Welcome to Day 23 of the 30 Days of Linux Challenge!
Today we’re entering the world of automation using one of the most powerful tools available in the Red Hat ecosystem: Ansible.
Ansible lets you automate repetitive tasks — like updating systems, installing packages, configuring files, and managing entire server fleets — using simple, human-readable YAML files.
📚 Table of Contents
- What is Ansible?
- Install Ansible on Red Hat Linux
- Configure Local Inventory
- Run Ad-Hoc Commands
- Write Your First Playbook
- Run the Playbook
- Try It Yourself
- Why This Matters
What is Ansible?
Ansible is a declarative automation engine:
- Uses YAML playbooks
- Connects over SSH (agentless)
- Scales from single node to 1000s of systems
- Works perfectly with Red Hat Enterprise Linux, CentOS, Fedora, and more
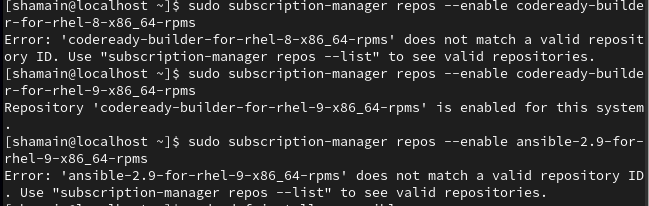
Install Ansible on Red Hat Linux
sudo subscription-manager repos --enable codeready-builder-for-rhel-9-x86_64-rpms
sudo subscription-manager repos --enable ansible-2.9-for-rhel-9-x86_64-rpms
Verify version:
ansible --version
Configure Local Inventory
Create an inventory file:
mkdir ~/ansible
cd ~/ansible
nano hosts
Add this to target your own machine:
localhost ansible_connection=local
Test connection:
ansible localhost -m ping -i hosts
Expected result:
json
Copy
localhost | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
Run Ad-Hoc Commands
List all users:
ansible localhost -m command -a "whoami" -i hosts
Install a package:
ansible localhost -m dnf -a "name=htop state=present" -i hosts --become
Write Your First Playbook
Create a YAML file:
nano setup.yml
Example playbook:
yaml
Copy
- name: Basic Setup Playbook hosts: localhost become: true
tasks:
- name: Install htop
dnf:
name: htop
state: present
- name: Ensure NTP is installed
dnf:
name: chrony
state: present
- name: Start and enable NTP service
service:
name: chronyd
state: started
enabled: true
Run the Playbook
ansible-playbook -i hosts setup.yml
This will:
Install htop and chrony
Start and enable the chronyd time service
Try It Yourself
🧪 Practice tasks:
- Install another package using a playbook (e.g. git, tree)
- Use Ansible to start or restart a service
- Create a user with the user module
- Run an ad-hoc uptime or df -h check across multiple hosts
Why This Matters
With Ansible, you can:
✅ Eliminate repetitive manual tasks
✅ Maintain consistency across systems
✅ Automate patching, provisioning, and configuration
✅ Scale easily from local to cloud infrastructure
Whether you’re a sysadmin or DevOps engineer, Ansible is your command center for intelligent automation.








Top comments (0)