Approach
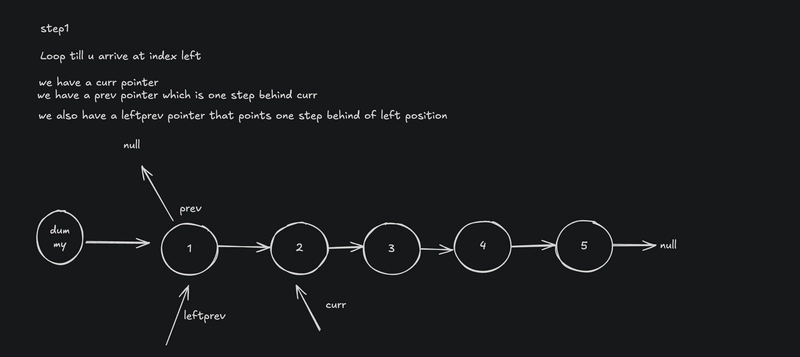
Find the leftPrev Node**
- Create a dummy node to handle edge cases (like when
left = 1). - Move
leftPrevto the node before theleftposition.
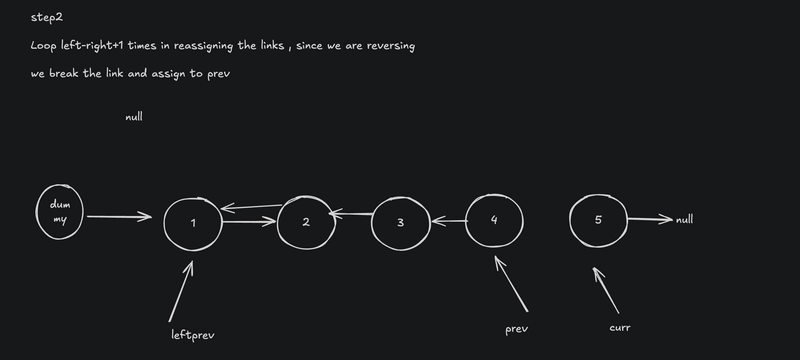
Reverse the Sublist
- Use the standard linked list reversal technique within the
lefttorightrange. - Keep track of
prev(previous node) andcurr(current node) while reversing.
Reconnect the Reversed Part
- The node at
leftPrev.nextis now the end of the reversed sublist, so connect it tocurr. - Connect
leftPrev.nexttoprev(the new head of the reversed sublist).
Code Implementation (JavaScript)
class ListNode {
constructor(val = 0, next = null) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
var reverseBetween = function(head, left, right) {
if (!head || left === right) return head;
let dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
let leftPrev = dummy;
// Step 1: Move leftPrev to the node before 'left'
for (let i = 1; i < left; i++) {
leftPrev = leftPrev.next;
}
// Step 2: Reverse sublist from 'left' to 'right'
let prev = null;
let curr = leftPrev.next;
for (let i = left; i <= right; i++) {
let next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
// Step 3: Reconnect reversed sublist
leftPrev.next.next = curr;
leftPrev.next = prev;
return dummy.next;
};
Time & Space Complexity
✅ Time Complexity: O(N), since we traverse the list at most twice (finding leftPrev + reversing a segment).
✅ Space Complexity: O(1), since we perform the reversal in-place.



Top comments (0)