Understanding Worker Threads and Child Processes in Node.js
Introduction
Node.js is known for its single-threaded, event-driven architecture, which allows it to handle many concurrent operations efficiently. However, when dealing with CPU-intensive tasks, a single thread can become a bottleneck. To address this, Node.js provides two mechanisms for parallel execution: Worker Threads and Child Processes. In this article, we will explore both concepts, their differences, and when to use them.
Worker Threads in Node.js
Worker Threads allow running JavaScript code in multiple threads, leveraging multi-core processors to improve performance for CPU-intensive tasks.
How Worker Threads Work
Worker Threads are part of the worker_threads module in Node.js. Unlike the main thread, each worker runs in isolation and has its own event loop, memory, and execution context.
Setting Up a Worker Thread
To use Worker Threads, create a separate JavaScript file and execute it within a worker:
Main Thread (index.js)
const { Worker } = require("worker_threads");
const worker = new Worker("./worker.js");
worker.on("message", (message) => {
console.log("Received from worker:", message);
});
worker.postMessage("Start processing");
Worker Thread (worker.js)
const { parentPort } = require("worker_threads");
parentPort.on("message", (message) => {
console.log("Worker received:", message);
parentPort.postMessage("Task completed");
});
When to Use Worker Threads
- Performing CPU-intensive computations (e.g., image processing, data parsing, cryptography).
- Running background tasks without blocking the main event loop.
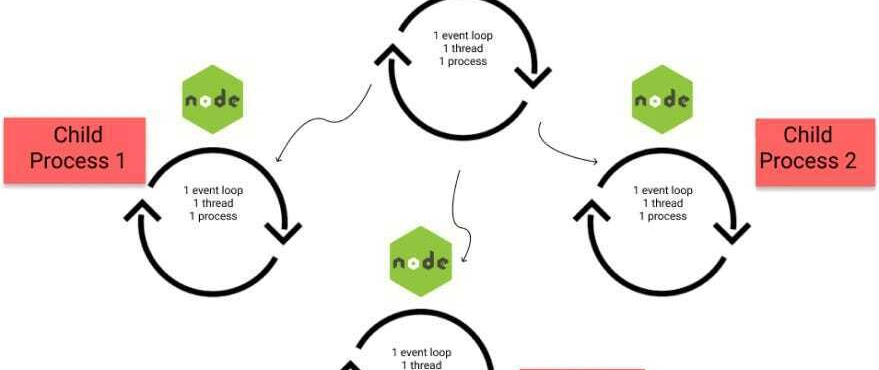
Child Processes in Node.js
Child Processes allow running separate Node.js instances to execute tasks independently.
How Child Processes Work
The child_process module provides four methods to create child processes:
-
spawn(): Starts a new process without blocking the event loop. -
exec(): Runs a shell command and buffers the output. -
execFile(): Similar toexec()but directly executes a file. -
fork(): Spawns a new Node.js process and establishes communication between parent and child.
Creating a Child Process
Using fork() for Inter-Process Communication
Main Process (index.js)
const { fork } = require("child_process");
const child = fork("./child.js");
child.on("message", (message) => {
console.log("Received from child:", message);
});
child.send("Start task");
Child Process (child.js)
process.on("message", (message) => {
console.log("Child received:", message);
process.send("Task done");
});
When to Use Child Processes
- Running separate Node.js scripts.
- Performing tasks that require multiple independent Node.js instances.
- Executing shell commands or external programs.
Worker Threads vs. Child Processes
| Feature | Worker Threads | Child Processes |
|---|---|---|
| Execution | Runs within the same Node.js instance | Runs as a separate Node.js process |
| Performance | Faster for CPU-intensive tasks | Slower due to process overhead |
| Memory Usage | Shares memory with the main thread | Separate memory allocation |
| Use Case | Heavy computations | Running external processes, separate scripts |
Conclusion
Both Worker Threads and Child Processes provide ways to handle parallel execution in Node.js. Use Worker Threads for CPU-heavy tasks that require shared memory, while Child Processes are better for independent tasks or external script execution. Choosing the right approach depends on your application's requirements.
Would you like to explore advanced implementations or performance benchmarks? Let me know in the comments! 🚀


Top comments (0)