In javascript
const obj1 = {}
const obj2 = {}
obj1 === obj2 // false
WHaT ?????
If you react like this, keep reading this article.
At first I need to explain about memory life cycle.
Don't worry, I'll show you simple way with image.
const name = 'kaziu' // string
let isShame = true // boolean
let age = 101 // number
in Javascript string, number, boolean, null, undefined, symbol calls primitive type
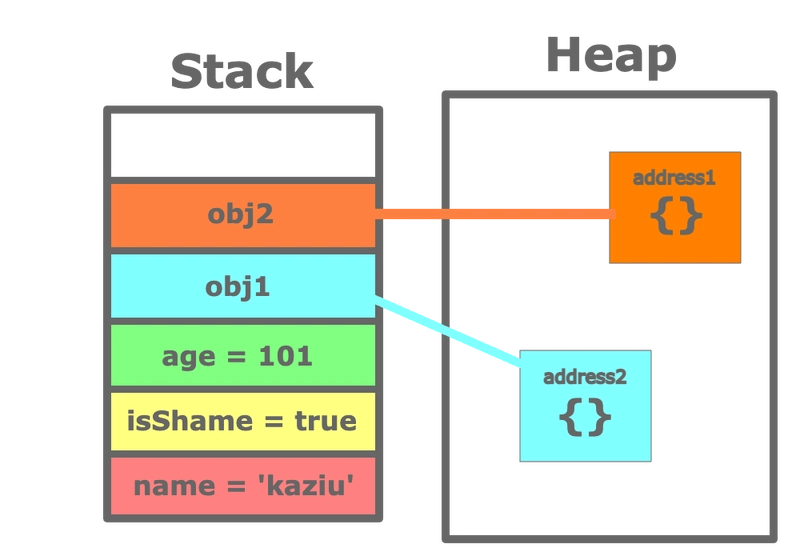
When declare like this in javascript primitive type, datas store on space which is called stack in memory.
On the other hand, object is reference type include function, array (actually function is one of objects)
const obj1 = {}
const obj2 = {}
When declare object, computer does not directly store that data type in that variable. property stores in heap
As you can see, each objects has different addresses. And obj1 === obj2 compares these addresses, that's why return false.
conclusion
This is normally called reference, but I used address because it's easy to understand. You could imagine there are two same looking houses in different places 🏠🏠
personally I take care of it as frontend engineer, specially when I use useMemo in React.



Top comments (0)