Web development is the process of creating websites and web applications that are accessible via the internet. To understand how this works, let’s break down the process using a simple example.
Accessing a Webpage: The Journey of a Browser Request
Imagine you’re trying to visit a website, say https://paulanik.com. As soon as you enter this URL in your browser and press enter, a series of behind-the-scenes actions take place.
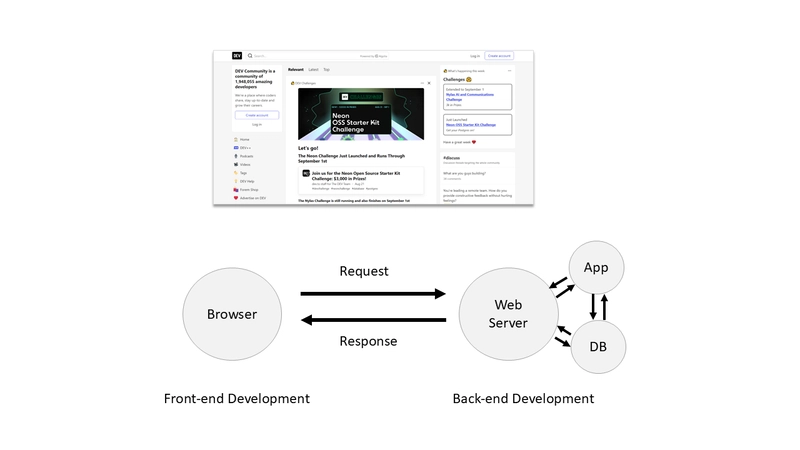
The Browser Sends a Request: Your browser sends a request to the server where the website is hosted. A server is essentially a powerful computer connected to the internet that stores websites and serves them to users on request.
The Server Responds: Upon receiving your request, the server gathers all the files that make up the website—such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript—and sends them back to your browser. This is called the server’s response.
Rendering the Website: Once your browser receives these files, it interprets the code and renders the website, displaying it on your screen. This entire process happens in just a few seconds.
The Core Technologies of Web Development
All the code that makes up a website is written using three core technologies: HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. These are the foundational languages that browsers understand and use to build and display web pages.
- HTML (HyperText Markup Language): HTML is the backbone of any web page. It defines the structure and content of a webpage, such as text, images, buttons, and other elements. HTML is not a programming language; rather, it is a markup language used to organize and display content.
- CSS (Cascading Style Sheets): CSS is responsible for the appearance and layout of the content defined by HTML. It allows developers to style web pages, controlling everything from fonts and colors to spacing and overall page layout. CSS is what makes a web page visually appealing and easy to navigate.
- JavaScript: JavaScript is the programming language of the web. It enables dynamic and interactive features, such as animations, form validation, and content updates without reloading the page. JavaScript can manipulate both HTML and CSS, making it a powerful tool for creating rich user experiences.
Front-End Development: Bringing Designs to Life
The process of writing HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to create the part of a website that users interact with directly is known as front-end development. Front-end developers focus on creating the layout, design, and interactive aspects of a website—the "front end" that users see and use.
When a website’s files are stored on a server and delivered to the browser without any modification, it’s referred to as a static website. Static websites are relatively simple and consist of fixed content that doesn't change unless a developer manually updates the files.
Back-End Development: Powering Dynamic Websites
Now, consider a website like https://dev.to/. Unlike a static website, Dev.to is dynamic, meaning its content is constantly changing—new articles, comments, and other data are frequently added.
Here’s what happens when you access such a website:
Request and Database Interaction: Just like before, your browser sends a request to the server. However, this time the server doesn’t just send back pre-made files. Instead, it runs a back-end application written in a language like Node.js, PHP, or Python.
Data Processing: This application interacts with a database where all the content—such as articles and user information—is stored. The back-end application retrieves the necessary data, assembles it into HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files, and then sends these files back to your browser.
Dynamic Content Delivery: Since the content is generated on the fly, it can be different every time you visit the site, depending on what’s new or relevant. This process is known as back-end development and is crucial for websites that need to deliver personalized or frequently updated content.
The Role of Front-End and Back-End Development
Together, front-end and back-end development are the two pillars of web development. While front-end development focuses on the user interface and experience, back-end development handles the logic, database interactions, and server-side operations that make dynamic websites possible.
Conclusion
Web development is a complex yet fascinating field that brings together various technologies and practices to create the websites we use every day. Whether you’re building a simple static site or a complex dynamic web application, understanding the roles of HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and back-end technologies is crucial.
By mastering both front-end and back-end development, you can create robust, interactive, and dynamic websites that provide a seamless user experience.
📬 Let’s Connect
🌐 Portfolio: paulanik.com
💼 LinkedIn: Anik Paul
🐙 GitHub: anikpaul99
📩 Email: hello@paulanik.com

![Cover image for [01] Understanding the Fundamentals of Web Development](https://media2.dev.to/dynamic/image/width=1000,height=420,fit=cover,gravity=auto,format=auto/https%3A%2F%2Fdev-to-uploads.s3.amazonaws.com%2Fuploads%2Farticles%2Fyc5499k25o79fg0emcj8.png)





Top comments (0)