Introduction
As part of mastering Apache Airflow, here is a documentation of a project where I extracted BTC price data from Polygonio. In this article, we'll walk through how to use Python to automatically retrieve cryptocurrency price data from an API, process it, and store it in a PostgreSQL database for later analysis.
Problem definition
Often, we need to access accurate and up-to-date cryptocurrency prices for specific dates, especially for backtesting strategies, conducting financial analysis, or building data-driven applications. Manually collecting this data from different platforms can be time-consuming and error-prone.
Solution
Automating this process allows us to consistently pull fresh data and integrate it into our systems for real-time or historical analysis.
I used Python to Query the Polygon.io API to fetch historical cryptocurrency data for a specific date. I then transformed the data and stored it in a PostgreSQL database. Automate the process to run regularly with the help of environment variables and secure configurations.
Step by step
1. Importing Necessary Libraries
import requests
import json
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
import pandas as pd
from datetime import datetime
2. Extraction
url='https://api.polygon.io/v1/open-close/crypto/BTC/USD/2025-03-31?adjusted=true&apiKey=YOUR_API_KEY'
response = requests.get(url)
3. Parsing the JSON Data
if response.status_code == 200:
data = response.json()
open_price = data.get('open')
close_price = data.get('close')
date = data.get('day')
symbol = data.get('symbol')
4. Preparing the Data for Insertion into PostgreSQL
data_df = {
'symbol': symbol,
'open_price': open_price,
'close_price': close_price,
'date': date
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data_df, index=[0])
df['date'] = pd.to_datetime(df['date']).dt.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
5. Storing the Data in PostgreSQL
load_dotenv()
dbname = os.getenv('dbname')
user = os.getenv('user')
password = os.getenv('password')
host = os.getenv('host')
port = os.getenv('port')
engine = create_engine(f'postgresql://{user}:{password}@{host}:{port}/{dbname}')
try:
df.to_sql("crypto_prices", con=engine, if_exists="append", index=False, schema="dataengineering")
print(f"Successfully loaded crypto data for {df[date]}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
CREATING A DAG
I created a DAG for orchestration and automation and scheduled it to run daily. Here is the step-by-step guide on how I did it.
1. Importing Required Libraries
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from airflow import DAG
from airflow.operators.bash_operator import BashOperator
from airflow.operators.python_operator import PythonOperator
2. Defining Default Arguments
default_args ={
"owner": "milcah",
"depends_on_past": False,
"start_date": datetime(2025, 3, 31),
"email": ["milcahredempter03@gmail.com"],
"email_on_failure": False,
"email_on_retry": True,
"retries": 2,
"retry_delay": timedelta(minutes=2)
}
3. Creating the DAG
with DAG(
'btc_data',
default_args=default_args,
schedule_interval='@daily',
) as dag:
4. Defining the Tasks
Task 1: Activate Virtual Environment
activate_venv = BashOperator(
task_id='activate_virtual_env',
bash_command='source /home/user/project/cbk_daily/venv/bin/activate',
)
Task 2: Execute Python Script
execute_file = BashOperator(
task_id='execute_python_file',
bash_command='python /home/user/project/crypto_price/app_data.py',
)
5. Defining Task Order
activate_venv >> execute_file
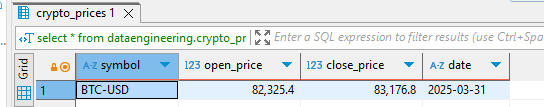
After creating the DAG, I accessed the airflow UI, triggered it, and then accessed DBeaver, where I queried the table.
Conclusion
The project adopts the best practices in Apache Airflow, like keeping the DAGs simple, hiding sensitive data, and defining the correct arguments. Also, most of the installation was done in a virtual environment to avoid overlapping dependencies.



Top comments (0)