Database normalization is the process of organizing data to reduce redundancy and improve data integrity. In this tutorial, we’ll go step-by-step from Unnormalized Table → 1NF → 2NF → 3NF, and implement it using **MySQL.
We’ll also write a JOIN query to display students along with their courses and instructors.
Insertion Anomaly: Cannot add a new course without assigning it to a student.
- Update Anomaly: If an instructor’s phone number changes, multiple rows must be updated.
- Deletion Anomaly: Removing a student could delete information about the course and instructor. 1.First Normal Form (1NF)
Rule: Each column should have atomic values.
Our table already satisfies 1NF.
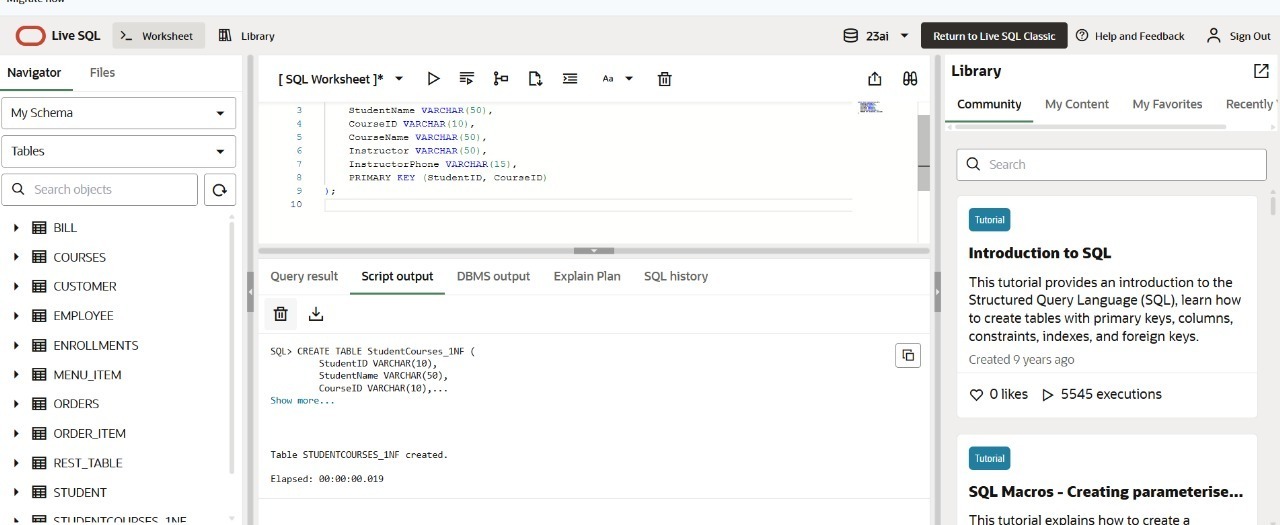
sql
CREATE TABLE StudentCourses_1NF (
StudentName VARCHAR(50),
CourseID VARCHAR(10),
CourseName VARCHAR(50),
Instructor VARCHAR(50),
InstructorPhone VARCHAR(15)
);
2. Second Normal Form (2NF)
Rule: Must be in 1NF, and remove partial dependencies.
CourseName, Instructor, InstructorPhone depend only on CourseID.
StudentName depends only on the student.
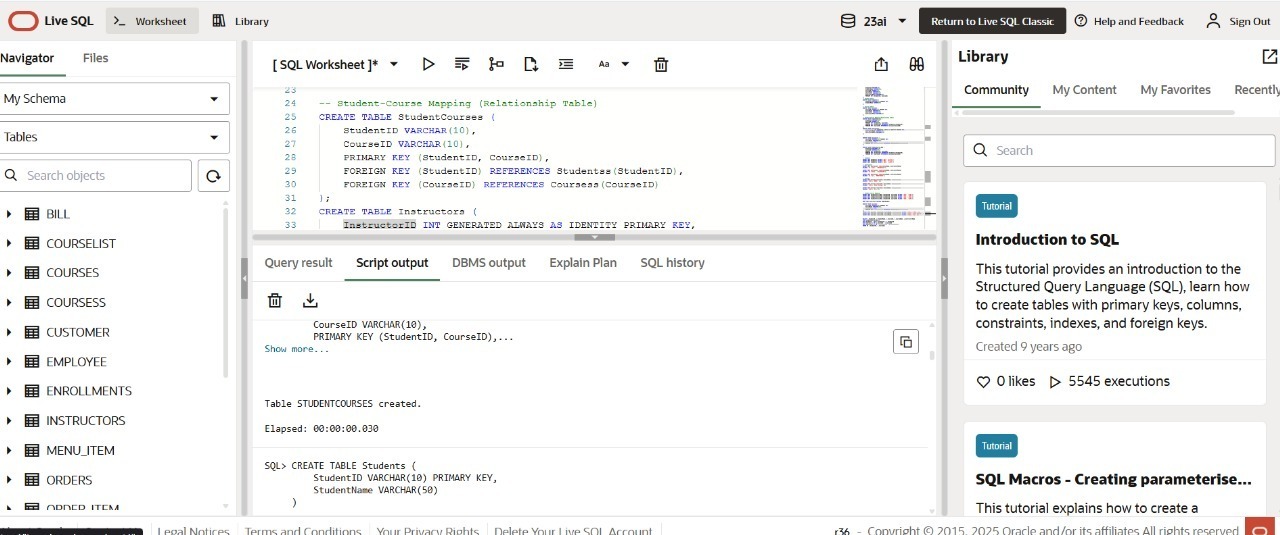
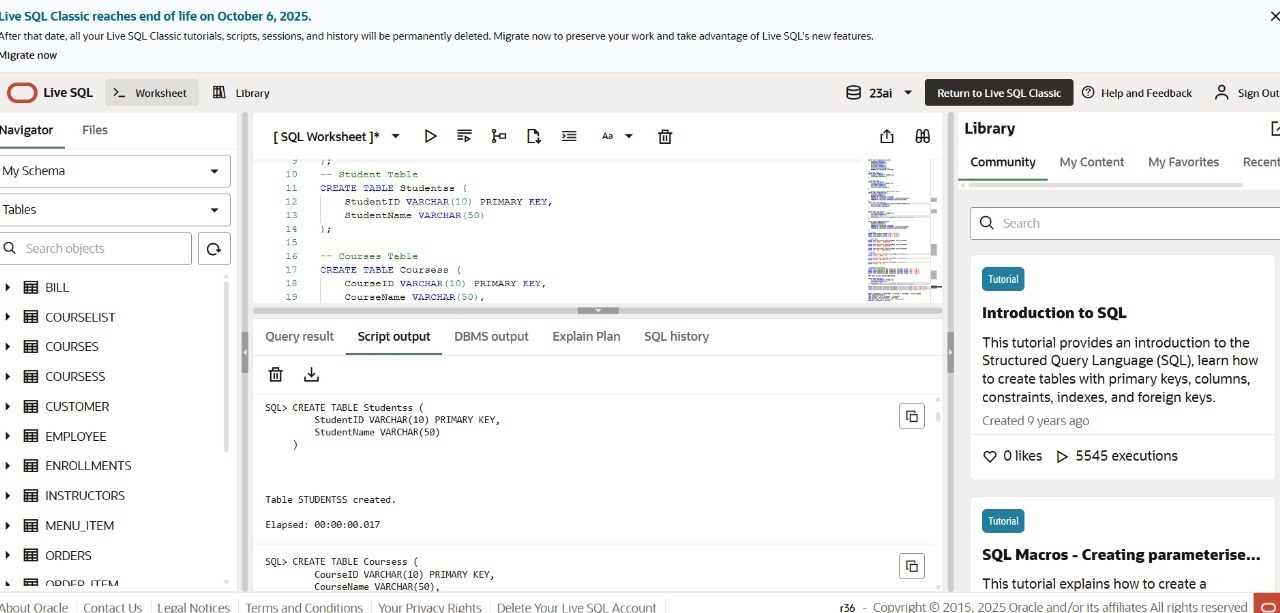
-- Students Table
CREATE TABLE Students (
StudentID INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
StudentName VARCHAR(50)
);
-- Courses Table
CREATE TABLE Courses (
CourseID VARCHAR(10) PRIMARY KEY,
CourseName VARCHAR(50),
Instructor VARCHAR(50),
InstructorPhone VARCHAR(15)
);
-- Enrollments Table (linking students to courses)
CREATE TABLE Enrollments (
StudentID INT,
CourseID VARCHAR(10),
PRIMARY KEY (StudentID, CourseID),
FOREIGN KEY (CourseID) REFERENCES Courses(CourseID)
);
3. Third Normal Form (3NF)
Rule: Must be in 2NF, and remove transitive dependencies.
InstructorPhone depends on Instructor.
Move instructors to a separate table.
-- Students Table
CREATE TABLE Students (
StudentID INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
StudentName VARCHAR(50)
);
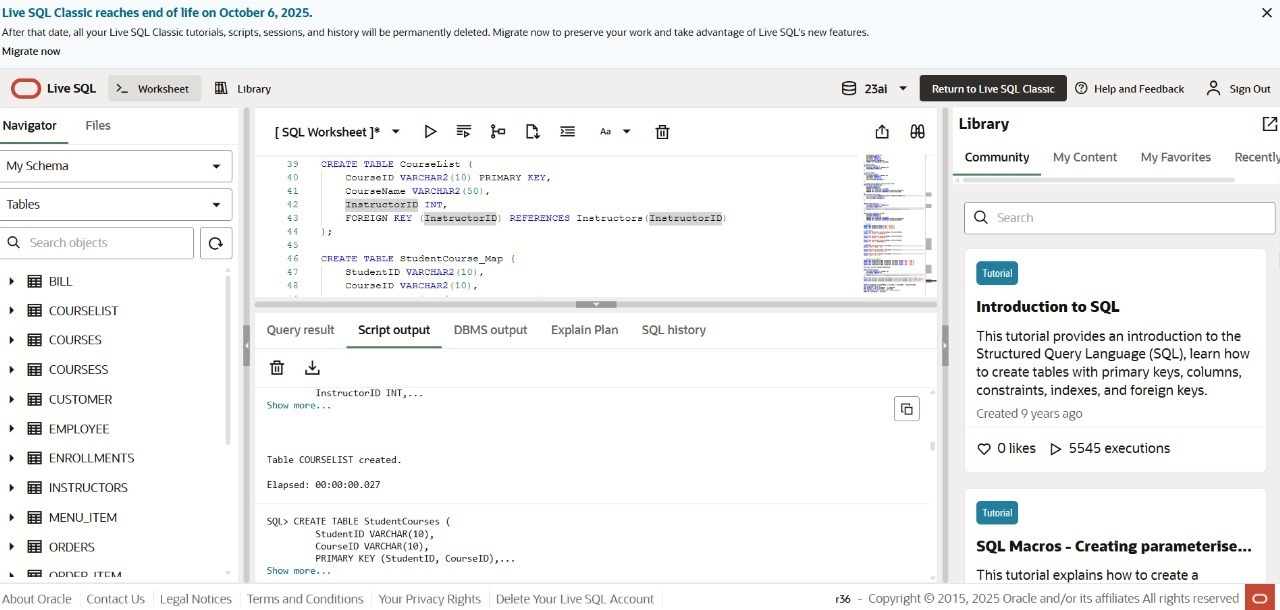
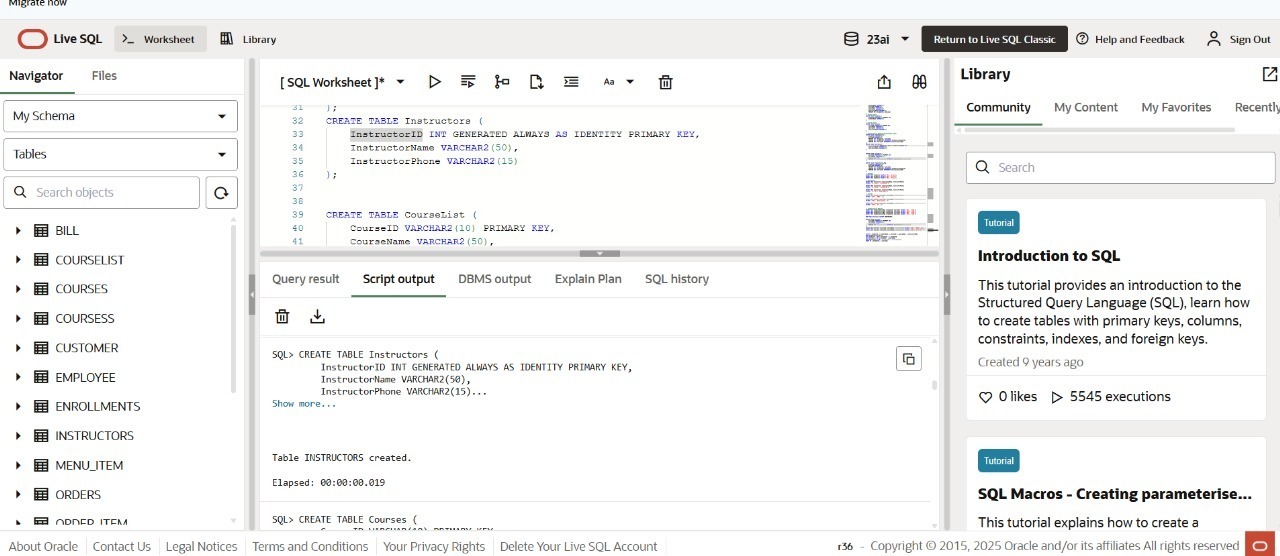
-- Instructors Table
CREATE TABLE Instructors (
InstructorID INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
InstructorName VARCHAR(50),
InstructorPhone VARCHAR(15)
);
-- Courses Table
CREATE TABLE Courses (
CourseID VARCHAR(10) PRIMARY KEY,
CourseName VARCHAR(50),
InstructorID INT,
FOREIGN KEY (InstructorID) REFERENCES Instructors(InstructorID)
);
-- Enrollments Table
CREATE TABLE Enrollments (
StudentID INT,
CourseID VARCHAR(10),
PRIMARY KEY (StudentID, CourseID),
FOREIGN KEY (StudentID) REFERENCES Students(StudentID),
FOREIGN KEY (CourseID) REFERENCES Courses(CourseID)
);
4. Insert Sample Data
-- Insert Students
INSERT INTO Students (StudentName) VALUES
('Arjun'),
('Priya'),
('Kiran');
-- Insert Instructors
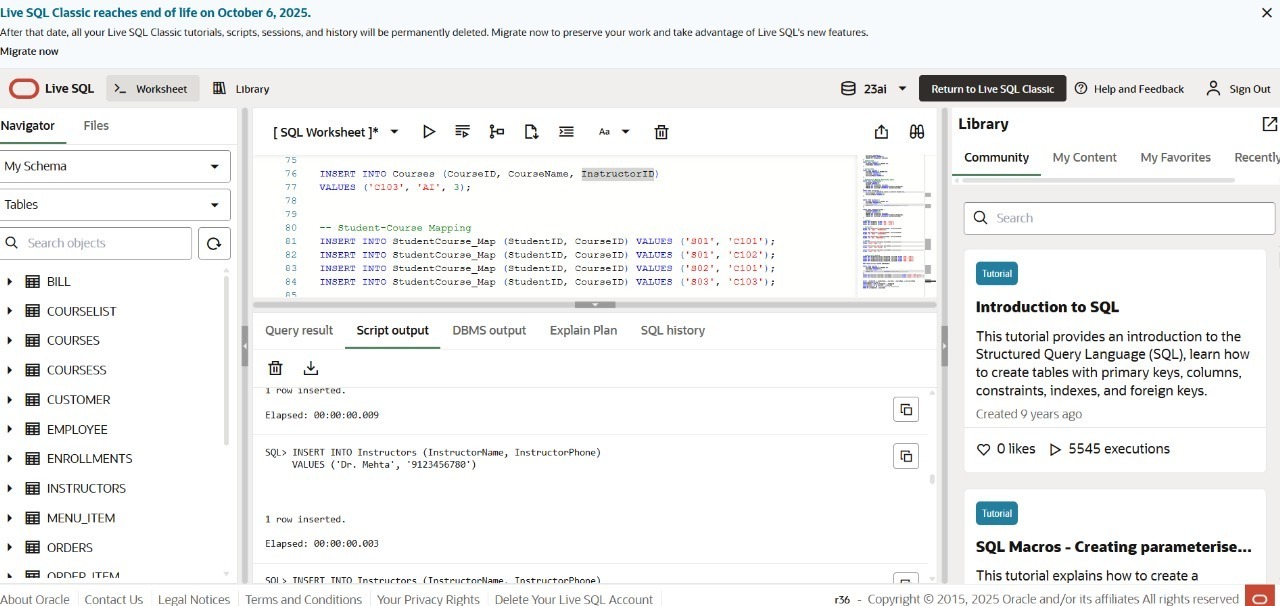
INSERT INTO Instructors (InstructorName, InstructorPhone) VALUES
('Dr. Kumar', '9876543210'),
('Dr. Mehta', '9123456780'),
('Dr. Rao', '9988776655');
-- Insert Courses
INSERT INTO Courses (CourseID, CourseName, InstructorID) VALUES
('C101', 'DBMS', 1),
('C102', 'Data Mining', 2),
('C103', 'AI', 3);
-- Insert Enrollments
INSERT INTO Enrollments (StudentID, CourseID) VALUES
(1, 'C101'),
(1, 'C102'),
(2, 'C101'),
(3, 'C103');
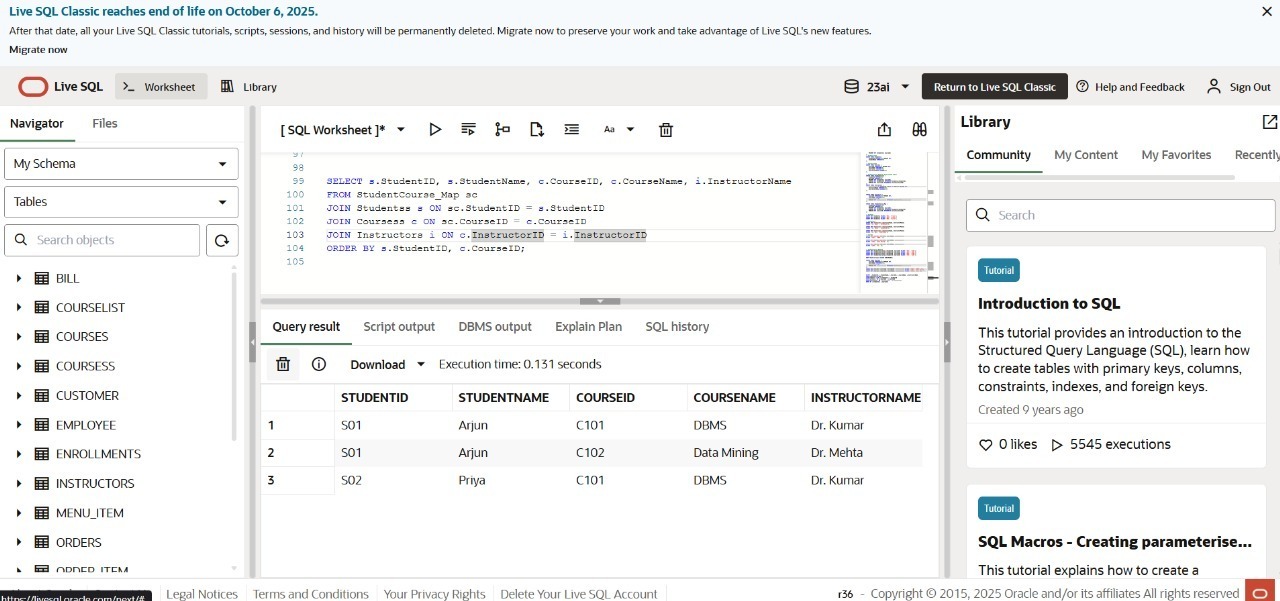
5. JOIN Query to List Students, Courses & Instructors
SELECT
s.StudentName,
c.CourseName,
i.InstructorName,
i.InstructorPhone
FROM Enrollments e
JOIN Students s ON e.StudentID = s.StudentID
JOIN Courses c ON e.CourseID = c.CourseID
JOIN Instructors i ON c.InstructorID = i.InstructorID;


Top comments (0)