Implementing a Real-World Credit Score Verification System
This project leverages Spring AI with Tool Calling capabilities to orchestrate multiple AI-driven tools, managed by the Qwen 2.5 model from Alibaba Cloud. The solution is seamlessly integrated with Slack via the Model Context Protocol (MCP), enabling efficient and intelligent credit score verification for specific users and automatically posting the results in a designated channel within the workspace.
Before we start to explain MCP, I think is important we start the discuss why almost times I tried use OpenSource technologies and why this time I choose Qwen 2.5
Why Open Source LLMs?
Open-source LLMs offer a blend of cost savings, adaptability, transparency, community-driven enhancements, scalability, and data control, making them a viable and often preferable alternative to proprietary models.
Cost-Effectiveness: Open-source LLMs eliminate licensing fees, reducing initial expenses. While operational costs like infrastructure remain, the absence of proprietary fees makes advanced AI capabilities more accessible, especially for smaller organizations.
Customization and Flexibility: These models can be fine-tuned to specific business needs, allowing for tailored applications across various industries. This adaptability enables seamless integration into existing systems, enhancing operational efficiency.
Transparency and Security: Access to the source code provides insights into the model's architecture and training data, fostering trust and aiding in audits for ethical and legal compliance. This transparency ensures robust and accountable AI applications.
Community Support and Collaboration: The open-source nature encourages contributions from a diverse set of developers and researchers, leading to continuous improvements and innovation. This collaborative environment accelerates advancements and ensures the models remain up-to-date with emerging trends.
Scalability: Open-source LLMs allow organizations to scale operations according to their requirements, such as handling large volumes of data or expanding into new applications and markets.
Privacy and Independence: Deploying open-source models locally ensures that sensitive data remains within an organization's infrastructure, reducing the risk of data leaks and unauthorized access. This autonomy allows for greater control over data management and compliance with privacy regulations.
Why Qwen 2.5
Qwen 2.5 is an advanced language model developed by Alibaba Cloud, designed to handle a wide range of artificial intelligence tasks. This model stands out for its code generation capabilities, multilingual support, and extensive context processing, making it a versatile tool for various applications.
Advantages of Using Qwen 2.5 in Implementations:
Versatility: With multilingual support and advanced capabilities in code generation and long-context processing, Qwen 2.5 can be applied across various industries, from software development to education and research.
Cost Efficiency: Compared to other AI models on the market, Qwen 2.5 offers a competitive pricing structure, making it an attractive option for startups and companies seeking high-performance AI solutions without a significant investment.
Processing Large Volumes of Data: Its ability to handle extensive contexts allows Qwen 2.5 to process long and complex texts without losing coherence, which is essential for tasks requiring detailed analysis and deep understanding.
Integration with Cloud Services: The model is optimized for cloud computing environments, enabling efficient scalability and integration with other Alibaba Cloud services, simplifying implementation in existing infrastructures.
Community and Support: As an open-source model, Qwen 2.5 benefits from an active community of developers, providing additional resources, support, and continuous updates, which is advantageous for organizations looking for robust and up-to-date AI solutions.
What is MCP Protocol?
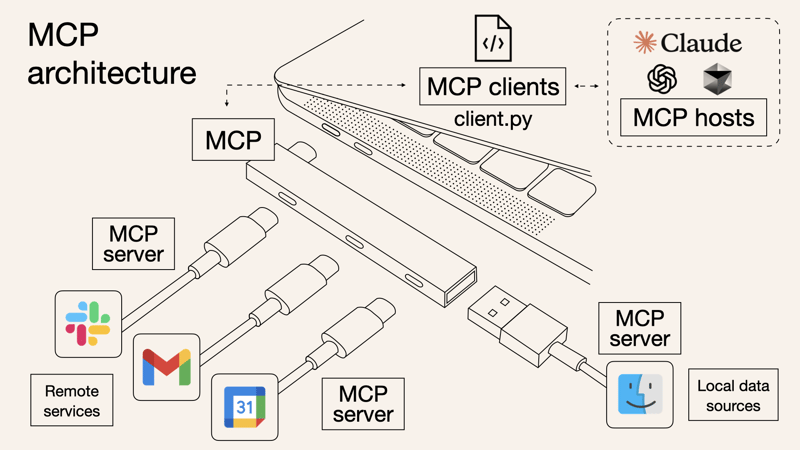
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open standard designed to facilitate the integration of AI systems with various external tools, databases, and services. It acts as a universal connector for AI applications, much like USB-C for devices, enabling seamless interactions between Large Language Models (LLMs) and different data sources.
MCP eliminates the need for multiple custom API integrations by providing a single, standardized method for AI tools to access and interact with external data dynamically.
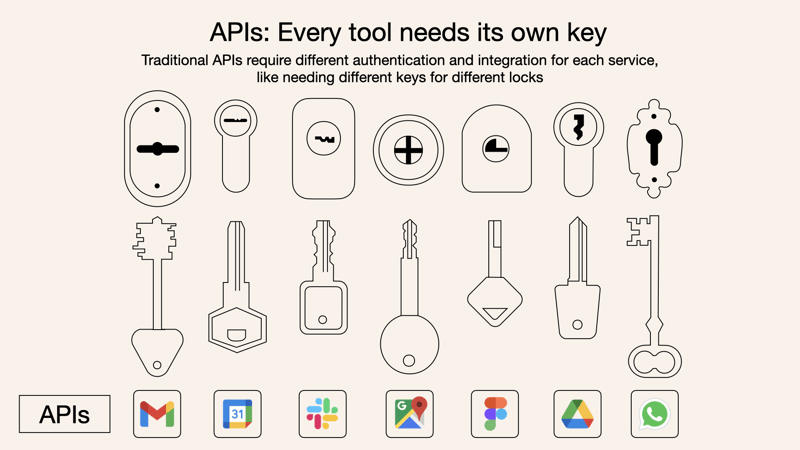
Why Use MCP Instead of Traditional APIs?
Traditional API-based integrations require separate connections for each external service, meaning:
- Each API has unique authentication and documentation.
- Developers need to write and maintain custom code for every integration.
- Communication is often one-way, limiting real-time interactions.
MCP solves these issues by offering:
- A single, standardized integration instead of multiple separate APIs.
- Real-time, two-way communication, allowing AI models to not only retrieve data but also trigger actions dynamically.
- Dynamic discovery of tools, meaning AI models can access new services without needing manual reconfiguration.
- Easier scalability, as developers can connect multiple data sources with minimal additional effort.
Who Created MCP?
Originally developed by Anthropic, MCP is now an open-source standard being adopted by various companies and developers, aiming to establish a universal method for AI-tool interactions.
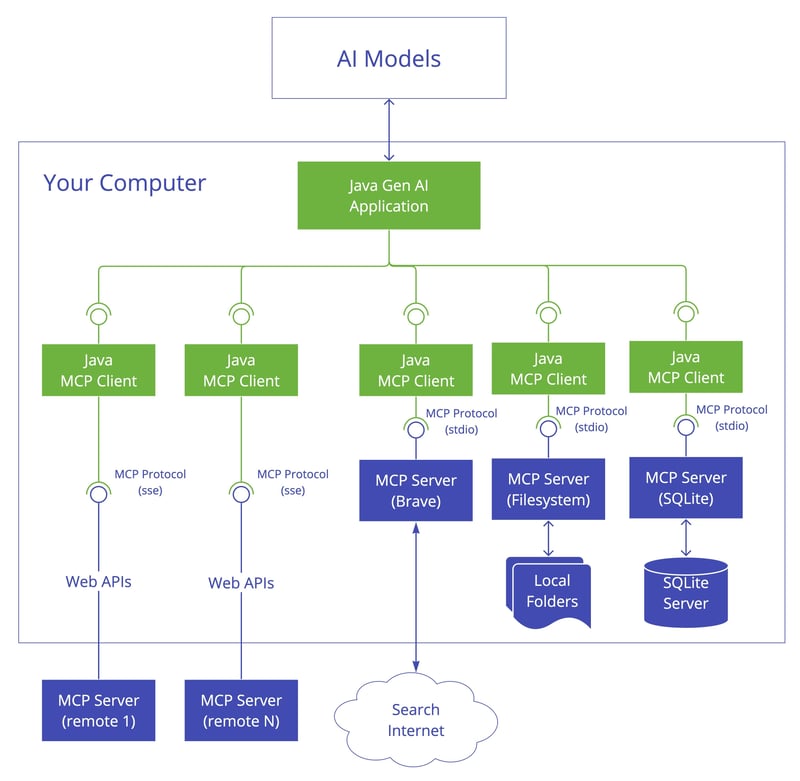
How MCP Works – Architecture Overview
MCP follows a client-server architecture, consisting of three main components:
- MCP Hosts – AI-driven applications (e.g., Claude, AI-powered IDEs) that need access to external tools.
- MCP Clients – Maintain one-to-one connections with MCP servers to exchange data.
- MCP Servers – Lightweight servers that expose specific functionalities, serving as bridges between AI models and data sources.
Data Flow in MCP
- Pull Data → AI queries an MCP server for context (e.g., checking a user’s calendar).
- Trigger Actions → AI instructs an MCP server to take action (e.g., reschedule meetings, send emails).
- Persistent Connection → Unlike APIs that require repeated calls, MCP maintains continuous communication between AI and tools.
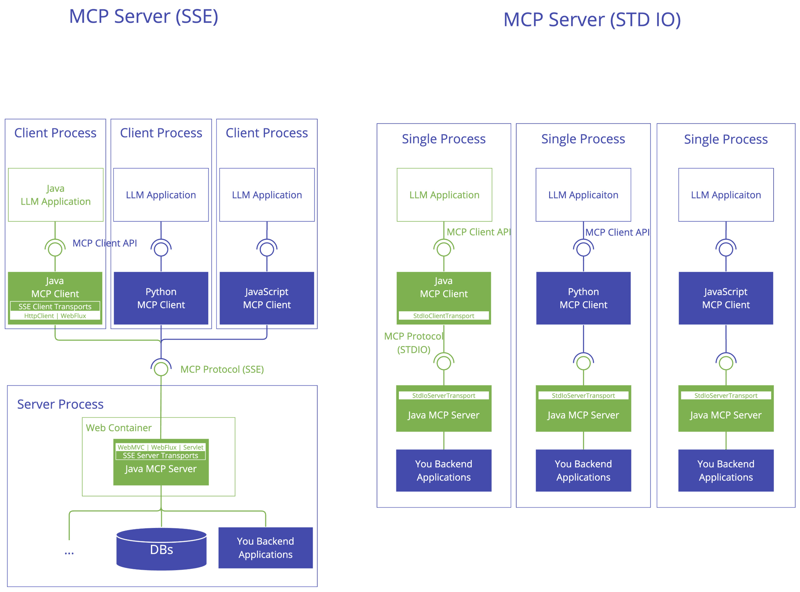
Implementing MCP with Spring AI
Client Starters
spring-ai-mcp-client-spring-boot-starter - Core starter providing STDIO and HTTP-based SSE support
spring-ai-mcp-client-webflux-spring-boot-starter - WebFlux-based SSE transport implementation
Server Starters
spring-ai-mcp-server-spring-boot-starter - Core server with STDIO transport support
spring-ai-mcp-server-webmvc-spring-boot-starter - Spring MVC-based SSE transport implementation
spring-ai-mcp-server-webflux-spring-boot-starter - WebFlux-based SSE transport implementation
Project Setup
Dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-mcp-client-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
Bean Setup
@Bean
public ChatClient chatClient(ChatClient.Builder chatClientBuilder, ToolCallbackProvider tools) {
return chatClientBuilder
.defaultTools(tools)
.build();
}
Config MCP Server File
{
"mcpServers": {
"slack": {
"command": "docker",
"args": [
"run",
"-i",
"--rm",
"-e",
"SLACK_BOT_TOKEN",
"-e",
"SLACK_TEAM_ID",
"mcp/slack"
],
"env": {
}
}
}
}
Add Specific function to be called by MCP Server in your prompt.
**4. Formatting for Slack:**
- Present the information in a structured and well-organized format
- Use **bold headings** (`*Decision and Recommendation*`)
- Post the summary to the **'#all-ai-agent-alerts'** Slack channel \t
\s
The summary should be concise, clear, and actionable to help the credit team quickly understand what decision we have to take.
Slack Setup
https://github.com/AVIMBU/slack-mcp-server


Top comments (0)