This is an opinionated guide to becoming a web3 developer in 2023.
I'll outline the exact steps that I personally took to land a role as a developer relations engineer at thirdweb; a suite of developer tools for building in web3.
Unlike other roadmaps, I'm not going to give you 300 things to learn and get you stuck in tutorial hell. This is an actionable, sequence of technologies for you to learn, including the exact resources I found most helpful throughout my journey.
Let's dive into it! Below is a preview of each layer of the stack we'll be covering.
Important Disclaimer (READ THIS)
Consuming resources alone will never teach you how to become a developer.
Every dev has to constantly fight their own battles on the journey to understanding how to code, and put together the pieces of the gigantic puzzle along the way.
As soon as you know how to START building, exit the roadmap and go at it alone. Just try to build something. It's going to suck. And that's the point!
Come back to the resources to fill in the gaps in your knowledge as you get stuck; learn what tools are available for you to use that solve your problems with the resources in this guide.
Every project you make will be better than the last, and you'll soon be embarrassed by your old code.
DO NOT just consume these resources, they are only there to help point you in the right direction in a logical order as you actually build your own projects.
It's not going to be easy, but it is worth it. Buckle up and let's get started!
The Roadmap
We're going to cover a lot of topics in this roadmap, and I'll provide you with resources that I personally used to develop my understanding at each step of the way. Here's a quick preview of some of the tools we'll cover:
The Fundamentals: HTML & CSS
Every website consists of three things:
HTML: Structure of elements on the page
CSS: Style of elements on the page
JavaScript: Interactivity of elements on the page
Any application you build, no matter what technology you use, is eventually transformed into these three languages and served to a user on a web page.
Hence it's an important foundational piece of knowledge to understand the very basics of HTML and CSS first before diving into any "programming" (adding interactivity or logic to your application).
HTML & CSS
CS50 is Harvard's introductory course to computer science. It's an outstanding resource taught by the best lecturers in the world. I have taken multiple of their free online courses including their previous years' CS50 course and cannot recommend it enough.
Below is lecture number nine (starting at index 0) of the course that focuses on HTML, CSS and JavaScript. It teaches you the fundamentals of how web pages work and introduces how the three languages work together to create interactive websites.
Even if you already know HTML and CSS, you'll be surprised at how much you learn from these lectures by going back to basics and gaining a deeper understanding of the fundamentals.
JavaScript
Picking up the basics of HTML and CSS is significantly easier than learning JavaScript; which is a behemoth in comparison; but also a lot more fun!
First, you need to learn the absolute basics of programming before diving deeper into JavaScript itself. This includes concepts key to any programming language; variables, functions, loops, and data structures.
A relatively concise resource that will teach you these basic fundamentals is the below video, "JavaScript Tutorial For Beginners".
The video above is just an example of beginner-friendly content to understand the basics of JavaScript. There are plenty of others out there and I encourage you to learn as much as you need before advancing further into this roadmap.
Here are some more great interactive resources that you can use to learn as a beginner:
Optional (For Now): Computer Science Fundamentals
JavaScript is beginner-friendly and abstracts away many complexities of programming; it's designed so that you can hit the ground running quickly.
If you are willing to spend significantly more time learning the fundamentals of computer science, consider watching the full playlist of lectures for CS50 2022; which is ~20 hours total.
My personal opinion is that it's better to come back to these fundamentals later and start building something as soon as possible.
I personally didn't learn these computer science fundamentals in detail until 1-2 years into working as a professional software engineer (which might sound crazy, I know). Again, these are my personal opinions and others will disagree with this.
Advanced JavaScript
Here's where the learning curve reached a steep point for me.
The resources I'm about to share may feel overwhelming at first; it took me several re-watches and many, many pages of notes to start to understand these concepts.
How JavaScript Really Works
The below video goes deep into the nuances of JavaScript and how the magic of the language works under the hood! 🧙
Topics like scope, closures, and prototypical inheritance are funnily enough the topics I've been asked about several times in job interviews over the past few years.
This is another CS50 lecture from 2018, and is still one of my personal favourite resources for learning JavaScript to this day!
Asynchronous JavaScript
The subsequent lecture in this playlist is also quite complex but covers incredibly important topics for understanding JavaScript at a deeper level. You'll be introduced to some of the more modern features of JavaScript introduced in ES6 such as callbacks, promises, and asynchronous functions.
(Optional) Paid Course: "ES6 for Everyone!" by Wes Bos
An additional resource I recommend (if you can afford it) is the "ES6 for Everyone!" course by Wes Bos. It's an excellent interactive course that teaches you a variety of super helpful syntactic sugar that are part of the later releases of ECMAScript.
It's not essential, but Wes is a great teacher and the course is a fun way to learn the more efficient ways of doing things in JavaScript.
This course is very beginner friendly and will help you write more modern Javascript.
(VERY Optional) Paid Course: Master the Coding Interview
As you're on your journey and are building your projects, some code you write is not going to be as efficient as it could be.
A paid course that taught me a tremendous amount about writing better code is the "Master the Coding Interview: Big Tech (FAANG) Interviews" course by Andrei Neagoie.
The title of the course is a bit clickbaity, but it teaches you almost everything there is to learn about data structures and algorithms; with 30 interactive questions for you to go through; all in JavaScript!
For me, this was extremely hard and took me many months to get through; which is why I put the "very optional" tag on this course. It's an amazing resource that I recommend you take at some point on your journey, but if you're a beginner it's likely going to be too hard for you.
React - Building User Interfaces
If you've started building your project by this point, you've probably realised that it is difficult to build an application by writing HTML, CSS, and JS alone.
Developers have come up with many different libraries and frameworks to address these issues over the past decade; jQuery, Angular, Svelte, Vue... the list goes on!
One library has come out on top; React, which is:
The most in-demand frontend framework for landing a job (too lazy to get a source for this stat, so... "probably" 😄).
React uses a syntax called JSX to combine writing your UI structure and design with your "interactivity" in the same location:
A great resource to understand the "why" of React is this CS50W lecture on user interfaces:
Get Started with Next.js
Next.js documentation is absolutely brilliant. Lee Robinson and his team of DX engineers have written fantastic, interactive documentation to help you learn Next.js and quiz your knowledge along the way.
For this reason, I recommend running through the interactive documentation first; and then diving into creating your first Next.js application with their CLI.
TypeScript
Another hot take on this article 🌶️: Start using TypeScript ASAP! JavaScript is a great language for beginners, but this is a double-edged sword. Part of the reason it's good for beginners is that it gives you a lot of freedom to write 💩 code and it doesn't complain about it!
TypeScript can be a real pain in the 🍑 at first, but once it clicks, you'll never want to go back. More and more developers and developer tools are defaulting to TypeScript and for good reason; type safety makes your code significantly less likely to have bugs!
My suggestion: turn strict mode off at the beginning. Use the any type whenever you get completely stuck and don't know what to do. These are bad practices in reality, but will help you onboard to TypeScript without wanting to break your keyboard.
As you write more and more code with TypeScript and pick up more tricks, you'll feel comfortable enabling strict mode and using the any type more sparingly; until you eventually have complete type safety in your codebase and look at JavaScript in disgust!
Styling
There are a number of options for you to build out more beautiful applications that are ultimately just different ways of abstracting CSS so that it's ... well basically CSS but easier.
The general consensus going into 2023 is that Tailwind CSS is the gold standard for adding styles to your application. I personally like to use a tool called Material UI that comes with pre-built components; however, most people don't agree with me on this.
A great video weighing up the different options available and their pros and cons is "The Best of CSS" by Theo:
Short answer: If you don't already know and love a UI library, pick Tailwind CSS.
Blockchain Fundamentals
If you don't already have knowledge of what a blockchain or smart contract is, a helpful resource for beginners is Patrick Collins' blockchain course.
I suggest you watch the first 2 hours of the 32-hour course which introduces the core concepts of blockchain, smart contracts and web3. You can pick and choose the other areas of the course that interest you as you wish!
Understanding the Web3 Stack
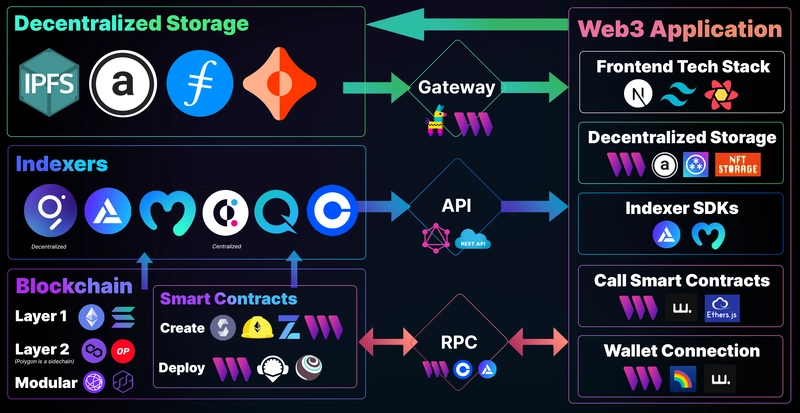
An introductory video I recommend watching is "Defining the Web3 Stack", by @Nader Dabit; which outlines the equivalent web3 tech stack compared to a traditional "web2" application.
As an updated graphic to Nader's talk in 2021, I have provided my thoughts on the tech stack of a web3 application below:
There are a lot of moving pieces to consider when building a web3 application. There are a plethora of tools available to help you build different aspects of your decentralized application, and it's up to you to learn what you like best.
Of course, I'll provide my recommendations here that I have come to after experimenting with a number of these tools in the past year.
Building a full stack web3 app "the hard way"
Arguably the best resource I consumed when I was entering the web3 space was @Nader Dabit's "Full Stack NFT Marketplace" video tutorial. You'll learn how to build almost every aspect of a full-stack web3 application at a rapid pace, including:
NFT Collection smart contract
NFT marketplace smart contract
Smart contract development environment and testing
IPFS file uploads and downloads
Frontend technologies & Next.js to build a web3 application
RPC nodes and IPFS Gateways
This might feel like quite the jump from the previous step, and you might not understand everything in this video immediately, and that's okay!
This resource taught me a tremendous amount about how the pieces of the web3 stack fit together and teach you how to build an epic project with modern technologies.
Extending Nader's Project
Something that really made me understand what was happening was adding more functionality to Nader's NFT marketplace project; specifically, adding a function to get an individual listing's information on the marketplace smart contract.
Adding this capability to the project might sound easy, but it tests to see if you really understand how the project is functioning; and is a great step to add on top of the build itself.
Why is this "the hard way"?
This resource introduces you to what I'd argue is a low-level abstraction of building a full-stack web3 app; it shows you every step of the process which is super important to understand.
However, I'd argue that the purpose of the video isn't to build a "production-ready" application in 2023. I say this because there are a large number of tools that have been released since mid-2021 (the time this video was made), that has abstracted away the complexity of building full-stack web3 applications significantly.
Let's quickly cover a few other core concepts and then dive into the more modern tools available to build web3 apps with.
RPC Nodes
To communicate to and from the blockchain, you need to use a node. Unless you want to run your own Node, you need to use a service provider such as Alchemy, Coinbase, or Moralis, (or thirdweb as we'll explain in the next section) to do so.
Below is a great resource outlining what an RPC Node is and why it's required to build web3 applications.
Interesting Project: Lava Network
A project I am excited to see in 2023 is Lava Network; which offers a decentralized alternative to the RPC Nodes. Check it out if you are interested!
Decentralized Storage Solutions
Not all information needs to be stored on the blockchain. Storing data on the blockchain itself costs gas fees and has a significant storage limit; for this reason, a common pattern is to store your information "off-chain" and store the URL of that data on the blockchain instead.
Storage solutions exist that aren't stored "on-chain" but are still not controlled by a centralized service such as AWS or Google Cloud. The two prominent decentalized storage solutions solutions in 2023 are:
IPFS
Below is a concise summary of what IPFS is, how it works, and how you can integrate it into your applications using thirdweb (we'll talk more about this next).
To access data stored on IPFS on most browsers such as Google Chrome, you'll need to use an IPFS Gateway. There are a couple of options available for you here:
Public gateway (available for everyone, not very reliable)
Private gateways - using services such as Pinata or nft.storage for faster speed and higher availability, (again, or just use thirdweb as we discuss next).
Arweave
Another excellent video by Nader Dabit is available for you to understand Arweave and other aspects of the Arweave ecosystem such as Smartweave and Warp.
I should mention a lot of these technologies such as Arweave have grant programs if you are building with them; if you're looking for some funding this might be interesting to you.
thirdweb
Full disclosure: I work on the thirdweb team!
I used Nader's NFT marketplace video as a starting point for a freelancing project I was working on as I began to increase my skills in web3 development. I came to the realisation that building smart contracts is HARD!
I didn't have the confidence at this point to write a fully-featured, gas-optimized, bug-free marketplace smart contract for my clients' requirements; so I started to ask myself: "someone must have done this and open-sourced it somewhere RIGHT!?"
Well, turns out I was right!
I stumbled upon thirdweb shortly after it was released and discovered they had open-source smart contracts for NFT collections, marketplaces, and more.
I basically planned to just copy-paste their solidity smart contracts into my existing project and carry on my way 😂! Here's proof (don't tell Furqan):
But as I explored the product more, I discovered they had an SDK! I didn't have to use ethers anymore! They also have tools to connect users' wallets, and manage my IPFS storage for me! I didn't even need my smart contract code in my project anymore as they had a dashboard I could deploy it with.
I was able to remove SO MUCH of the code I wrote for my marketplace project and replace them with thirdweb tools that I ended up falling in love with the product; and applied for my current position at thirdweb a few months after completing my freelance work!
So, while I do get paid to advocate thirdweb's products, I do it from my heart, not from my ... wallet? 🥲 I was really out here using their tools before I joined the team.
Learning thirdweb
I've spent a lot of time refining the Getting Started flow of the thirdweb documentation to get you up and running from building a smart contract to building a front-end Next.js application in no time! So, my recommendation is to start there!
Alternatively, there is a getting started video that covers the same content:
Once you get the power of thirdweb's stack, you won't want to go back! 🤠 Since I joined, we have shipped even more features that make the web3 building process simpler:
Free IPFS gateway and IPFS rendering components in the SDK.
Free RPC included directly in the SDK (which can be overridden).
IPFS upload and downloads in React hooks with Storage.
React hooks for everything you can imagine on the frontend; for both user wallets and interacting with smart contracts.
Full Solidity SDK called "ContractKit" which is similar to OpenZeppelin.
An Explore page; for you to deploy the most popular smart contract standards.
Much more!
Deploy a smart contract with thirdweb and connect to it in your Next.js application and I promise you'll never want to go back to your old stack.
Other Web3 Frontend Libraries
So that I'm not completely biased, I'll also recommend you some of the other modern libraries available for you to build more robust frontends for your web3 apps.
wagmi
wagmi is a library of React Hooks for building EVM frontends. Much like the thirdweb React SDK, it has hooks for pretty much everything you can imagine and is significantly better than using ethers or web3.js alone.
The documentation is a great starting point for you to understand how to use it in your Next.js/React apps.
Rainbow Kit
RainbowKit is an excellent library for adding connect wallet capabilities into your application and supporting a variety of different connection options for your users.
Their documentation is concise and includes helpful short videos to get you up and running quickly.
Indexing Solutions
Some web3 applications require information that isn't directly available from any smart contract; such as what NFTs a wallet owns, or how many times an NFT has been transferred.
When it comes to indexing solutions, you can use The Graph; a decentralized solution, and again use Nader's resources to learn how to get started:
You might prefer to use SDKs or API endpoints to get your indexed information, and there are a number of popular solutions you can use, each with helpful resources and videos on their documentation:
These tools have similar capabilities with various pros and cons, you can use their documentation to explore which tool is right for you.
Smart Contracts
This might seem crazy that the smart contracts section is all the way down here. 🤯
The reason I placed smart contracts after learning the full frontend tech stack is that you are often going to be building on top of smart contracts that other people have deployed already; such as Lens Protocol, or deploying gas-optimized, audited smart contracts that suit your needs such as those available on thirdweb Explore.
To land a job in web3 you don't need to be an expert in writing your own smart contracts. At thirdweb, we have a team that is dedicated to writing Solidity smart contracts and building out our Solidity SDK; the rest of our engineers understand the Solidity code; but aren't actively writing smart contracts on a daily basis.
This might be a hot take 🌶️🥵 but you should learn the details of building smart contracts after learning how to actually build stuff people interact with; which usually means you need some kind of frontend application skills.
Some people will disagree with that; as almost everything in web3 depends on the foundational layer of decentralized applications; which is smart contracts. I'm not saying it's correct, this is just the path that I personally took to learn web3.
There are many resources you can use to learn Solidity itself, such as:
CryptoZombies (interactive course)
Literally, just read the Solidity documentation 🥸
Object Oriented Programming
OOP. more like oof, am I right? 😑
Solidity is an object-oriented programming language to build your own smart contracts. If you know OOP principles you are already most of the way there to be able to write basic Solidity.
Usually, you don't see JavaScript used for object-oriented programming; other languages like Java, C#, or Python are better suited for this style of writing code.
To get the basics of OOP down, I recommend you consume as many resources as you need to to get the basic principles down. Below is an introduction to OOP in JavaScript that will help you get the core concepts:
OOP In Solidity
Once you know what OOP is, I recommend you return back to Patrick's video at this timestamp (chapter 3), to see how inheritance and overrides work in Solidity:
Using OSS Smart Contracts
Usually, you'll want to build some variety of ERC standards such as ERC20 fungible tokens, ERC721 NFTs, or marketplaces, with a twist that makes your project unique.
Now that you know how to utilize inheritance in Solidity, you can make use of libraries such as OpenZeppelin Contracts and thirdweb ContractKit to import core chunks of logic into your smart contracts; and customize them as you wish!
ContractKit
thirdweb's ContractKit has a vast array of plug-and-play smart contracts for you to extend, customize, and include in your own smart contracts; including ERC721, ERC1155, ERC20, staking, airdrop, and more 🤠!
Smart Contract Security
It is important to know the most common vulnerabilities of smart contracts, which again Patrick covers thoroughly in his 32-hour Solidity course in Chapter 18 at this timestamp.
There is also a detailed open-source repository outlining common attack vectors for smart contracts and historical exploits using these attacks:
 kadenzipfel
/
smart-contract-vulnerabilities
kadenzipfel
/
smart-contract-vulnerabilities
A collection of smart contract vulnerabilities along with prevention methods
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
A collection of smart contract vulnerabilities along with prevention methods
Access Control
- Authorization Through tx.origin
- Insufficient Access Control
- Delegatecall to Untrusted Callee
- Signature Malleability
- Missing Protection against Signature Replay Attacks
Math
Control Flow
- Reentrancy
- DoS with Block Gas Limit
- DoS with (Unexpected) revert
- Using
msg.valuein a Loop - Transaction-Ordering Dependence
- Insufficient Gas Griefing
Data Handling
- Unchecked Return Value
- Write to Arbitrary Storage Location
- Unbounded Return Data
- Uninitialized Storage Pointer
- Unexpected
ecrecovernull address
Unsafe Logic
- Weak Sources of Randomness from Chain Attributes
- Hash Collision when using abi.encodePacked() with Multiple Variable-Length Arguments
- Timestamp Dependence
- Unsafe Low-Level Call
- Unsupported Opcodes
- Unencrypted Private Data On-Chain
- Asserting Contract from Code Size
Code Quality
Conclusion
That's it! These are the resources I personally used to develop my knowledge in web3 and land a job as a developer relations engineer at thirdweb!
I'd like to reiterate that tutorials and resources alone will never be enough to become a dev. You need to get your hands dirty ASAP, come back to these resources as you run into problems in your project, and constantly fight battles on your own over many years to come.
The goal of this article isn't to give you months of resources to consume, it's here so you can come back to trusted sources of high-quality information as you build your own projects alone! 🦸
If you want to join a community of devs on your journey, jump into my community Discord server and introduce yourself! 👋








Top comments (1)
If you want to learn more deeper blockchain,I recommend to Stephen Grider course on udemy