connecting to a PostgreSQL database from Python.
Installation:
- Install PostgreSQL, If you haven’t installed it.
- We need to install the psycopg2 library to connect to a PostgreSQL database. Open the command prompt and run the below command to install psycopg2 ```bash
pip3 install psycopg2
# Creating a Database
You can create a Database in 2 Ways:
1. Using pgAdmin 4 UI
2. Using command
**1. Using pgAdmin 4 UI**
Go to pgAdmin and Follow these Steps.
- Local_server[Right Click] -> Create -> Database
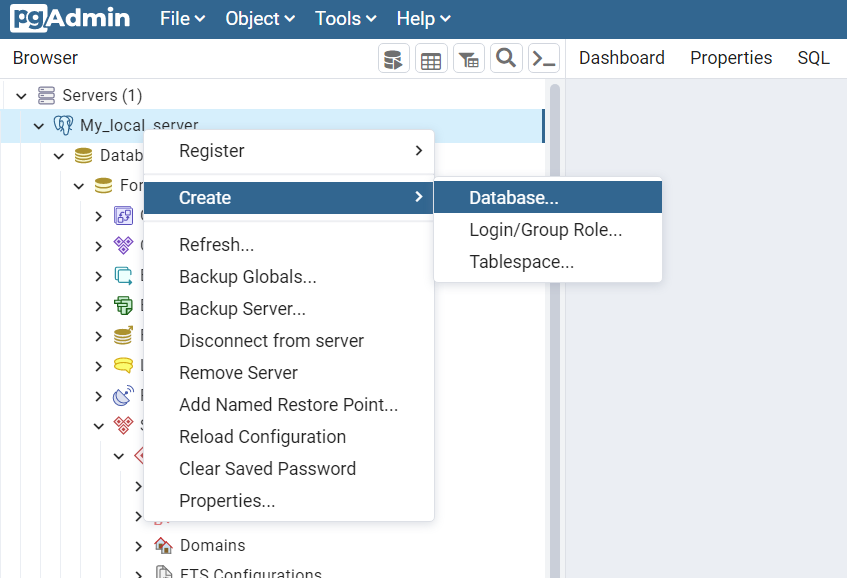
- Next, Fill out the form Database: WorkSpace and Save.
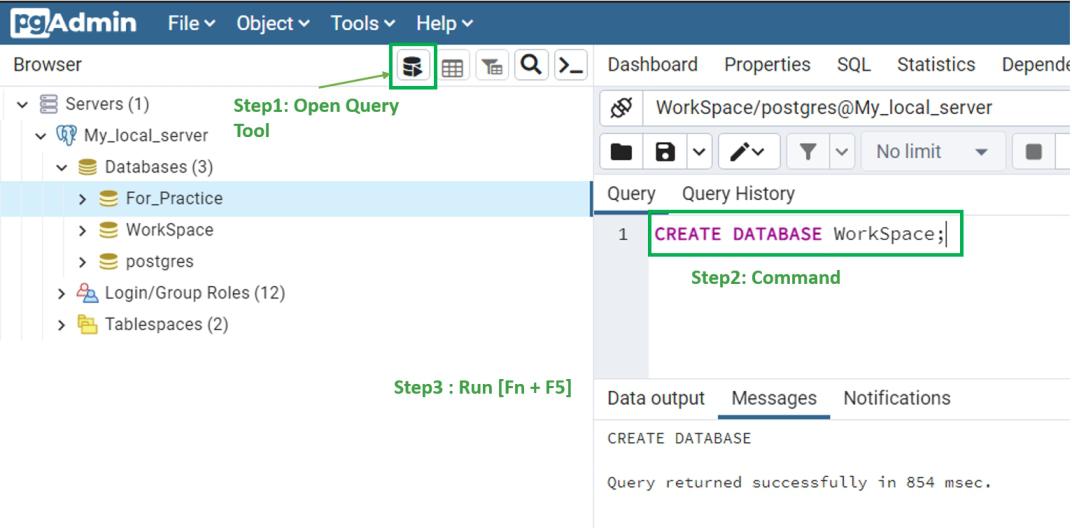
**2. Create Database Using SQL query**
Go to pgAdmin and follow these Steps:
- Run the below Command in the Query tab
CREATE DATABASE WorkSpace;
## Connecting to the database
We need to connect to a PostgreSQL database using psycopg2.connect() function.
**Where the attributes of connect() function are:**
```python
host = hostname,
dbname = databaseName,
user = username,
password = [Your Password],
port = [port_id]
In case you don’t know any of these connect() function attributes, you can follow the below steps:


Now You Know All the properties of this Database. Let’s continue.
Now, to connect to the database, we need to pass the attributes as arguments to the connect() function.
Syntax:
conn = psycopg2.connect(
host = 'localhost',
dbname = 'For_Practice',
user = 'postgres',
password = '[Password]',
port = 5432
)
Create a cursor:
- Create a cursor(i.e., curr) object and call its execute() method to execute queries.
- Where execute() method is used to run a query that is passed as a string. Syntax: ```python
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute('[SQL queries]')
In the end, We need to save the changes using commit() method and finally close the opened connection using `close()` method.
```python
conn.commit()
cur.close()
import psycopg2
conn = None
try:
# connect to the PostgreSQL server
print('Connecting to the PostgreSQL database...')
conn = psycopg2.connect(
host = 'localhost',
dbname = 'For_Practice',
user = 'postgres',
password = '321654',
port = 5432
)
# Creating a cursor with name cur.
cur = conn.cursor()
print('Connected to the PostgreSQL database')
# Execute a query:
# To display the PostgreSQL
# database server version
cur.execute('SELECT version()')
print(cur.fetchone())
# Close the connection
cur.close()
except(Exception, psycopg2.DatabaseError) as error:
print(error)
finally:
if conn is not None:
conn.close()
print('Database connection closed.')




Top comments (1)
Just one comment, please encourage people to use venv or comparable approaches