✨ What if you could eliminate the complexity of asynchronous data management in your React and React Native application? React Query can help you by simplifying and optimizing server state ✨
How the also known as TanStack Query works:
-
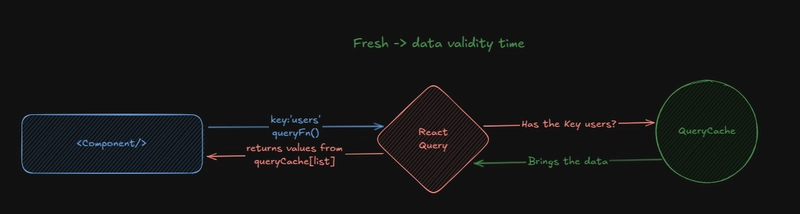
📦Cache(QueryCache):
- React Query stores data in the cache, avoiding repeated server requests.
-
Data Status:
- 👶Fresh → Like the data's validity, after a certain time the data becomes stale.
- 👴Stale → Obsolete data, meaning a new server request is needed to update it.
-
♻️ SWR (Stale-While-Revalidate):
- SWR ensures your data is always fresh.
- It displays cached data immediately (even if "stale" or obsolete) while fetching the latest version in the background. Thus, the user sees the content instantly, and the update is smooth.
-
𝗦𝗶𝗺𝗽𝗹𝗶𝗳𝗶𝗲𝗱 𝗗𝗮𝘁𝗮 𝗠𝗮𝗻𝗮𝗴𝗲𝗺𝗲𝗻𝘁
- React Query eliminates the need to write complex code to fetch, update, and manage server state. It takes care of:
- ⚙️**Automatic cache: **No need to implement manual logic.
- 🔁Revalidation: Automatic data update.
- ⚠️Error handling: Handles request errors.
- 🚀Optimistic updates: Improves perceived performance by updating the interface before server confirmation.
- React Query eliminates the need to write complex code to fetch, update, and manage server state. It takes care of:
With React Query, you focus only on application logic!



Top comments (1)
Great post on React Query! It’s such a powerful tool for handling server-state in React applications. If anyone is looking for a beginner-friendly guide to setting up React Query in a Next.js app, I wrote an article that covers the setup, usage, and common patterns with some practical examples. Feel free to check it out here: Guide to React Query.