Understanding Carry in Linked List Addition
Key Concepts
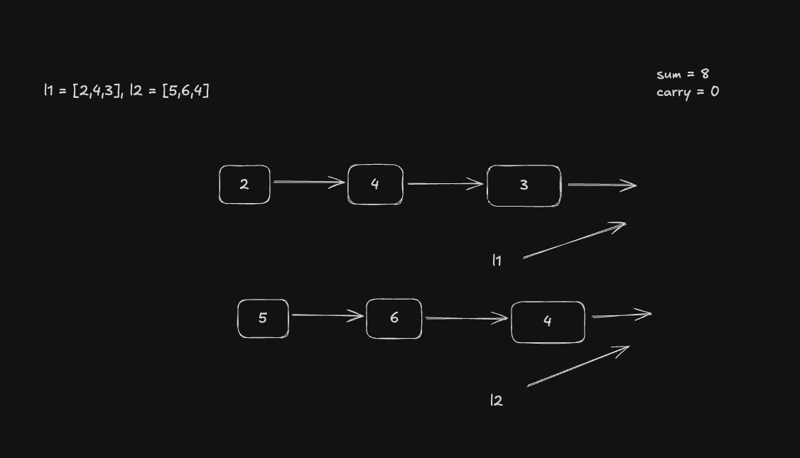
- Numbers are stored in reverse order as linked lists.
- Each node contains a single digit.
- Carry is needed when sum > 9.
- Result is returned as a new linked list.
Approach
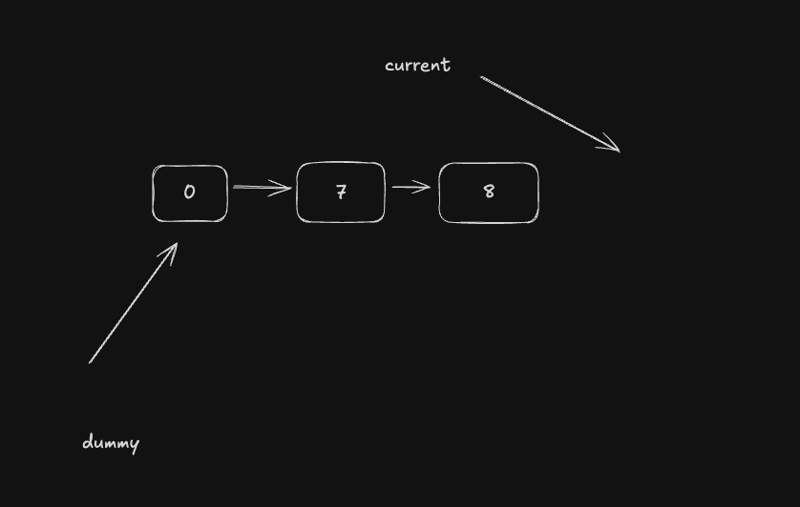
- Initialize a dummy node to simplify list construction.
- Use a carry variable to handle sums exceeding 9.
- Traverse
l1 and l2, summing corresponding nodes.
- If one list is shorter, treat missing nodes as
0.
- Continue processing even if one list is exhausted.
- Add a new node if there’s a leftover carry.
Complexity Analysis
-
Time Complexity: O(max(N, M)) (where N, M are the lengths of
l1 and l2).
-
Space Complexity: O(max(N, M)) (for the new linked list).
Code Implementation
var addTwoNumbers = function (l1, l2) {
let dummy = new ListNode(0);
let current = dummy;
let carry = 0;
while (l1 !== null || l2 !== null || carry > 0) {
let sum = (l1 ? l1.val : 0) + (l2 ? l2.val : 0) + carry;
carry = Math.floor(sum / 10);
current.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
current = current.next;
if (l1) l1 = l1.next;
if (l2) l2 = l2.next;
}
return dummy.next;
};




Top comments (0)