Introduction
In today's streaming landscape, viewers expect Netflix-quality experiences on everything from 4K TVs to smartphones on spotty cellular connections. Meanwhile, content creators need robust protection against increasingly sophisticated piracy attempts. The solution? HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) with adaptive quality encoding and security-focused segmentation.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through building a production-ready video streaming platform with Express.js and AWS S3, complete with multi-quality encoding and security features.
Setting Up Your Express Server
First, let's create the Express server that will handle video uploads and processing:
// server.ts
import express from 'express';
import multer from 'multer';
import { uploadVideoController } from './controllers/videoController';
const app = express();
const upload = multer({
storage: multer.memoryStorage(),
limits: {
fileSize: 1024 * 1024 * 1024, // 1GB limit
},
});
// Video upload endpoint
app.post('/api/videos/upload',
upload.single('video'),
uploadVideoController
);
// Error handling middleware
app.use((err: Error, req: express.Request, res: express.Response, next: express.NextFunction) => {
console.error('🔥 Server error:', err);
res.status(500).json({
success: false,
message: 'Internal server error',
error: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development' ? err.message : undefined
});
});
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 3000;
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`🚀 Server running on port ${PORT}`);
});
The Magic of Multi-Quality Encoding
Configuration Setup
Before diving into the implementation, let's set up our AWS configuration:
// config/index.ts
import { S3Client } from "@aws-sdk/client-s3";
export const BUCKET_NAME = process.env.AWS_BUCKET_NAME;
export const s3 = new S3Client({
region: process.env.AWS_REGION,
credentials: {
accessKeyId: process.env.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID!,
secretAccessKey: process.env.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY!,
},
});
Quality Profiles
Our implementation supports multiple quality levels to ensure optimal viewing across devices:
const videoQualities = [
{
name: "360p",
height: 360,
bitrate: "800k",
maxrate: "856k",
bufsize: "1200k",
},
{
name: "720p",
height: 720,
bitrate: "2500k",
maxrate: "2675k",
bufsize: "3750k",
},
{
name: "1080p",
height: 1080,
bitrate: "5000k",
maxrate: "5350k",
bufsize: "7500k",
},
];
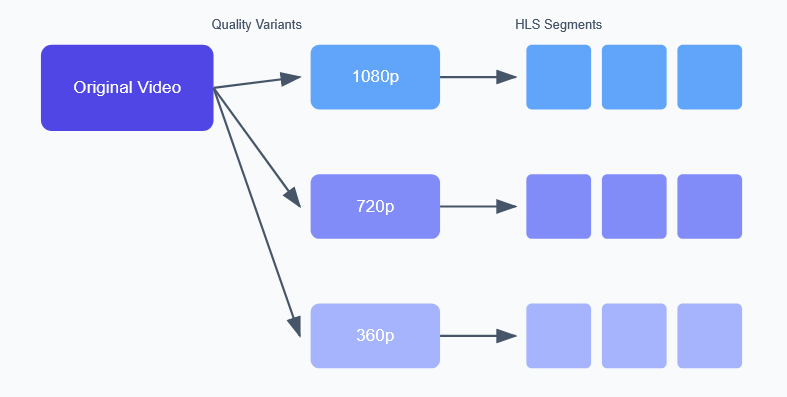
Image here showcasing how the ffmpeg convert quality levels through one video:
Advanced Video Processing Pipeline
FFmpeg Integration
Our solution uses FFmpeg for video processing. Here's how we ensure FFmpeg is available:
async function checkFFmpeg(): Promise<void> {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const ffmpeg = spawn("ffmpeg", ["-version"]);
ffmpeg.on("error", (error) => {
if (error.message.includes("ENOENT")) {
reject(new Error("FFmpeg is not installed or not found in system PATH"));
} else {
reject(error);
}
});
ffmpeg.on("close", (code) => {
if (code === 0) {
resolve();
} else {
reject(new Error(`FFmpeg check failed with code ${code}`));
}
});
});
}
Segment Generation
The heart of our HLS implementation is the segment generation process:
async function convertToHLSSegments(
videoBuffer: Buffer,
outputDir: string
): Promise<Record<string, Buffer>> {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const segments: Record<string, Buffer> = {};
const inputPath = path.join(outputDir, `input_${Date.now()}.mp4`);
try {
fs.writeFileSync(inputPath, videoBuffer);
// Generate master playlist content
const masterPlaylistContent =
"#EXTM3U\n#EXT-X-VERSION:3\n" +
videoQualities
.map(
(quality) =>
`#EXT-X-STREAM-INF:BANDWIDTH=${
parseInt(quality.bitrate) * 1000
},RESOLUTION=${quality.height}p\n${quality.name}.m3u8`
)
.join("\n");
// Write master playlist
fs.writeFileSync(
path.join(outputDir, "master.m3u8"),
masterPlaylistContent
);
const ffmpegArgs = [
"-i",
inputPath,
"-preset",
"veryfast",
"-tune",
"fastdecode",
"-sc_threshold",
"0",
"-g",
"48",
"-keyint_min",
"48",
"-movflags",
"+faststart",
];
// Add arguments for each quality
videoQualities.forEach((quality) => {
ffmpegArgs.push(
"-vf",
`scale=-2:${quality.height}`,
"-c:v",
"libx264",
"-profile:v",
"main",
"-crf",
"23",
"-maxrate",
quality.maxrate,
"-bufsize",
quality.bufsize,
"-c:a",
"aac",
"-ar",
"48000",
"-b:a",
"128k",
"-ac",
"2",
"-hls_time",
"10",
"-hls_playlist_type",
"vod",
"-hls_segment_filename",
path.join(outputDir, `${quality.name}_%03d.ts`),
"-hls_flags",
"independent_segments",
path.join(outputDir, `${quality.name}.m3u8`)
);
});
const ffmpegProcess = spawn("ffmpeg", ffmpegArgs);
let errorOutput = "";
ffmpegProcess.stderr.on("data", (data) => {
errorOutput += data.toString();
console.log(`FFmpeg progress: ${data}`);
});
ffmpegProcess.on("close", (code) => {
try {
if (code !== 0) {
throw new Error(
`FFmpeg process exited with code ${code}\nError output: ${errorOutput}`
);
}
// Read all generated files
const files = fs.readdirSync(outputDir);
for (const file of files) {
if (file.endsWith(".ts") || file.endsWith(".m3u8")) {
segments[file] = fs.readFileSync(path.join(outputDir, file));
}
}
resolve(segments);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
} finally {
// Clean up input file
if (fs.existsSync(inputPath)) {
fs.unlinkSync(inputPath);
}
}
});
ffmpegProcess.on("error", (error) => {
reject(new Error(`FFmpeg process error: ${error.message}`));
});
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
});
}
Upload to AWS S3
async function uploadToS3(
segments: Record<string, Buffer>,
hlsKey: string
): Promise<void> {
const uploadPromises = Object.entries(segments).map(([filename, data]) => {
const upload = new Upload({
client: s3,
params: {
Bucket: BUCKET_NAME,
Key: `${hlsKey}/${filename}`,
Body: data,
ContentType: filename.endsWith(".m3u8")
? "application/x-mpegURL"
: "video/MP2T",
},
tags: [{ Key: "videoId", Value: hlsKey.split("/")[1] }],
queueSize: 4,
partSize: 1024 * 1024 * 5,
});
upload.on("httpUploadProgress", (progress) => {
console.log(
`Progress for ${filename}: ${(
((progress.loaded || 0) / (progress.total || 1)) *
100
).toFixed(2)}%`
);
});
return upload.done();
});
await Promise.all(uploadPromises);
}
Security Features
Input Validation
We implement strict input validation to prevent security issues:
function validateFile(file: Express.Multer.File): void {
const allowedTypes = ["video/mp4", "video/quicktime", "video/x-msvideo"];
if (!allowedTypes.includes(file.mimetype)) {
throw new Error("Invalid file type. Only MP4, AVI, and MOV are allowed");
}
const fileSizeMB = file.buffer.length / (1024 * 1024);
if (fileSizeMB > MAX_VIDEO_SIZE_MB) {
throw new Error(`File too large. Maximum size is ${MAX_VIDEO_SIZE_MB}MB`);
}
}
An image showcasing how the video processing work and being uploaded to AWS S3
 %}
%}
Full Version of the Code
import { Upload } from "@aws-sdk/lib-storage";
import { s3, BUCKET_NAME } from "../config";
import type { Request, Response } from "express";
import { spawn } from "child_process";
import * as fs from "fs";
import * as path from "path";
import * as crypto from "crypto";
const TEMP_DIR = path.join(process.cwd(), "temp");
const MAX_VIDEO_SIZE_MB = 1024;
if (!fs.existsSync(TEMP_DIR)) {
fs.mkdirSync(TEMP_DIR, { recursive: true });
}
const videoQualities = [
{
name: "360p",
height: 360,
bitrate: "800k",
maxrate: "856k",
bufsize: "1200k",
},
{
name: "720p",
height: 720,
bitrate: "2500k",
maxrate: "2675k",
bufsize: "3750k",
},
{
name: "1080p",
height: 1080,
bitrate: "5000k",
maxrate: "5350k",
bufsize: "7500k",
},
];
async function checkFFmpeg(): Promise<void> {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const ffmpeg = spawn("ffmpeg", ["-version"]);
ffmpeg.on("error", (error) => {
if (error.message.includes("ENOENT")) {
reject(
new Error("FFmpeg is not installed or not found in system PATH")
);
} else {
reject(error);
}
});
ffmpeg.on("close", (code) => {
if (code === 0) {
resolve();
} else {
reject(new Error(`FFmpeg check failed with code ${code}`));
}
});
});
}
function validateFile(file: Express.Multer.File): void {
const allowedTypes = ["video/mp4", "video/quicktime", "video/x-msvideo"];
if (!allowedTypes.includes(file.mimetype)) {
throw new Error("Invalid file type. Only MP4, AVI, and MOV are allowed");
}
const fileSizeMB = file.buffer.length / (1024 * 1024);
if (fileSizeMB > MAX_VIDEO_SIZE_MB) {
throw new Error(`File too large. Maximum size is ${MAX_VIDEO_SIZE_MB}MB`);
}
}
// Main function to convert video to HLS segments
async function convertToHLSSegments(
videoBuffer: Buffer,
outputDir: string
): Promise<Record<string, Buffer>> {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const segments: Record<string, Buffer> = {};
const inputPath = path.join(outputDir, `input_${Date.now()}.mp4`);
try {
fs.writeFileSync(inputPath, videoBuffer);
// Generate master playlist content
const masterPlaylistContent =
"#EXTM3U\n#EXT-X-VERSION:3\n" +
videoQualities
.map(
(quality) =>
`#EXT-X-STREAM-INF:BANDWIDTH=${
parseInt(quality.bitrate) * 1000
},RESOLUTION=${quality.height}p\n${quality.name}.m3u8`
)
.join("\n");
// Write master playlist
fs.writeFileSync(
path.join(outputDir, "master.m3u8"),
masterPlaylistContent
);
const ffmpegArgs = [
"-i",
inputPath,
"-preset",
"veryfast",
"-tune",
"fastdecode",
"-sc_threshold",
"0",
"-g",
"48",
"-keyint_min",
"48",
"-movflags",
"+faststart",
];
// Add arguments for each quality
videoQualities.forEach((quality) => {
ffmpegArgs.push(
"-vf",
`scale=-2:${quality.height}`,
"-c:v",
"libx264",
"-profile:v",
"main",
"-crf",
"23",
"-maxrate",
quality.maxrate,
"-bufsize",
quality.bufsize,
"-c:a",
"aac",
"-ar",
"48000",
"-b:a",
"128k",
"-ac",
"2",
"-hls_time",
"10",
"-hls_playlist_type",
"vod",
"-hls_segment_filename",
path.join(outputDir, `${quality.name}_%03d.ts`),
"-hls_flags",
"independent_segments",
path.join(outputDir, `${quality.name}.m3u8`)
);
});
const ffmpegProcess = spawn("ffmpeg", ffmpegArgs);
let errorOutput = "";
ffmpegProcess.stderr.on("data", (data) => {
errorOutput += data.toString();
console.log(`FFmpeg progress: ${data}`);
});
ffmpegProcess.on("close", (code) => {
try {
if (code !== 0) {
throw new Error(
`FFmpeg process exited with code ${code}\nError output: ${errorOutput}`
);
}
// Read all generated files
const files = fs.readdirSync(outputDir);
for (const file of files) {
if (file.endsWith(".ts") || file.endsWith(".m3u8")) {
segments[file] = fs.readFileSync(path.join(outputDir, file));
}
}
resolve(segments);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
} finally {
// Clean up input file
if (fs.existsSync(inputPath)) {
fs.unlinkSync(inputPath);
}
}
});
ffmpegProcess.on("error", (error) => {
reject(new Error(`FFmpeg process error: ${error.message}`));
});
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
});
}
// Helper function to upload segments to S3
async function uploadToS3(
segments: Record<string, Buffer>,
hlsKey: string
): Promise<void> {
const uploadPromises = Object.entries(segments).map(([filename, data]) => {
const upload = new Upload({
client: s3,
params: {
Bucket: BUCKET_NAME,
Key: `${hlsKey}/${filename}`,
Body: data,
ContentType: filename.endsWith(".m3u8")
? "application/x-mpegURL"
: "video/MP2T",
},
tags: [{ Key: "videoId", Value: hlsKey.split("/")[1] }],
queueSize: 4,
partSize: 1024 * 1024 * 5,
});
upload.on("httpUploadProgress", (progress) => {
console.log(
`Progress for ${filename}: ${(
((progress.loaded || 0) / (progress.total || 1)) *
100
).toFixed(2)}%`
);
});
return upload.done();
});
await Promise.all(uploadPromises);
}
// Main controller function
export const uploadVideoController = async (req: Request, res: Response) => {
const tempDir = path.join(TEMP_DIR, `hls_${Date.now()}`);
fs.mkdirSync(tempDir, { recursive: true });
try {
// Check for FFmpeg installation
await checkFFmpeg();
const file = req.file;
if (!file) {
throw new Error("No file uploaded");
}
validateFile(file);
// Generate unique ID and key for the video
const videoId = crypto.randomBytes(16).toString("hex");
const hlsKey = `hls/${videoId}`;
// Convert video to HLS segments
const segments = await convertToHLSSegments(file.buffer, tempDir);
// Upload segments to S3
console.log("📤 Uploading HLS segments to S3...");
await uploadToS3(segments, hlsKey);
const hlsUrl = `https://${BUCKET_NAME}.s3.${process.env.AWS_REGION}.amazonaws.com/${hlsKey}/master.m3u8`;
return res.status(200).json({
success: true,
message: "Video processed successfully",
data: { hlsUrl, videoId },
});
} catch (error) {
console.error("❌ Video processing error:", error);
const errorMessage =
error instanceof Error ? error.message : "Failed to process video";
return res.status(errorMessage.includes("Invalid file") ? 400 : 500).json({
success: false,
message: errorMessage,
});
} finally {
// Clean up temporary directory
if (fs.existsSync(tempDir)) {
fs.rmSync(tempDir, { recursive: true, force: true });
}
}
};
export default { uploadVideoController };
Best Practices and Recommendations
1. Error Handling
- Implement comprehensive error handling
- Use appropriate HTTP status codes
- Provide meaningful error messages
2. Security
- Implement authentication for upload endpoints
- Use signed URLs for S3 access
- Validate file types and sizes
3. Performance
- Use chunked uploads for large files
- Implement retry mechanisms
- Consider using a CDN
4. Monitoring
- Track processing times
- Monitor S3 usage
- Set up alerts for failures
Conclusion
This implementation provides a robust foundation for a production-ready video streaming platform. Key benefits include:
- Adaptive quality streaming
- Secure content delivery
- Scalable architecture
- Production-ready error handling
- Progress tracking
- Cloud storage integration
Additionally, this is a simple way for video processing, converting to HLS. However, processing may be slow. To improve performance, we can use a Redis queue with a master-worker pattern in Express.js, along with various FFmpeg arguments like threads, hardware acceleration (hwaccel), and more.
For next steps, consider implementing:
- User authentication
- Content management system
- Analytics tracking
- Custom player interface
- DRM integration
The complete source code is available in the implementation sections above. Happy streaming! 🚀



Top comments (0)