What is Amazon EKS?
- "Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) is a managed service that eliminates the need to install, operate, and maintain your own Kubernetes control plane on Amazon Web Services (AWS). Kubernetes is an open-source system that automates the management, scaling, and deployment of containerized applications."
- It provisions and scales control plane, API Servers, and backend persistence layers across multiple AZs for high availability and fault tolerance.
- Also, it automatically detects and replaces the unhealthy control plane nodes for patching.
- Amazon EKS is integrated with many AWS Services like ELB for load distribution, IAM for authentication, Amazon VPC for isolation and CloudTrail for logging.
- You can Create an Amazon EKS cluster without specifying a VPC. This is because Amazon EKS can automatically create a VPC for your cluster. However, if you do specify a VPC, you will have more control over the networking configuration of your cluster.
Please visit my GitHub Repository for EKS articles on various topics being updated on constant basis.
Let’s get started!
Objectives:
1. Sign into AWS Management Console.
2. Create your Amazon EKS cluster role
3. Create Security Group
4. Create an EKS Cluster
5. Create an Environment in CloudShell
6. Install kubectl on AWS CloudShell
7. Configure your AWS CloudShell to communicate with your cluster
8. Test your configuration
Pre-requisites:
- AWS user account with admin access, not a root account.
- CloudShell environment
Resources Used:
Steps for implementation to this project:
1. Sign into AWS Management Console.
- Make sure you're in the N. Virginia (us-east-1) region
2. Create your Amazon EKS cluster role
1.
2.
- Next
3.
4. Create role R-EKSClusterRole
5.
6. Summary
3. Create Security Group
1.
2. Inbound rules
- Create Security group
4. Create an EKS Cluster
1.
Take defaults
Next
2. Remove the subnets us-east-1e and us-east-1f
3. Select the security group my-EKS-SG
4. Cluster endpoint access: Public
5. Configure Logging
- Next
- Take all the defaluts
- Next, Next
- Create
6. Note: Wait to create the Cluster, will take about 4-5 minutes.
5. Create an Environment in CloudShell
1. Click on Arrow icon (Cloud Shell)
2.
6. Install kubectl on AWS CloudShell
1. Download the Amazon EKS vended kubectl binary for your cluster's Kubernetes version from Amazon S3
curl -o kubectl https://amazon-eks.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/1.18.9/2020-11-02/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl
2. Apply execute permissions to the binary.
chmod +x ./kubectl
3. Copy the binary to a folder in your PATH.
- If you have already installed a version of kubectl, then create a $HOME/bin/kubectl and ensure that $HOME/bin comes first in your $PATH.
mkdir -p $HOME/bin && cp ./kubectl $HOME/bin/kubectl && export PATH=$PATH:$HOME/bin
4. After you install kubectl, you can verify its version with the following command:
kubectl version --short --client
7. Configure your AWS CloudShell to communicate with your cluster
1. Once the environment is ready on CloudShell, you create a kubeconfig file for your cluster.
The settings in this file enable the kubectl CLI to communicate with your cluster.
-
To create a kubeconfig file, run the following command:
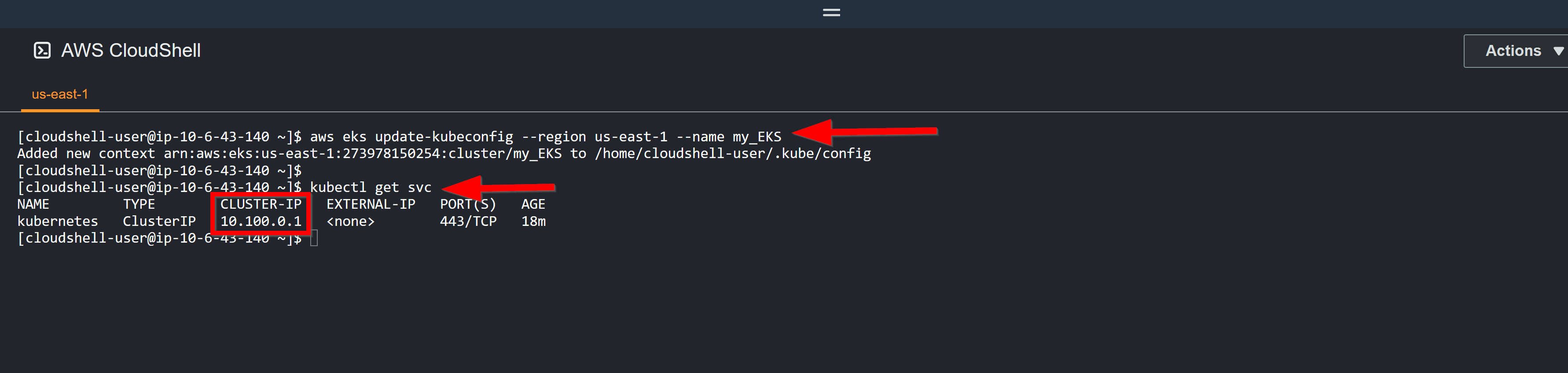
aws eks update-kubeconfig --region us-east-1 --name my_EKS
## 8. Test your configuration, with the following command:
kubectl get svc
# Cleanup
- Delete EKS cluster
- Delete CloudShell directory
- Delete EKS role and Security Group
# What we have done so far
- We have successfully created and launched Amazon EKS Cluster, installed Kubectl in AWS Cloudshell and configured AWS Cloudshell to communicate with AWS EKS Cluster.






















Top comments (0)