on two: Narrow AI and General AI
Narrow AI (Weak AI)
Narrow AI (or weak AI) is a type of artificial intelligence specialized in performing a limited set of tasks . Examples include:
- Voice assistants like Siri or Alexa.
- Recommendation systems (e.g., YouTube, Netflix).
- Tesla’s driver-assist system (Autopilot).
These systems excel at specific tasks but lack general intelligence.
General AI (AGI or Strong AI)
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), also called Strong AI, is a theoretical form of AI that would possess human-level intelligence. It could:
- Reason, solve problems, and perform any intellectual task a human can do .
- Learn new skills dynamically, similar to human adaptability.
AGI remains hypothetical, and no real-world examples exist today . Current AI systems are all Narrow AI.
How does Artificial Intelligence (AI) work?
AI works by simulating human intelligence in computer systems or machines. It makes use of algorithms, data, and computational power to simulate human-like intelligence, learn, solve problems, make decisions, recognize patterns, and more.
To understand how AI works, let's look at some of the foundational elements that make AI function:
Data
AI relies on large datasets. The data is used for training and decision-making. The quality and quantity of data directly influence the performance of AI models.
The data can be either structured, such as data from databases, or unstructured, such as images, audio, etc.
Algorithm
Algorithms are sets of instructions or rules that determine how AI should process the data and learn from it. Some examples include supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning.
Neural Networks
Neural networks are computational models inspired by the human brain. They are designed to make decisions in a manner similar to the human brain. Neural networks rely on training data to learn and improve their accuracy over time. They are widely used in deep learning and natural language processing.
Training
Training in the context of AI refers to teaching an AI model to perform a specific task or set of tasks. Training involves a process of trial and error, and as training progresses, the AI models need to be fine-tuned.
Inference
Inference is the stage where AI performs its intended task based on what it has learned.
Now that we've discussed how AI works by using data, algorithms, neural networks, training, and inference, let's dive deeper into three key branches of AI where these different components of an AI system come together: Machine Learning (ML), Natural Language Processing (NLP), and Neural Networks (NN).
Branches of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is a vast and multifaceted field, which is why the need for different branches of AI arises. Each branch focuses on solving specific types of challenges using particular techniques, tools, and approaches.
Machine Learning (ML)
Machine Learning (ML) is a branch of AI that focuses on enabling computer systems or machines to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. ML allows systems to simulate the way humans learn, perform tasks autonomously, and improve their performance through experience and exposure to large datasets.
There are three major categories of machine learning methods: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning.
Neural networks, linear regression, logistic regression, clustering, and decision trees are some of the commonly used machine learning algorithms.
For instance, recommendation systems (such as those used by Netflix, YouTube, etc.) use ML to analyze user behavior (data), apply algorithms to find patterns, and suggest personalized recommendations (inference).
Neural Networks (NN)
A neural network (NN) is a machine learning model inspired by the human brain, consisting of interconnected nodes (neurons) that process information through weighted connections and layers. Neural networks are a part of machine learning and enable tasks such as pattern recognition, speech processing, and decision-making.
A basic neural network typically consists of three layers:
- Input Layer : Receives the raw data
- Hidden Layer(s) : Processes the data
- Output Layer : Provides the final result
Deep Learning (DL)
Deep Learning is a specialized subfield of neural networks. Deep Learning and neural networks are often used interchangeably, which can lead to confusion. The word deep in deep learning refers to the depth of layers in a neural network.
A neural network that has only two to three hidden layers is considered a basic neural network, while a neural network with more than three layers is referred to as a deep learning model.
For example, self-driving cars use neural networks to process visual data (data), recognize objects, pedestrians, traffic signs, and other vehicles (training), and make real-time traffic decisions (inference).
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a branch of AI that focuses on enabling computer systems or machines to understand and communicate in human language.
NLP allows computer systems or machines to recognize, understand, interpret, and generate human language in a way that is both meaningful and useful. NLP combines computational linguistics, machine learning, and deep learning models to process human language.
Some approaches to NLP include Supervised NLP, Unsupervised NLP, Natural Language Understanding (NLU), and Natural Language Generation (NLG).
NLP is being utilized to automate various tasks, such as processing and analyzing large datasets, running chatbots, and more.
How Machine Learning (ML), Neural Networks (NNs), and Natural Language Processing (NLP) Work Together
Now that we've explored machine learning, neural networks, and natural language processing as key branches of AI, let's see how they all come together in a real-world application.
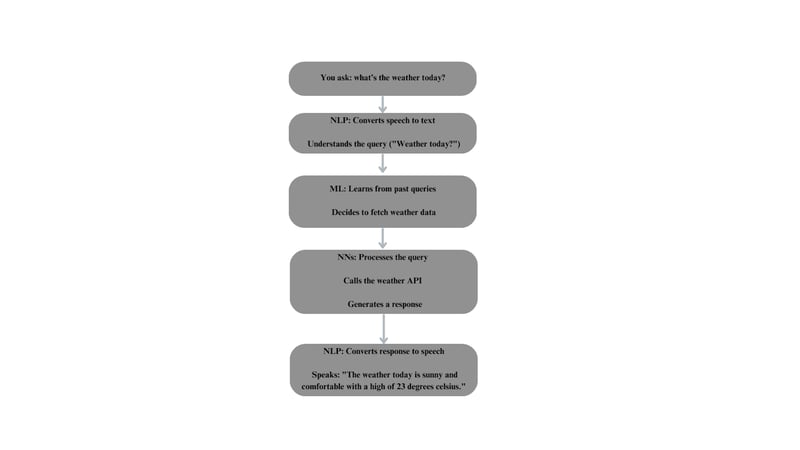
To make the picture clearer, let's take the example of a virtual assistant like Siri or Alexa answering a question about the weather.
Step 1: You ask Siri, "Hey Siri, what's the weather like today?"
Once you ask Siri about the weather, it uses NLP to convert your spoken words into text. This part is called speech recognition.
Step 2: Understanding the text
The system behind Siri uses NLP and neural networks to understand what you are asking.
NLP breaks down the sentence into smaller parts, identifying that you are asking about the weather and that you want information for today.
Neural networks help in recognizing patterns. For instance, they might identify that the word "weather" is associated with querying an external weather API.
Modern NLP often uses transformers (a type of neural network, such as BERT or GPT) to understand the context and relationships between words.
Step 3: Learning from past interactions
The role of ML comes into play when deciding what to do next based on what it has learned. The virtual assistant uses ML to improve over time by learning from past interactions. The ML algorithms analyze patterns in user queries to predict the best response or action.
Step 4: Fetching the weather data
The system fetches the weather information for today. A neural network might be used to process the query and decide which API to call. For example, the system sends a request to a weather API and retrieves the current temperature.
Step 5: Generating a response
Once the weather API provides the current weather details, such as (23, "degrees", "celsius", ["sunny", "comfortable"]), the system combines the data to form a grammatically correct sentence structure.
For example, it might form a sentence like: The weather today is sunny and comfortable with a high of 23 degrees Celsius.
Here, NLP helps to generate the response, and neural networks ensure the response is contextually appropriate.
Step 6: Converting Text to Speech
As a final step, the virtual assistant speaks the response back to you. NLP converts the generated response into speech using a process called Text-To-Speech (TTS). Neural networks are often used in TTS to make the voice sound more natural and human-like.
That's it! We have come to the end of the introductory blog on AI. I hope the blog will be helpful for anyone who wants to begin their journey of learning about AI. We'll be coming up with more exciting content on AI soon!


Top comments (0)